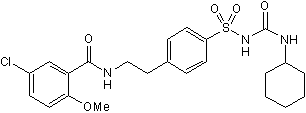
Glibenclamide
Chemical Name: 5-Chloro-N-[2-[4-[[[(Cylcohexylamino)carbonyl]amino]sulphonyl]phenyl]ethyl]-2-methoxybenzamide
Purity: ≥99%
Biological Activity
Glibenclamide is an ATP-dependent K+ channel (Kir6, KATP) and CFTR Cl- channel blocker. Inhibits Kir6 currents in the pancreas, causing an increase in intracellular Ca2+ and insulin secretion. Inhibits recombinant CFTR Cl- channels with an IC50 of 20 μM.Technical Data
The technical data provided above is for guidance only.
For batch specific data refer to the Certificate of Analysis.
Tocris products are intended for laboratory research use only, unless stated otherwise.
Background References
-
Glibenclamide: a review.
Brogden et al.
Drugs, 1979;18:329 -
Potassium channel modulators: scientific applications and therapeutic promise.
Robertson et al.
J.Med.Chem., 1990;33:1529 -
Effect of ATP-sensitive K+ channel regulators on cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator chloride channels.
Sheppard and Welsh
J.Gen.Physiol., 1992;100:573
Product Datasheets
Reconstitution Calculator
Molarity Calculator
Citations for Glibenclamide
The citations listed below are publications that use Tocris products. Selected citations for Glibenclamide include:
15 Citations: Showing 1 - 10
-
TRPM4 Conductances in Thalamic Reticular Nucleus Neurons Generate Persistent Firing during Slow Oscillations
Authors: O'Malley Et al.
J Neurosci 2020;40:4813
-
Antidiarrhoeal, antisecretory and antispasmodic activities of Matricaria chamomilla are mediated predominantly through K(+)-channels activation.
Authors: Mehmood Et al.
Neuroscience 2015;15:75
-
Dissecting out the complex Ca2+-mediated phenylephrine-induced contractions of mouse aortic segments.
Authors: Fransen Et al.
Biomed Res Int 2015;10:e0121634
-
Regulation of neurons in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus by SIRT1.
Authors: Jiang and Zsombok
Front Neurosci 2014;7:270
-
Characterization of imidazoline receptors in blood vessels for the development of antihypertensive agents.
Authors: Chen Et al.
J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2014;2014:182846
-
Acute SimV. inhibits K ATP channels of porcine coronary artery myocytes.
Authors: Seto Et al.
J Neurophysiol 2013;8:e66404
-
Effect of the ginsenoside Rb1 on the spontaneous contraction of intestinal smooth muscle in mice.
Authors: Xu
World J Gastroenterol 2012;18:5462
-
Activation of peripheral δ-opioid receptors leads to anti-hyperalgesic responses in the masseter muscle of male and female rats.
Authors: Saloman Et al.
PLoS One 2011;190:379
-
The acute antinociceptive effect of HBO2 is mediated by a NO-cyclic GMP-PKG-KATP channel pathway in mice.
Authors: Quock Et al.
Brain Res 2011;1368:102
-
Role of perivascular adipose tissue-derived methyl palmitate in vascular tone regulation and pathogenesis of hypertension.
Authors: Lee Et al.
Circulation 2011;124:1160
-
Expression and functional properties of TRPM2 channels in DArgic neurons of the substantia nigra of the rat.
Authors: Chung Et al.
J Korean Med Sci 2011;106:2865
-
ATP-sensitive potassium channel-mediated lactate effect on orexin neurons: implications for brain energetics during arousal.
Authors: Parsons
J Neurosci 2010;30:8061
-
Polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin gallate during ischemia limits infarct size via mitochondrial K(ATP) channel activation in isolated rat hearts.
Authors: Song Et al.
PLoS One 2010;25:380
-
Inflammation and fibrosis during Chlamydia pneumoniae infection is regulated by IL-1 and the NLRP3/ASC inflammasome.
Authors: He Et al.
J Immunol 2010;184:5743
-
Nesfatin-1 inhibits NPY neurons in the arcuate nucleus.
Authors: Price Et al.
Brain Res 2008;1230:99
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Small Molecule FAQsReviews for Glibenclamide
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Glibenclamide and earn rewards!
Have you used Glibenclamide?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image