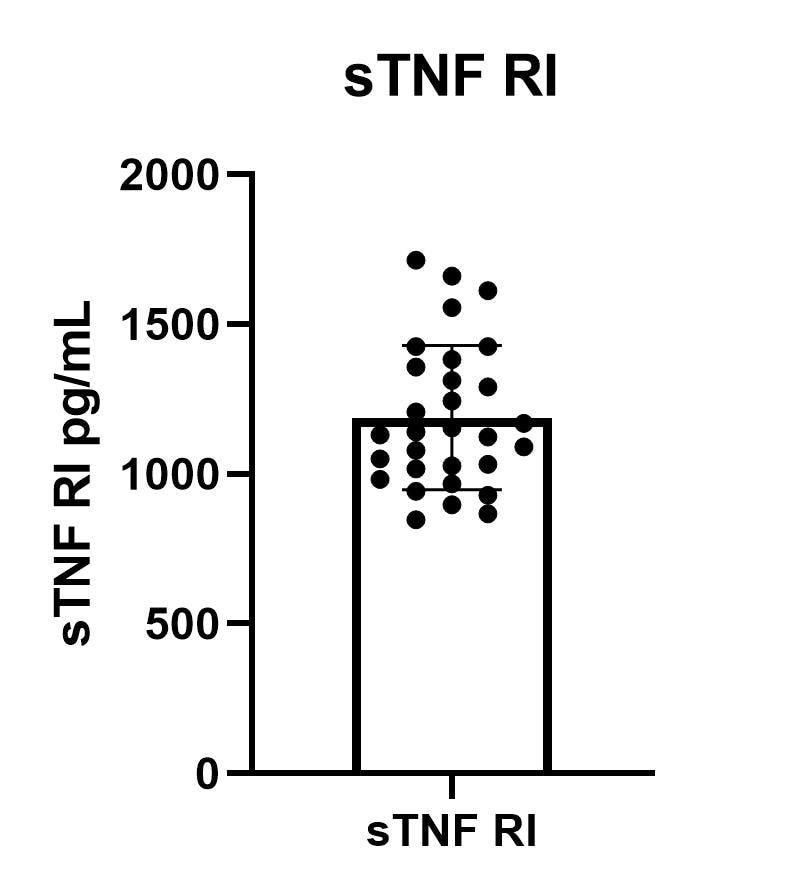
Human TNF RI/TNFRSF1A Quantikine ELISA Kit Summary
Product Summary
Precision
Cell Culture Supernates, Urine
| Intra-Assay Precision | Inter-Assay Precision | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| n | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Mean (pg/mL) | 41.5 | 122 | 231 | 54 | 251 | 350 |
| Standard Deviation | 2.14 | 5.38 | 11 | 2.7 | 9.7 | 23.3 |
| CV% | 5.2 | 4.4 | 4.8 | 5 | 3.9 | 6.7 |
Serum, EDTA Plasma, Heparin Plasma, Citrate Plasma
| Intra-Assay Precision | Inter-Assay Precision | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| n | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Mean (pg/mL) | 69 | 198 | 355 | 54.8 | 252 | 356 |
| Standard Deviation | 3.24 | 7.17 | 17.8 | 4.8 | 9.3 | 20.6 |
| CV% | 4.7 | 3.6 | 5 | 8.8 | 3.7 | 5.8 |
Recovery
The recovery of sTNF RI spiked to three levels in samples throughout the range of the assay in various matrices was evaluated.
| Sample Type | Average % Recovery | Range % |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Culture Media (n=8) | 85 | 80-92 |
| EDTA Plasma (n=8) | 86 | 70-97 |
| Heparin Plasma (n=8) | 93 | 79-103 |
| Serum (n=8) | 90 | 77-103 |
| Urine (n=8) | 85 | 71-109 |
Linearity
Scientific Data
Product Datasheets
Preparation and Storage
Background: TNF RI/TNFRSF1A
Tumor necrosis factors (TNFs) are pleiotropic cytokines that are considered primary modifiers of the inflammatory and immune reactions of animals produced in response to injury or infection. Two forms of TNF, designated TNF-alpha (or cachectin) and TNF-beta (or lymphotoxin), have been described that share 30% sequence similarity and compete for binding to the same receptors. TNFs play a necessary and beneficial role as mediators of host resistance to infections and tumor formation. However, over-production or inappropriate expression of these factors can lead to a variety of pathological conditions, including wasting, systemic toxicity, and septic shock. For reviews of the literature relating to these factors, see references 1 and 2.
Assay Procedure
Refer to the product- Prepare all reagents, standard dilutions, and samples as directed in the product insert.
- Remove excess microplate strips from the plate frame, return them to the foil pouch containing the desiccant pack, and reseal.
- Add 50 µL of Assay Diluent to each well.
- Add 200 µL of Standard, control, or sample to each well. Cover with a plate sealer, and incubate at room temperature for 2 hours.
- Aspirate each well and wash, repeating the process twice for a total of 3 washes.
- Add 200 µL of Conjugate to each well. Cover with a new plate sealer, and incubate at room temperature for 2 hours.
- Aspirate and wash 3 times.
- Add 200 µL Substrate Solution to each well. Incubate at room temperature for 20 minutes. PROTECT FROM LIGHT.
- Add 50 µL of Stop Solution to each well. Read at 450 nm within 30 minutes. Set wavelength correction to 540 nm or 570 nm.



Citations for Human TNF RI/TNFRSF1A Quantikine ELISA Kit
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
86
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Circulating TNF receptor levels are associated with estimated glomerular filtration rate even in healthy individuals with normal kidney function
Authors: Gohda, T;Murakoshi, M;Shibata, T;Suzuki, Y;Takemura, H;Tsuchiya, K;Okada, T;Wakita, M;Horiuchi, Y;Tabe, Y;Kamei, N;
Scientific reports
Species: Human hepegivirus
Sample Types: Serum
-
Correlation of Increased Soluble Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor 1 with Mortality and Dependence on Treatment in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients: A Longitudinal Cohort Study
Authors: Hassan, L;Bedir, A;Kraus, FB;Ostheimer, C;Vordermark, D;Mikolajczyk, R;Seliger, B;Medenwald, D;
Cancers
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis With Elevated Cytokines Related to Macrophage Activation After Liver Transplantation for Autoimmune Hepatitis: A Case Report
Authors: Nakanuma, S;Gabata, R;Okazaki, M;Seki, A;Hosokawa, K;Yokoyama, T;Katano, K;Sugita, H;Tokoro, T;Takada, S;Makino, I;Taniguchi, T;Harada, K;Yagi, S;
Transplantation proceedings
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
High molar ratios of tumor necrosis factor ? (TNF ?) soluble receptors I and II to the TNF ligand in human plasma from male veterans with comorbid posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI)
Authors: Morales, TI;Stamper, CE;Brenner, LA;
The European journal of psychiatry
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Elevated Soluble TNF-Receptor 1 in the Serum of Predementia Subjects with Cerebral Small Vessel Disease
Authors: KHT Salai, LY Wu, JR Chong, YL Chai, B Gyanwali, C Robert, S Hilal, N Venketasub, GS Dawe, CP Chen, MKP Lai
Biomolecules, 2023-03-13;13(3):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Circulating tumor necrosis factor receptors are associated with mortality and disease severity in COVID-19 patients
Authors: T Gohda, M Murakoshi, Y Suzuki, M Hiki, T Naito, K Takahashi, Y Tabe
PLoS ONE, 2022-10-11;17(10):e0275745.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Improved prediction of radiation pneumonitis by combining biological and radiobiological parameters using a data-driven Bayesian network analysis
Authors: T Hinton, D Karnak, M Tang, R Jiang, Y Luo, P Boonstra, Y Sun, DJ Nancarrow, E Sandford, P Ray, C Maurino, M Matuszak, MJ Schipper, MD Green, GA Yanik, M Tewari, IE Naqa, CA Schonewolf, RT Haken, S Jolly, TS Lawrence, D Ray
Translational Oncology, 2022-04-20;21(0):101428.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Inflammatory Markers and Risk of Heart Failure With Reduced to Preserved Ejection Fraction
Authors: Z Albar, M Albakri, J Hajjari, M Karnib, SE Janus, SG Al-Kindi
The American journal of cardiology, 2022-01-03;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Synergistic association of the copper/zinc ratio under inflammatory conditions with diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: The Asahi Diabetes Complications Study
Authors: T Takao, H Yanagisawa, M Suka, Y Yoshida, Y Onishi, T Tahara, T Kikuchi, A Kushiyama, M Anai, K Takahashi, S Wakabayash, H Yamazaki, S Kawazu, Y Iwamoto, M Noda, M Kasuga
Journal of diabetes investigation, 2021-10-07;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Circulating miRNA expression in asthmatics is age-related and associated with clinical asthma parameters, respiratory function and systemic inflammation
Authors: A Wardzy?ska, M Pawe?czyk, J Rywaniak, J Makowska, J Jamroz-Brz, ML Kowalski
Respiratory Research, 2021-06-10;22(1):177.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
TNFR1 and the TNF&alpha axis as a targetable mediator of liver injury from stereotactic body radiation therapy
Authors: MM Cousins, E Morris, C Maurino, TP Devasia, D Karnak, D Ray, ND Parikh, D Owen, RK Ten Haken, MJ Schipper, TS Lawrence, KC Cuneo
Translational Oncology, 2020-12-13;14(1):100950.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Identification of distinct immune activation profiles in adult humans
Authors: R Cezar, A Winter, D Desigaud, M Pastore, L Kundura, AM Dupuy, C Cognot, T Vincent, C Reynes, C Dunyach-Re, JP Lavigne, R Sabatier, P Le Merre, E Maggia, P Corbeau
Scientific Reports, 2020-11-30;10(1):20824.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Comparison of Circulating Biomarkers in Predicting Diabetic Kidney Disease Progression With Autoantibodies to Erythropoietin Receptor
Authors: M Oshima, A Hara, T Toyama, M Jun, C Pollock, M Jardine, S Harrap, N Poulter, ME Cooper, M Woodward, J Chalmers, V Perkovic, MG Wong, T Wada
Kidney international reports, 2020-11-10;6(2):284-295.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
The association between change of soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor R1 (sTNF-R1) measurements and cardiovascular and all-cause mortality-Results from the population-based (Cardiovascular Disease, Living and Ageing in Halle) CARLA study 2002-2016
Authors: L Hassan, D Medenwald, D Tiller, A Kluttig, B Ludwig-Kra, FB Kraus, KH Greiser, R Mikolajczy
PLoS ONE, 2020-10-26;15(10):e0241213.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
The transition to family caregiving and its effect on biomarkers of inflammation
Authors: DL Roth, WE Haley, OC Sheehan, J Huang, JD Rhodes, P Durda, VJ Howard, JD Walston, M Cushman
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2020-06-24;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Circulating Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptors: A Potential Biomarker for the Progression of Diabetic Kidney Disease
Authors: M Murakoshi, T Gohda, Y Suzuki
Int J Mol Sci, 2020-03-13;21(6):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Factor Xa Inhibition Reduces Coagulation Activity but Not Inflammation Among People With HIV: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Authors: JV Baker, J Wolfson, T Peterson, M Mooberry, M Gissel, H Mystakelis, MW Henderson, K Garcia-Mye, FS Rhame, TW Schacker, KE Brummel-Zi, I Sereti, NS Key, RP Tracy
Open Forum Infect Dis, 2020-02-01;7(2):ofaa026.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Pretransplant Levels of C-Reactive Protein,�Soluble TNF Receptor-1, and�CD38+HLADR+ CD8 T Cells Predict Risk of Allograft Rejection in HIV+ Kidney Transplant Recipients
Authors: JF Camargo, S Pallikkuth, I Moroz, Y Natori, ML Alcaide, A Rodriguez, G Guerra, GW Burke, S Pahwa
Kidney Int Rep, 2019-08-19;4(12):1705-1716.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Store-operated calcium entry (SOCE) contributes to phosphorylation of p38 MAPK and suppression of TNF-α signalling in the intestinal epithelial cells
Authors: J Uwada, T Yazawa, H Nakazawa, D Mikami, SM Krug, M Fromm, K Sada, I Muramatsu, T Taniguchi
Cell. Signal., 2019-07-08;63(0):109358.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Systemic Inflammation Precedes Microalbuminuria in Diabetes
Authors: FG Scurt, J Menne, S Brandt, A Bernhardt, PR Mertens, H Haller, C Chatzikyrk
Kidney Int Rep, 2019-06-21;4(10):1373-1386.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Serum soluble ST2 as a marker of renal scar in pediatric upper urinary tract infection
Authors: N Ohta, H Yasudo, M Mizutani, T Matsushige, R Fukano, S Kittaka, K Maehara, K Ichihara, S Ohga, S Hasegawa
Cytokine, 2019-05-29;120(0):258-263.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Inflammatory biomarkers, geriatric assessment, and treatment outcomes in acute myeloid leukemia
Authors: KP Loh, JA Tooze, BJ Nicklas, SB Kritchevsk, JD Williamson, LR Ellis, BL Powell, TS Pardee, NG Goyal, HD Klepin
J Geriatr Oncol, 2019-04-05;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and Fas/Fas ligand signaling pathways in chronic spontaneous urticaria
Authors: R Grzanka, A Damasiewic, A Kasperska-
Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol, 2019-03-14;15(0):15.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Infliximab Pharmacokinetics are Influenced by Intravenous Immunoglobulin Administration in Patients with Kawasaki Disease
Authors: N Vande Cast, J Oyamada, C Shimizu, BM Best, EV Capparelli, AH Tremoulet, JC Burns
Clin Pharmacokinet, 2018-12-01;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Elevated Inflammatory Plasma Biomarkers in Patients With Fabry Disease: A Critical Link to Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction
Authors: H Yogasundar, A Nikhanj, BN Putko, M Boutin, S Jain-Ghai, A Khan, C Auray-Blai, ML West, GY Oudit
J Am Heart Assoc, 2018-11-06;7(21):e009098.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Biomarkers and immunoprofiles associated with fetal abnormalities of ZIKV-positive pregnancies
Authors: SS Foo, W Chen, Y Chan, WS Lee, SA Lee, G Cheng, K Nielsen-Sa, P Brasil, JU Jung
JCI Insight, 2018-11-02;3(21):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
HIV-1 proviral landscapes distinguish posttreatment controllers from noncontrollers
Authors: R Sharaf, GQ Lee, X Sun, B Etemad, LM Aboukhater, Z Hu, ZL Brumme, E Aga, RJ Bosch, Y Wen, G Namazi, C Gao, EP Acosta, RT Gandhi, JM Jacobson, D Skiest, DM Margolis, R Mitsuyasu, P Volberding, E Connick, DR Kuritzkes, MM Lederman, XG Yu, M Lichterfel, JZ Li
J. Clin. Invest., 2018-08-20;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Host Immunological Effects of Partial Splenic Embolization in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis
Authors: Y Matsukiyo, H Nagai, T Matsui, Y Igarashi
J Immunol Res, 2018-07-15;2018(0):1746391.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
ST6Gal-I sialyltransferase promotes tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-mediated cancer cell survival via sialylation of the TNF receptor 1 (TNFR1) death receptor
Authors: AT Holdbrooks, CM Britain, SL Bellis
J. Biol. Chem., 2017-12-12;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Reevaluation of immune activation in the era of cART and an aging HIV-infected population
Authors: LR de Armas, S Pallikkuth, V George, S Rinaldi, R Pahwa, KL Arheart, S Pahwa
JCI Insight, 2017-10-19;2(20):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Prospective Analysis of Lipid Composition Changes with Antiretroviral Therapy and Immune Activation in Persons Living with HIV
Authors: MA Belury, E Bowman, J Gabriel, B Snyder, M Kulkarni, M Palettas, X Mo, JE Lake, D Zidar, SF Sieg, B Rodriguez, MP Playford, A Andrade, DR Kuritzkes, NN Mehta, MM Lederman, NT Funderburg
Pathog Immun, 2017-10-06;2(3):376-403.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Distinctive inflammatory profile between acute focal bacterial nephritis and acute pyelonephritis in children
Authors: M Mizutani, S Hasegawa, T Matsushige, N Ohta, S Kittaka, M Hoshide, T Kusuda, K Takahashi, K Ichihara, S Ohga
Cytokine, 2017-07-03;99(0):24-29.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Activation of muscarinic receptors prevents TNF-?-mediated intestinal epithelial barrier disruption through p38 MAPK
Authors: J Uwada, T Yazawa, MT Islam, MRI Khan, SM Krug, M Fromm, SI Karaki, Y Suzuki, A Kuwahara, H Yoshiki, K Sada, Muramatsu, T Taniguchi
Cell. Signal., 2017-04-12;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Circulating TNF Receptors 1 and 2 Predict Mortality in Patients with End-stage Renal Disease Undergoing Dialysis
Authors: T Gohda, S Maruyama, N Kamei, S Yamaguchi, T Shibata, M Murakoshi, S Horikoshi, Y Tomino, I Ohsawa, H Gotoh, S Nojiri, Y Suzuki
Sci Rep, 2017-03-03;7(0):43520.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Soluble Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptors and Arterial Stiffness in Patients With Coronary Atherosclerosis
Authors: Hack-Lyoung Kim
Am. J. Hypertens, 2017-03-01;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Effects of an Encapsulated Fruit and Vegetable Juice Concentrate on Obesity-Induced Systemic Inflammation: A Randomised Controlled Trial
Authors: EJ Williams, KJ Baines, BS Berthon, LG Wood
Nutrients, 2017-02-08;9(2):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Prevalent peripheral arterial disease and inflammatory burden
BMC Geriatr, 2016-12-09;16(1):213.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Anti-TNF-? Drugs Differently Affect the TNF?-sTNFR System and Monocyte Subsets in Patients with Psoriasis
PLoS ONE, 2016-12-09;11(12):e0167757.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Altered Monocyte and Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule Expression Is Linked to Vascular Inflammation in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection
Authors: M Kulkarni, E Bowman, J Gabriel, T Amburgy, E Mayne, DA Zidar, C Maierhofer, AN Turner, JA Bazan, SL Koletar, MM Lederman, SF Sieg, NT Funderburg
Open Forum Infect Dis, 2016-10-15;3(4):ofw224.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Anti-Drug Antibodies, Drug Levels, Interleukin-6 and Soluble TNF Receptors in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients during the First 6 Months of Treatment with Adalimumab or Infliximab: A Descriptive Cohort Study
PLoS ONE, 2016-09-08;11(9):e0162316.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Local TNF causes NFATc1-dependent cholesterol-mediated podocyte injury
J Clin Invest, 2016-08-02;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Inflammatory Markers and the Risk of Hip and Vertebral Fractures in Men: the Osteoporotic Fractures in Men (MrOS)
J Bone Miner Res, 2016-07-25;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Association between serum soluble tumor necrosis factor-? receptors and early childhood obesity
Authors: S Ouyang, W Li, Z Liu, Y Li, S Li, J Wu
Endocr J, 2016-03-31;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Late Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) Initiation Is Associated with Long-Term Persistence of Systemic Inflammation and Metabolic Abnormalities.
Authors: Ghislain M, Bastard J, Meyer L, Capeau J, Fellahi S, Gerard L, May T, Simon A, Vigouroux C, Goujard C
PLoS ONE, 2015-12-04;10(12):e0144317.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
T. vaginalis Infection Is Associated with Increased IL-8 and TNFr1 Levels but with the Absence of CD38 and HLADR Activation in the Cervix of ESN.
Authors: Jarrett O, Brady K, Modur S, Plants J, Landay A, Ghassemi M, Golub E, Spear G, Novak R
PLoS ONE, 2015-06-17;10(6):e0130146.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cervical Fluid
-
Plasma TNF-alpha and Soluble TNF Receptor Levels after Doxorubicin with or without Co-Administration of Mesna-A Randomized, Cross-Over Clinical Study.
Authors: Hayslip J, Dressler E, Weiss H, Taylor T, Chambers M, Noel T, Miriyala S, Keeney J, Ren X, Sultana R, Vore M, Butterfield D, St Clair D, Moscow J
PLoS ONE, 2015-04-24;10(4):e0124988.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Circulating TNF receptors 1 and 2 are associated with the severity of renal interstitial fibrosis in IgA nephropathy.
Authors: Sonoda Y, Gohda T, Suzuki Y, Omote K, Ishizaka M, Matsuoka J, Tomino Y
PLoS ONE, 2015-04-10;10(4):e0122212.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
A case-control study of pre-operative levels of serum neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and other potential inflammatory markers in colorectal cancer.
Authors: Duvillard L, Ortega-Deballon P, Bourredjem A, Scherrer M, Mantion G, Delhorme J, Deguelte-Lardiere S, Petit J, Bonithon-Kopp C
BMC Cancer, 2014-12-03;14(0):912.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
The expression of cytokines and chemokines in the blood of patients with severe weight loss from anorexia nervosa: an exploratory study.
Authors: Pisetsky D, Trace S, Brownley K, Hamer R, Zucker N, Roux-Lombard P, Dayer J, Bulik C
Cytokine, 2014-06-14;69(1):110-5.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Circulating levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptor 2 are increased in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction relative to heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: evidence for a divergence in pathophysiology.
Authors: Putko B, Wang Z, Lo J, Anderson T, Becher H, Dyck J, Kassiri Z, Oudit G
PLoS ONE, 2014-06-12;9(6):e99495.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
The effect of rosuvastatin on inflammation, matrix turnover and left ventricular remodeling in dilated cardiomyopathy: a randomized, controlled trial.
Authors: Broch K, Askevold E, Gjertsen E, Ueland T, Yndestad A, Godang K, Stueflotten W, Andreassen J, Svendsmark R, Smith H, Aakhus S, Aukrust P, Gullestad L
PLoS ONE, 2014-02-25;9(2):e89732.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Blood
-
Dynamics of immune reconstitution and activation markers in HIV+ treatment-naive patients treated with raltegravir, tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and emtricitabine.
Authors: Funderburg N, Andrade A, Chan E, Rosenkranz S, Lu D, Clagett B, Pilch-Cooper H, Rodriguez B, Feinberg J, Daar E, Mellors J, Kuritzkes D, Jacobson J, Lederman M
PLoS ONE, 2013-12-18;8(12):e83514.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
IL-18-based combinatorial adjuvants promote the intranodal production of CCL19 by NK cells and dendritic cells of cancer patients.
Authors: Wong J, Muthuswamy R, Bartlett D, Kalinski P
Oncoimmunology, 2013-09-12;2(9):e26245.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
-
Risk of ESRD and all cause mortality in type 2 diabetes according to circulating levels of FGF-23 and TNFR1.
Authors: Lee J, Gohda T, Walker W, Skupien J, Smiles A, Holak R, Jeong J, McDonnell K, Krolewski A, Niewczas M
PLoS ONE, 2013-03-20;8(3):e58007.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Compensated inflammation in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis: role of alternatively activated macrophages.
Authors: Shimizu M, Yachie A
Cytokine, 2012-06-08;60(1):226-32.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Inflammatory markers and the risk of hip fracture: the Women's Health Initiative.
Authors: Barbour KE, Boudreau R, Danielson ME, Youk AO, Wactawski-Wende J, Greep NC, LaCroix AZ, Jackson RD, Wallace RB, Bauer DC, Allison MA, Cauley JA
J. Bone Miner. Res., 2012-05-01;27(5):1167-76.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Inflammation marker and risk of pancreatic cancer: a nested case-control study within the EPIC cohort.
Authors: Grote VA, Kaaks R, Nieters A, Tjonneland A, Halkjaer J, Overvad K, Skjelbo Nielsen MR, Boutron-Ruault MC, Clavel-Chapelon F, Racine A, Teucher B, Becker S, Pischon T, Boeing H, Trichopoulou A, Cassapa C, Stratigakou V, Palli D, Krogh V, Tumino R, Vineis P, Panico S, Rodriguez L, Duell EJ, Sanchez MJ, Dorronsoro M, Navarro C, Gurrea AB, Siersema PD, Peeters PH, Ye W, Sund M, Lindkvist B, Johansen D, Khaw KT, Wareham N, Allen NE, Travis RC, Fedirko V, Jenab M, Michaud DS, Chuang SC, Romaguera D, Bueno-de-Mesquita HB, Rohrmann S
Br. J. Cancer, 2012-04-26;106(11):1866-74.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Cytokine Response Patterns in Severe Pandemic 2009 H1N1 and Seasonal Influenza among Hospitalized Adults.
Authors: Lee N, Wong CK, Chan PK, Chan MC, Wong RY, Lun SW, Ngai KL, Lui GC, Wong BC, Lee SK, Choi KW, Hui DS
PLoS ONE, 2011-10-13;6(10):e26050.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Elevated CSF levels of TACE activity and soluble TNF receptors in subjects with mild cognitive impairment and patients with Alzheimer's disease.
Authors: Jiang H, Hampel H, Prvulovic D, Wallin A, Blennow K, Li R, Shen Y
Mol Neurodegener, 2011-10-06;6(0):69.
Species: Human
Sample Types: CSF
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-9 and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 are associated with right ventricular structure and function: the MESA-RV Study.
Authors: Kawut SM, Barr RG, Johnson WC
Biomarkers, 2010-10-05;15(8):731-8.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Adrenomedullin and endothelin-1 are related to inflammation in chronic heart failure.
Authors: Gombos T, Forhecz Z, Pozsonyi Z, Wallentin S, Papassotiriou J, Kunde J, Morgenthaler NG, Janoskuti L, Prohaszka Z
Inflamm. Res., 2009-06-01;58(6):298-305.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Secretory lysosome targeting and induced secretion of human soluble TNF-alpha receptor in murine hematopoietic cells in vivo as a principle for immunoregulation in inflammation and malignancy.
Authors: Johansson AC, Nandakumar KS, Persson AM, Olsson I, Hansson M
Exp. Hematol., 2009-05-30;37(8):969-78.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Selective effects of CPAP on sleep apnoea-associated manifestations.
Authors: Vgontzas AN, Zoumakis E, Bixler EO, Lin HM, Collins B, Basta M, Pejovic S, Chrousos GP
Eur. J. Clin. Invest., 2008-08-01;38(8):585-95.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Change in plasma tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 levels in the first week after myeloablative allogeneic transplantation correlates with severity and incidence of GVHD and survival.
Authors: Choi SW, Kitko CL, Braun T, Paczesny S, Yanik G, Mineishi S, Krijanovski O, Jones D, Whitfield J, Cooke K, Hutchinson RJ, Ferrara JL, Levine JE
Blood, 2008-05-23;112(4):1539-42.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Comparing Type D personality and older age as correlates of tumor necrosis factor-alpha dysregulation in chronic heart failure.
Authors: Denollet J, Vrints CJ, Conraads VM
Brain Behav. Immun., 2008-02-20;22(5):736-43.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Microparticles of human atherosclerotic plaques enhance the shedding of the tumor necrosis factor-alpha converting enzyme/ADAM17 substrates, tumor necrosis factor and tumor necrosis factor receptor-1.
Authors: Canault M, Leroyer AS, Peiretti F, Leseche G, Tedgui A, Bonardo B, Alessi MC, Boulanger CM, Nalbone G
Am. J. Pathol., 2007-09-14;171(5):1713-23.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Inflammatory markers and incident fracture risk in older men and women: the Health Aging and Body Composition Study.
Authors: Cauley JA, Danielson ME, Boudreau RM, Forrest KY, Zmuda JM, Pahor M, Tylavsky FA, Cummings SR, Harris TB, Newman AB
J. Bone Miner. Res., 2007-07-01;22(7):1088-95.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Selective functional exhaustion of hematopoietic progenitor cells in the bone marrow of patients with postinfarction heart failure.
Authors: Kissel CK, Lehmann R, Assmus B, Aicher A, Honold J, Fischer-Rasokat U, Heeschen C, Spyridopoulos I, Dimmeler S, Zeiher AM
J. Am. Coll. Cardiol., 2007-06-04;49(24):2341-9.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Muscle atrophy and hypertrophy signaling in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Authors: Doucet M, Russell AP, Leger B, Debigare R, Joanisse DR, Caron MA, LeBlanc P, Maltais F
Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med., 2007-05-03;176(3):261-9.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Serum interleukin-18 and soluble tumour necrosis factor receptor 2 are associated with disease severity in patients with paracoccidioidomycosis.
Authors: Corvino CL, Mamoni RL, Fagundes GZ, Blotta MH
Clin. Exp. Immunol., 2007-03-01;147(3):483-90.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
The shedding activity of ADAM17 is sequestered in lipid rafts.
Authors: Tellier E, Rebsomen L
Exp. Cell Res., 2006-09-05;312(20):3969-80.
Species: Primate - Cholrocebus pygerythrus (Vervet Monkey)
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
-
Proinflammatory cytokines, insulin resistance, and insulin secretion in chronic hepatitis C patients: A case-control study.
Authors: Lecube A, Hernandez C, Genesca J, Simo R
Diabetes Care, 2006-05-01;29(5):1096-101.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Neutrophils from patients with TNFRSF1A mutations display resistance to tumor necrosis factor-induced apoptosis: pathogenetic and clinical implications.
Authors: D'Osualdo A
Arthritis Rheum., 2006-03-01;54(3):998-1008.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Experimental heatstroke in baboon: analysis of the systemic inflammatory response.
Authors: Bouchama A, Ollivier V, Roberts G, Al Mohanna F, de Prost D, Eldali A, Saussereau E, El-Sayed R, Chollet-Martin S
Shock, 2005-10-01;24(4):332-5.
Species: Primate - Papio hamadryas (Hamadyras Baboon)
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Effects of the active metabolite of leflunomide, A77 1726, on cytokine release and the MAPK signalling pathway in human rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes.
Authors: Vergne-Salle</LastName><F P</Initial, Vergne-Salle P, Leger DY, Bertin P, Treves R, Beneytout JL, Liagre B
Cytokine, 2005-09-07;31(5):335-48.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Regulation of peritoneal and systemic neutrophil-derived tumor necrosis factor-alpha release in patients with severe peritonitis: role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha converting enzyme cleavage.
Authors: Kermarrec N, Selloum S, Plantefeve G, Chosidow D, Paoletti X, Lopez A, Mantz J, Desmonts JM, Gougerot-Pocidalo MA, Chollet-Martin S
Crit. Care Med., 2005-06-01;33(6):1359-64.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Levels of soluble cytokine factors in temporomandibular joint effusions seen on magnetic resonance images.
Authors: Kaneyama K, Segami N, Sun W, Sato J, Fujimura K
Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod, 2005-04-01;99(4):411-8.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Synovial Fluid
-
Growth hormone-induced reduction of soluble apoptosis mediators is associated with reverse cardiac remodelling and improvement of exercise capacity in patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy.
Authors: Parissis JT, Adamopoulos S, Karatzas D, Paraskevaidis J, Livanis E, Kremastinos D
Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil, 2005-04-01;12(2):164-8.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Analysis of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-6, interleukin-1beta, soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors I and II, interleukin-6 soluble receptor, interleukin-1 soluble receptor type II, interleukin-1 receptor antagonist, and protein in the synovial fluid of patients with temporomandibular joint disorders.
Authors: Kaneyama K, Segami N, Sun W, Sato J, Fujimura K
Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod, 2005-03-01;99(3):276-84.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Synovial Fluid
-
Gene transfer of tumor necrosis factor inhibitor improves the function of lung allografts.
Authors: Tagawa T, Kozower BD, Kanaan SA, Daddi N, Muraoka M, Oka T, Ritter JH, Patterson GA
J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg., 2004-06-01;127(6):1558-63.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
-
Pro- and anti-inflammatory responses in respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis.
Authors: McNamara PS, Flanagan BF, Selby AM, Hart CA, Smyth RL
Eur. Respir. J., 2004-01-01;23(1):106-12.
Species: Human
Sample Types: BALF
-
Arenavirus-mediated liver pathology: acute lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection of rhesus macaques is characterized by high-level interleukin-6 expression and hepatocyte proliferation.
Authors: Lukashevich IS, Tikhonov I, Rodas JD, Zapata JC, Yang Y, Djavani M, Salvato MS
J. Virol., 2003-02-01;77(3):1727-37.
Species: Primate - Macaca mulatta (Rhesus Macaque)
Sample Types: Serum
-
Age-related autoantibody production in a nonhuman primate model.
Authors: Attanasio R, Brasky KM, Robbins SH, Jayashankar L, Nash RJ, Butler TM
Clin. Exp. Immunol., 2001-03-01;123(3):361-5.
Species: Primate - Papio cynocephalus (Yellow Baboon)
Sample Types: Serum
-
An analysis of 14 molecular markers for monitoring osteoarthritis: segregation of the markers into clusters and distinguishing osteoarthritis at baseline.
Authors: Otterness IG, Swindell AC, Zimmerer RO, Poole AR, Ionescu M, Weiner E
Osteoarthr. Cartil., 2000-05-01;8(3):180-5.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Proinflammatory cytokines increase in sepsis after anti-adhesion molecule therapy.
Authors: Welty-Wolf KE, 2016, Carraway MS, Ghio A, Kantrow SP, Huang YC, Piantadosi CA
1-23, 2000-05-01;13(5):404-9.
Species: Primate - Papio cynocephalus (Yellow Baboon)
Sample Types: Serum
-
Tumour necrosis factor alpha and its soluble receptors in juvenile chronic arthritis.
Authors: Rooney M, Varsani H, Martin K, Lombard PR, Dayer JM, Woo P
Rheumatology (Oxford), 2000-04-01;39(4):432-8.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all ELISA FAQsReviews for Human TNF RI/TNFRSF1A Quantikine ELISA Kit
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 2 Reviews)
Have you used Human TNF RI/TNFRSF1A Quantikine ELISA Kit?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by: