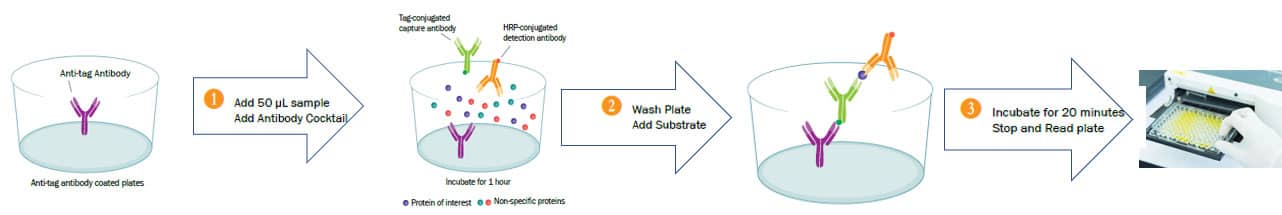
Human TNF RI/TNFRSF1A Quantikine QuicKit ELISA Summary
Sample Type & Volume Required Per Well
Cell Culture Supernates (50 uL), Serum (13 uL), EDTA Plasma (13 uL), Heparin Plasma (13 uL), Urine (13 uL)
Assay Range
15.6 - 1,000 pg/mL (Cell Culture Supernates, Serum, EDTA Plasma, Heparin Plasma, Urine)
Specificity
Natural and recombinant human TNF RI.
Cross-reactivity
< 0.5% cross-reactivity observed with available related molecules.< 50% cross-species reactivity observed with species tested.
Interference
No significant interference observed with available related molecules.
Product Summary
The Quantikine® QuicKit™ Human TNF RI/TNFRSF1A Immunoassay is a one step, 80-minute solid phase ELISA designed to measure human TNF RI levels in cell culture supernates, serum, plasma, and urine. It contains E. coli-expressed recombinant human TNF RI and antibodies raised against the recombinant protein. Results obtained for natural human TNF RI showed linear curves that were parallel to the standard curves obtained using the recombinant QuicKit™ standards. These results indicate that this kit can be used to determine relative mass values for natural human TNF RI.
Precision
Intra-Assay Precision (Precision within an assay) Two samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess intra-assay precision
Inter-Assay Precision (Precision between assays) Two samples of known concentration were tested in ten separate assays to assess inter-assay precision. Assays were performed by at least three technicians
Cell Culture Supernates, Serum, EDTA Plasma, Heparin Plasma, Urine
|
Intra-Assay Precision |
Inter-Assay Precision |
| Sample |
1 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
| n |
20 |
20 |
10 |
10 |
| Mean (pg/mL) |
100 |
624 |
619 |
99.9 |
| Standard Deviation |
1.75 |
17 |
39.3 |
6.78 |
| CV% |
1.8 |
2.7 |
6.3 |
6.8 |
Recovery
The recovery of human TNF RI spiked to three different levels in samples throughout the range of the assay in various matrices was evaluated.
| Sample Type |
Average % Recovery |
Range % |
| Cell Culture Media (n=4) |
101 |
92-109 |
| EDTA Plasma (n=2) |
98 |
88-109 |
| Heparin Plasma (n=2) |
98 |
85-109 |
| Serum (n=2) |
99 |
91-113 |
| Urine (n=2) |
96 |
92-100 |
Linearity
To assess the linearity of the assay, samples containing and/or spiked with high concentrations of human TNF RI were diluted with calibrator diluent to produce samples with values within the dynamic range of the assay.
Scientific Data
Human TNF RI ELISA Standard Curve
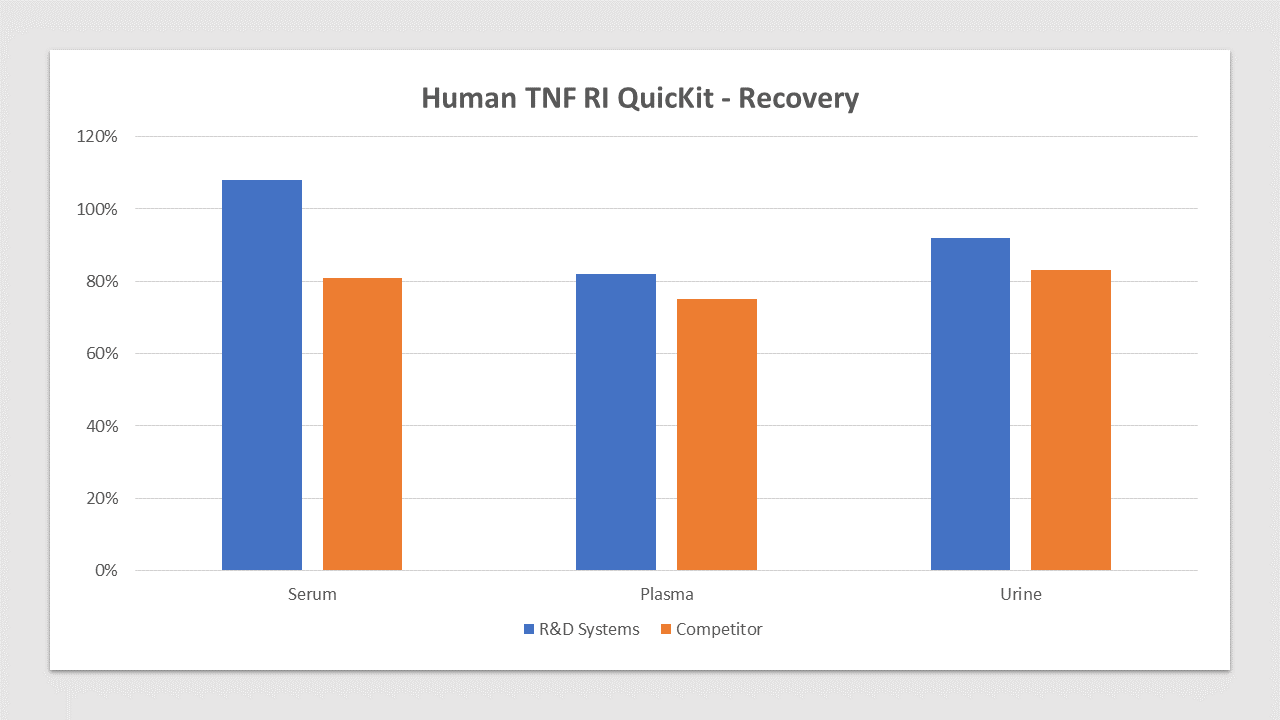
Human TNF RI QuicKit Spiked Recovery Competitor Comparison
TNF RI is spiked at three known concentrations throughout the range of the assay and run to measure response of the spiked sample matrix. Serum recovery is 108% compared to 81% for the top competitor. Plasma recovery is 82% compared to 75% for the top competitor. Urine recovery is 92% compared to 83% for the top competitor. In spike and recovery experiments, natural samples are spiked with the recombinant target analyte of interest to identify interference caused by sample matrices.
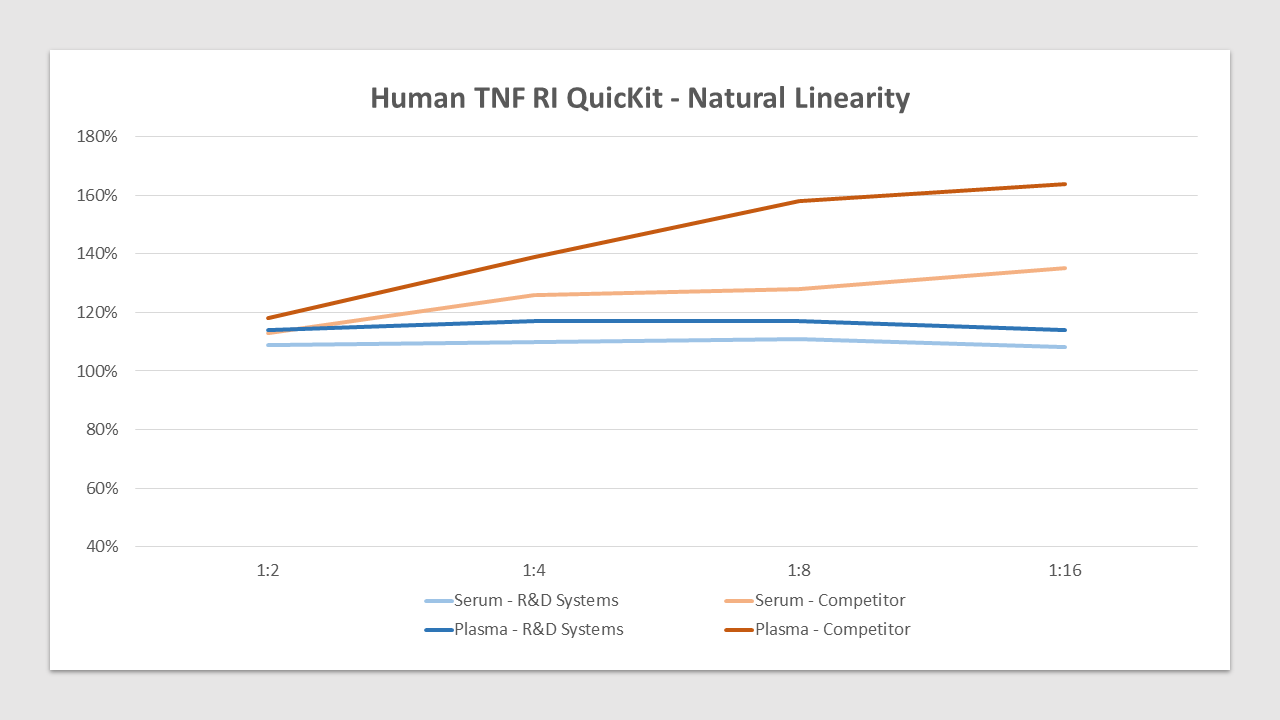
Human TNF RI QuicKit Natural Linearity Competitor Comparison
Samples containing TNF RI were diluted with appropriate Calibrator Diluent to produce samples with values within the dynamic range of the assay. The linearity is between 108%-117% compared to 113%-164% for the top competitor.
Product Datasheets
You must select a language.
x
Preparation and Storage
Shipping
The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below.
Storage
Store the unopened product at 2 - 8 °C. Do not use past expiration date.
Background: TNF RI/TNFRSF1A
Tumor necrosis factors (TNFs) are pleiotropic cytokines that are considered primary modifiers
of the inflammatory and immune reactions of animals produced in response to injury or
infection. Two forms of TNF, designated TNF-alpha (or cachectin) and TNF-beta (or lymphotoxin), have
been described that share 30% sequence similarity and compete for binding to the same
receptors. TNFs play a necessary and beneficial role as mediators of host resistance to
infections and tumor formation. However, over-production or inappropriate expression of
these factors can lead to a variety of pathological conditions, including wasting, systemic
toxicity, and septic shock. For reviews of the literature relating to these factors, see references
1 and 2.
The actions of TNFs are produced subsequent to binding of the factors to cell surface receptors.
Two distinct TNF receptors have been identified and cloned. Virtually all cell types studied
show the presence of one or both of these receptor types. One receptor type, termed TNF RII
(Type A, Type a, 75 kDa or utr antigen), shows an apparent molecular weight of 75 kDa. The
gene for this receptor encodes a presumptive transmembrane protein of 439 amino acid (aa)
residues (3, 19). The other receptor type, termed TNF RI (Type B, Type b, 55 kDa or htr antigen),
shows an apparent molecular weight of 55 kDa. The gene for this protein encodes a
transmembrane protein of 426 aa residues (4, 5, 19). Both receptor types show high affinity
binding of either TNF-alpha or TNF-beta. The two receptor types are immunologically distinct but their
extracellular domains show similarities in the pattern of cysteine residue locations in four
domains (3). The intracellular domains of the two receptor types are apparently unrelated,
suggesting the possibility that the two receptor types employ different signal transduction
pathways.
Several groups have identified soluble TNF binding proteins in human serum and urine (6-8)
that can neutralize the biological activities of TNF-alpha and TNF-beta. Two types have been identified
and designated sTNF RI (or TNF BPI) and sTNF RII (or TNF BPII). These soluble forms have now
been shown to represent truncated forms of the two types of TNF receptors discussed above.
The soluble receptor forms apparently arise as a result of shedding of the extracellular domains
of the receptors, and concentrations of about 1-2 ng/mL are found in the serum and urine of
healthy subjects (9, 10). The levels of the soluble receptors vary from individual to individual
but are stable over time for given individuals (9).
Elevated levels of TNF receptors have been found in the amniotic fluid and urine of pregnant
women (11), in serum or plasma in association with pathological conditions such as
endotoxinemia (12, 13), meningiococcemia (14), and HIV infection (15), and in plasma and
ascites of patients in association with infections and malignancies (16). The mechanisms
involved in the induction of shedding of the TNF receptors are not well understood. There are
reports of correlations between increased TNF levels and soluble receptor levels, suggesting
generally that stimuli that cause TNF levels to rise also induce shedding of TNF receptors
(12-14, 17). There is also evidence, however, that suggests the shedding of the two types of
soluble receptors is independently regulated (13).
2 For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
The physiological role of the soluble TNF receptors is not known. It is known that both types of
soluble receptors can bind to TNF in vitro and inhibit its biological activity by competing with
cell surface receptors for TNF binding. Consequently it has been suggested that shedding of
soluble receptors in response to TNF release could serve as a mechanism for binding and
inhibiting the TNF not immediately bound to surface receptors, thus protecting other cells
from the effects of TNF and localizing the inflammatory response (12, 17). It is also possible that
shedding of receptors represents a mechanism for desensitizing the cells that shed the
receptors from the effects of TNF (17). On the other hand, it has been reported that at low
concentrations of TNF, binding to soluble receptors can stabilize TNF and augment some of its
activities (18). Thus it is possible that under some conditions the pool of TNF bound to soluble
receptors could represent a reservoir for the stabilization and controlled release of TNF.
Long Name:
Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor I
Entrez Gene IDs:
7132 (Human); 21937 (Mouse); 25625 (Rat); 102135285 (Cynomolgus Monkey)
Alternate Names:
CD120a antigen; CD120a; FPF; p55; p55-R; p60; TNF RI; TNFARMGC19588; TNF-R; TNF-R1; TNFR1TBP1; TNFR55; TNF-R55; TNFR60; TNFRI; TNF-RI; TNF-R-I; TNFR-I; TNFRSF1A; tumor necrosis factor binding protein 1; Tumor necrosis factor receptor 1; tumor necrosis factor receptor 1A isoform beta; tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 1A; tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 1A; tumor necrosis factor receptor type 1; Tumor necrosis factor receptor type I; tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptor
 View Larger
View Larger
 View Larger
View Larger