Methylcellulose Stock Solution Summary
For the growth and differentiation of human, mouse, and rat hematopoietic stem cells using Iscove’s Modified Dulbecco’s Media.
Key Benefits
- Can be supplemented with user-defined cytokines and growth factors
- Excellent optical clarity facilitates colony identification
- High lot-to-lot consistency decreases variation
Why is it Important to Verify Hematopoietic Progenitor Cell Identity using Established Markers?
Colony forming cell (CFC) assays, which are used to enumerate and quantify multi-potent and single lineage hematopoietic progenitors, can be time consuming and laborious.
Successful growth and enumeration of cell colonies is dependent on factors such as accurate cell counts, the presence of growth factors and/or cytokines, adequate humidity, and the use of high quality media. R&D Systems offers high quality Methylcellulose Stock Solution with superior optical clarity to support optimal colony growth, enumeration, and identification.
R&D Systems Methylcellulose Stock Solution:
- Optical clarity facilitates colony identification.
- High lot-to-lot consistency decreases variation.
- Supports reproducible in vitro growth of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells.
- Can be supplemented with user-defined cytokines and growth factors.
- Increased cloning efficiency and improved colony growth compared to agar.
- 100 mL of 3% Methylcellulose in Iscove's Modified Dulbecco's Medium.
| Contents | Concentration |
| Methylcellulose (1500 cps) in Iscove’s Modified Dulbecco's Medium |
3.0% |
Stability and Storage
Methylcellulose Stock Solution should be stored at =-20 °C upon receipt. Storage at 2 °C to 8 °C is not recommended.
Precautions
The acute and chronic effects of overexposure to this media are unknown. Safe laboratory procedures should be followed and protective clothing should be worn when handling this media.
Limitations
- The safety and efficacy of this product in diagnostic or other clinical uses has not been established.
- The reagent should not be used beyond the expiration date indicated on the label.
- Human hematopoietic progenitors derived from different individuals may cause results to vary.
Human Methylcellulose Stock and Base Media
| Catalog # | Product Description | Volume | Colonies Selected for | Contains Serum | Cytokines Included |
| HSC001 | Methylcellulose Stock Solution | 100 mL | N/A* | No | None |
| HSC002 | Human Methylcellulose Base Media |
90 mL | N/A* | Yes | None |
| HSC002SF | Human Methylcellulose Serum-Free Base Media |
90 mL | N/A* | No | None |
| HSC011 | StemXVivo® Methylcellulose Concentrate |
50 mL | N/A* | No | None |
Complete Human Methylcellulose Media
| Catalog # | Product Description | Volume | Colonies Selected for | Contains Serum | Cytokines Included |
| HSC003 | Human Methylcellulose Complete Media | 100 mL | BFU-E CFU-E CFU-G CFU-GEMM CFU-GM CFU-M |
Yes | Epo GM-CSF IL-3 SCF |
| HSC004 | Human Methylcellulose Complete Media without Epo | 100 mL | CFU-G CFU-GM CFU-M |
Yes | SCF GM-CSF IL-3 |
| HSC005 | Human Methylcellulose Enriched Media |
100 mL | BFU-E CFU-E CFU-G CFU-GEMM CFU-GM CFU-M |
Yes | Epo G-CSF GM-CSF IL-3 IL-6 SCF |
| HSC005SF | Human Methylcellulose Serum-Free Enriched Media |
100 mL | BFU-E CFU-E CFU-G CFU-GEMM CFU-GM CFU-M |
No | Epo G-CSF GM-CSF IL-3 IL-6 SCF |
| HSC010SF | Human Methylcellulose Serum-Free Enriched Media without Epo |
100 mL | CFU-G CFU-GM CFU-M |
No | G-CSF GM-CSF IL-3 IL-6 SCF |
Mouse Methylcellulose Stock and Base Media
| Catalog # | Product Description | Volume | Colonies Selected for | Contains Serum | Cytokines Included |
| HSC001 | Methylcellulose Stock Solution | 100 mL | N/A* | No | None |
| HSC006 | Mouse Methylcellulose | 90 mL | N/A* | Yes | None |
| HSC011 | StemXVivo® Methylcellulose Concentrate |
50 mL | N/A* | No | None |
Complete Mouse Methylcellulose Media
| Catalog # | Product Description | Volume | Colonies Selected for | Contains Serum | Cytokines Included |
| HSC007 | Mouse Methylcellulose Complete Media | 100 mL | BFU-E CFU-E CFU-G CFU-GEMM CFU-GM CFU-M |
Yes | Epo IL-3 IL-6 SCF |
| HSC008 | Mouse Methylcellulose Complete Media Without Epo | 100 mL | CFU-G CFU-GM CFU-M |
Yes | IL-3 IL-6 SCF |
| HSC009 | Mouse Methylcellulose Complete Media for Pre-B Cells | 100 mL | CFU-Pre-B | Yes | IL-7 |
*Base media and stock solutions do not contain cytokines and will not support colony growth unless conditioned media, cytokines, or other culture supplements are added.
Specifications
Product Datasheets
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Human Hematopoietic Colony Formation Using the Methylcellulose-based Colony Forming Cell Assay. Colony forming unit-erythroid (CFU-E) are clonogenic progenitors that produce only one or two clusters with each cluster containing from 8 to approximately 100 hemoglobinized erythroblasts. It represents the more mature erythroid progenitors that have less proliferative capacity.B. Colony forming unit-granulocyte (CFU-G) are clonogenic progenitors of granulocytes that give rise to a homogeneous population of eosinophils, basophils, or neutrophils.C. Colony forming unit-granulocyte, macrophage (CFU-GM) are progenitors that give rise to colonies containing a heterogeneous population of macrophages and granulocytes. The morphology is similar to the CFU-M and CFU-G descriptions.D. Burst forming unit-erythroid (BFU-E) colonies can be described as small (3 to 8 clusters), intermediate (9 to 16 clusters), or large (more than 16 clusters) according to the number of clusters present. These are primitive erythroid progenitors that have high proliferative capacity.E. Colony forming unit-macrophage (CFU-M) are clonogenic progenitors of macrophages that give rise to a homogenous population of macrophages.F. Colony forming unit-granulocyte, erythrocyte, macrophage, megakaryocyte (CFU-GEMM) are multi-lineage progenitors that give rise to erythroid, granulocyte, macrophage and megakaryocyte lineages, as the name indicates.
 View Larger
View Larger
Mouse Hematopoietic Colony Formation Using the Methylcellulose-based Colony Forming Cell Assay. A. Burst forming unit-erythroid (BFU-E) colonies are defined as clusters with a minimal of 30 cells that can be seen from day 7 onward. Each individual cluster consisted of tiny, irregular shaped cells that may appear fused together. Each cluster normally contains 5-8 cells, and the size of the cluster is similar to that of a single macrophage. The cluster may vary in sizes and color. A large BFU-E is usually bright red and is differentiable even without the use of a microscope. Smaller BFU-E may not appear red in color but is distinguishable based on the morphology. B. Colony forming unit-macrophage (CFU-M; left) are clonogenic progenitors of macrophages that give rise to a homogenous population of macrophages. Colony forming unit-granulocyte (CFU-G; right) are clonogenic progenitors of granulocytes that give rise to a homogeneous population of eosinophils, basophils, or neutrophils. C. Colony forming unit-granulocyte, macrophage (CFU-GM) are progenitors that give rise to colonies containing a heterogeneous population of macrophages and granulocytes. The morphology is similar to the CFU-M and CFU-G descriptions. D. Colony forming unit-granulocyte, erythrocyte, macrophage, megakaryocyte (CFU-GEMM) are multi-lineage progenitors that give rise to the lineage of erythroid, granulocytes, macrophages, and megakaryocytes as the name indicates. It can be identified as reddish colored cells (erythroid) mixed with colorless cells (granulocytes, macrophages, and megakaryocytes) in a single colony. This progenitor is typically the largest colony on the culture dish; occasionally CFU-GM may attain a size comparable or larger than that of CFU-GEMM.
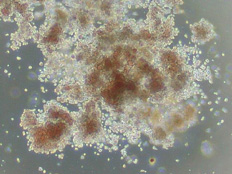 View Larger
View Larger
Tips to Identify CFU-GEMM Colonies in the Human Colony Forming Unit Assay. CFU-GEMMs contain a mixture of granulocytes, erythrocytes, megakaryocytes, and macrophages. Human CFU-GEMMs have the obvious red color of the BFU-E as well as the complex morphological features of both the small, compact granulocytes and the large, round macrophages. Viewing the cluster in multiple focal planes is again important to ensure that the colony contains all of the GEMM cell types. CFU-GEMM appearance is similar for human and mouse cells. For more tips please visit watch our CFC Assay video tutorial.
Assay Procedure
Refer to the product datasheet for complete product details.
Briefly, Methylcellulose Stock Solution is used in the Colony Forming Cell Assay using the following procedure:
- Prepare human mononuclear cells or mouse bone marrow cells
- Add cells and desired supplements to Methylcellulose Stock Solution
- Plate and incubate cells
- Identify and count colonies
Reagent supplied in the Methylcellulose Stock Solution (Catalog # HSC001):
- 100 mL of 3% Methylcellulose in Iscove’s Modified Dulbecco’s Medium.
| Contents | Concentration |
| Methylcellulose (1500 cps) in Iscove’s Modified Dulbecco's Medium |
3.0% |
Reagents
- Cells derived from bone marrow, blood, or enriched CD34+ cells
- Iscove's Modified Dulbecco's Media (IMDM)
- Ca2+/Mg2+-Free Hank's Balanced Salt Solution (HBSS)
- Ficoll-Paque™ PLUS (GE Healthcare) or equivalent
Materials
- 100 mm culture plates
- 35 mm culture plates
- 15 mL centrifuge tubes
- 50 mL centrifuge tubes
- 10 mL syringes
- 3 mL syringes
- 5 mL vials
- 16 gauge 1½ inch needle
- 14 gauge laboratory pipetting needle
- Heparinized syringes or Vacutainers®
- Serological pipettes
- Pipettes and pipette tips
Equipment
- 37 °C and CO2 humidified incubator
- Centrifuge
- Vortex mixer
- Hemocytometer
- Inverted Microscope
Reagents
- Cells derived from mouse bone marrow, spleen, peripheral blood, or fetal liver. Mice are routinely used between 6 - 12 weeks.
- Iscove's Modified Dulbecco’s Media (IMDM)
- Fetal Bovine Serum
- IMDM/2% Fetal Bovine Serum
- (Optional) Flow Cytometry Mouse Lyse Buffer (Catalog # FC003)
Materials
- 100 mm culture plates
- 35 mm culture plates
- 15 mL centrifuge tubes
- 10 mL syringes
- 3 mL syringes
- 5 mL vials
- 16 gauge 1½ inch needle
- 14 gauge laboratory pipetting needle
- Serological pipettes
- Pipettes and pipette tips
Equipment
- 37 °C and CO2 humidified incubator
- Centrifuge
- Vortex mixer
- Hemocytometer
- Inverted Microscope
Procedure for the Human Colony Forming Cell Assay
Prepare mononuclear cells by Ficoll-Paque gradient centrifugation.
Wash the cells two times with HBSS and pool the cells.
Centrifuge the cells at 400 x g for 10 minutes.

Thaw aliquots of Methylcellulose Stock Solution at room temperature.

Resuspend mononuclear cells in 10 mL of IMDM.

Perform a cell count.

Transfer the appropriate volume of cells plus a slight excess into a new 15 mL centrifuge tube.
Centrifuge at 300 x g for 10 minutes.

Remove the supernatant.
Resuspend the cells in IMDM to the desired stock cell number to generate a 10X stock concentration.

Combine the appropriate volume of 10X cell stock with the desired cell culture supplements/cytokines, and Methylcellulose Stock Solution. The final Methylcellulose concentration should be 1.27%.

Vortex the samples vigorously.
Wait approximately 20 minutes to allow air bubbles to escape.
Add 1.1 mL of the cell mixture to a 35 mm culture plate using a 3 mL syringe and a 16 gauge needle.
Spread the media evenly by gently rotating the plate.

Place two 35 mm plates into a 10 cm plate.
Add one uncovered 35 mm plate that contains 3-4 mL of sterile water.
Cover the 10 cm plate and place it in a 37 °C and 5% CO2 incubator.
Incubate the cells for 14-16 days.

Use an inverted microscope and a scoring grid to identify and count individual colonies.

Procedure for the Mouse Colony Forming Cell Assay
Pass a suspension of mouse bone marrow cells through a 70 μm nylon strainer to remove clumps and debris.
Remove red blood cells if necessary.
Wash the cells with IMDM/2% FBS by centrifugation at 300 x g for 8 minutes and pool the cells.

Remove the supernatant.
Resuspend the cells in 10 mL of IMDM/2% FBS.

Thaw aliquots of Methylcellulose Stock Solution at room temperature for approximately 30 minutes.

Perform a cell count.

Transfer the appropriate volume of cells plus a slight excess into a new 15 mL centrifuge tube.
Centrifuge at 300 x g for 10 minutes.

Remove the supernatant.
Resuspend the cells in IMDM to the desired stock cell number to generate a 10X stock concentration.

Combine the appropriate volume of 10X cell stock with the desired cell culture supplements/cytokines, and Methylcellulose Stock Solution. The final Methylcellulose concentration should be 1.27%.

Vortex the samples vigorously.
Wait approximately 20 minutes to allow air bubbles to escape.
Add 1.1 mL of the cell mixture to a 35 mm culture plate using a 3 mL syringe and a 16 gauge needle.
Spread the media evenly by gently rotating the plate.

Place two 35 mm plates into a 10 cm plate.
Add one uncovered 35 mm plate that contains 3-4 mL of sterile water.
Cover the 10 cm plate and place it in a 37 °C and 5% CO2 incubator.
Incubate the cells for 8-12 days.

Use an inverted microscope and a scoring grid to identify and count individual colonies.

Citations for Methylcellulose Stock Solution
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
23
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Pancreatic cancer cells upregulate LPAR4 in response to isolation stress to promote an ECM-enriched niche and support tumour initiation
Authors: C Wu, T Rakhshande, HI Wettersten, A Campos, T von Schals, S Jain, Z Yu, J Tan, E Mose, BG Childers, AM Lowy, SM Weis, DA Cheresh
Nature Cell Biology, 2023-01-16;0(0):. 2023-01-16
-
Metabolomic and Mitochondrial Fingerprinting of the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in Non-Tumorigenic and Tumorigenic Human Breast Cells
Authors: E Cuyàs, S Fernández-, S Verdura, R Lupu, J Joven, JA Menendez
Cancers, 2022-12-16;14(24):. 2022-12-16
-
Targeting PEA3 transcription factors to mitigate small cell lung cancer progression
Authors: DW Shia, W Choi, P Vijayaraj, V Vuong, JM Sandlin, MM Lu, A Aziz, C Marin, CJ Aros, C Sen, A Durra, AJ Lund, A Purkayasth, TM Rickabaugh, TG Graeber, BN Gomperts
Oncogene, 2022-12-13;0(0):. 2022-12-13
-
Extracellular fluid viscosity enhances cell migration and cancer dissemination
Authors: K Bera, A Kiepas, I Godet, Y Li, P Mehta, B Ifemembi, CD Paul, A Sen, SA Serra, K Stoletov, J Tao, G Shatkin, SJ Lee, Y Zhang, A Boen, P Mistriotis, DM Gilkes, JD Lewis, CM Fan, AP Feinberg, MA Valverde, SX Sun, K Konstantop
Nature, 2022-11-02;611(7935):365-373. 2022-11-02
-
Small molecule allosteric inhibitors of RORgammat block Th17-dependent inflammation and associated gene expression in vivo
Authors: SA Saenz, A Local, T Carr, A Shakya, S Koul, H Hu, L Chourb, J Stedman, J Malley, LA D'Agostino, V Shanmugasu, J Malona, CE Schwartz, L Beebe, M Clements, G Rajaraman, J Cho, L Jiang, A Dubrovskiy, M Kreilein, R Shimanovic, LG Hamann, L Escoubet, JM Ellis
PLoS ONE, 2021-11-09;16(11):e0248034. 2021-11-09
-
Theoretical and Experimental Investigation of Alginate Microtube Extrusion for Cell Culture Applications
Authors: M Nusterer, J Rauch, H Viljoen
Biochemical engineering journal, 2021-10-14;177(0):. 2021-10-14
-
Growth and site-specific organization of micron-scale biomolecular devices on living mammalian cells
Authors: S Jia, SC Phua, Y Nihongaki, Y Li, M Pacella, Y Li, AM Mohammed, S Sun, T Inoue, R Schulman
Nature Communications, 2021-09-30;12(1):5729. 2021-09-30
-
CD109-GP130 interaction drives glioblastoma stem cell plasticity and chemoresistance through STAT3 activity
Authors: P Filppu, JT Ramanathan, KJ Granberg, E Gucciardo, H Haapasalo, K Lehti, M Nykter, V Le Joncour, P Laakkonen
JCI Insight, 2021-05-10;6(9):. 2021-05-10
-
The Expression Levels and Cellular Localization of Pigment Epithelium Derived Factor (PEDF) in Mouse Testis: Its Possible Involvement in the Differentiation of Spermatogonial Cells
Authors: N Bagdadi, A Sawaied, A AbuMadighe, E Lunenfeld, M Huleihel
International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021-01-24;22(3):. 2021-01-24
-
Greater epithelial ridge cells are the principal organoid-forming progenitors of the mouse cochlea
Authors: M Kubota, M Scheibinge, TA Jan, S Heller
Cell Reports, 2021-01-19;34(3):108646. 2021-01-19
-
RAD52 aptamer regulates DNA damage repair and STAT3 in BRCA1/BRCA2?deficient human acute myeloid leukemia
Authors: Y Xu, Y Lin, Y Luo, Y Yang, B Long, Z Fang, L Liu, J Zhang, X Zhang
Oncology reports, 2020-08-10;44(4):1455-1466. 2020-08-10
-
Vulnerability of invasive glioblastoma cells to lysosomal membrane destabilization
Authors: V Le Joncour, P Filppu, M Hyvönen, M Holopainen, SP Turunen, H Sihto, I Burghardt, H Joensuu, O Tynninen, J Jääskeläin, M Weller, K Lehti, R Käkelä, P Laakkonen
EMBO Mol Med, 2019-06-01;0(0):. 2019-06-01
-
Transcriptional repressor GATA binding 1-mediated repression of SRY-box 2 expression suppresses cancer stem cell functions and tumor initiation
Authors: X Gong, W Liu, L Wu, Z Ma, Y Wang, S Yu, J Zhang, H Xie, G Wei, F Ma, L Lu, L Chen
J. Biol. Chem., 2018-10-12;0(0):. 2018-10-12
-
Dysregulation of Iron Metabolism in Cholangiocarcinoma Stem-like Cells
Authors: C Raggi, E Gammella, M Correnti, P Buratti, E Forti, JB Andersen, G Alpini, S Glaser, D Alvaro, P Invernizzi, G Cairo, S Recalcati
Sci Rep, 2017-12-15;7(1):17667. 2017-12-15
-
Prokineticin 1 is up-regulated by insulin in decidualizing human endometrial stromal cells
Authors: D Ujvari, I Jakson, C Oldmark, S Attarha, T Alkasalias, D Salamon, S Gidlöf, AL Hirschberg
J. Cell. Mol. Med., 2017-08-07;0(0):. 2017-08-07
-
Hhex Regulates Hematopoietic Stem Cell Self-Renewal and Stress Hematopoiesis via Repression of Cdkn2a
Authors: JT Jackson, BJ Shields, W Shi, L Di Rago, D Metcalf, NA Nicola, MP McCormack
Stem Cells, 2017-06-19;0(0):. 2017-06-19
-
Metalloprotease-disintegrin ADAM12 actively promotes the stem cell-like phenotype in claudin-low breast cancer
Authors: S Duhachek-M, Y Qi, R Wise, L Alyahya, H Li, J Hodge, A Zolkiewska
Mol. Cancer, 2017-02-01;16(1):32. 2017-02-01
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibition in leukemia induces an altered metabolic state sensitive to mitochondrial perturbations.
Authors: Alvarez-Calderon F, Gregory M, Pham-Danis C, Deryckere D, Stevens B, Zaberezhnyy V, Hill A, Gemta L, Kumar A, Kumar V, Wempe M, Pollyea D, Jordan C, Serkova N, Graham D, DeGregori J
Clin Cancer Res, 2014-12-29;21(6):1360-72. 2014-12-29
-
CoCl2, a mimic of hypoxia, induces formation of polyploid giant cells with stem characteristics in colon cancer.
Authors: Lopez-Sanchez L, Jimenez C, Valverde A, Hernandez V, Penarando J, Martinez A, Lopez-Pedrera C, Munoz-Castaneda J, De la Haba-Rodriguez J, Aranda E, Rodriguez-Ariza A
PLoS ONE, 2014-06-16;9(6):e99143. 2014-06-16
-
THY-1 receptor expression differentiates cardiosphere-derived cells with divergent cardiogenic differentiation potential.
Authors: Gago-Lopez N, Awaji O, Zhang Y, Ko C, Nsair A, Liem D, Stempien-Otero A, MacLellan W
Stem Cell Reports, 2014-04-18;2(5):576-91. 2014-04-18
-
miR-9 is a tumor suppressor in pediatric AML with t(8;21).
Authors: Emmrich, S, Katsman-Kuipers, J E, Henke, K, Khatib, M E, Jammal, R, Engeland, F, Dasci, F, Zwaan, C M, den Boer, M L, Verboon, L, Stary, J, Baruchel, A, de Haas, V, Danen-van Oorschot, A A, Fornerod, M, Pieters, R, Reinhardt, D, Klusmann, J H, van den Heuvel-Eibrink, M M
Leukemia, 2013-11-25;28(5):1022-32. 2013-11-25
-
Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibition is a novel therapeutic strategy targeting tumor in the bone marrow microenvironment in multiple myeloma.
Authors: Tai Y, Chang B, Kong S, Fulciniti M, Yang G, Calle Y, Hu Y, Lin J, Zhao J, Cagnetta A, Cea M, Sellitto M, Zhong M, Wang Q, Acharya C, Carrasco D, Buggy J, Elias L, Treon S, Matsui W, Richardson P, Munshi N, Anderson K
Blood, 2012-06-11;120(9):1877-87. 2012-06-11
-
Sox2 expression in breast tumours and activation in breast cancer stem cells.
Authors: Leis O, Eguiara A, Lopez-Arribillaga E, Alberdi MJ, Hernandez-Garcia S, Elorriaga K, Pandiella A, Rezola R, Martin AG
Oncogene, 2011-08-08;31(11):1354-65. 2011-08-08
FAQs
-
What is the difference between Methylcellulose Stock (Catalog # HSC001) and Base Media (Catalog # HSC002)?
- The Methylcellulose Stock (Catalog # HSC001) contains methylcellulose in Iscove's Modified Dulbecco's Medium. The Base Media (Catalog # HSC002) contains methylcellulose in Iscove's Modified Dulbecco's Medium along with serum, albumin, L-glutamine, and 2-mercaptoethanol. The additional components of HSC002 are needed to sustain the viability and growth of HSCs. The advantage to using HSC002 is that R&D Systems has already evaluated the serum, albumin, L-glutamine, and 2-mercaptoethanol in-house to ensure lot-to-lot consistency, eliminating the need for the researcher to evaluate these components individually.
-
Can the CFU assay using Methycellulose based media be performed using frozen PBMCs instead of fresh PBMCs?
Yes, the CFU assay can be performed using frozen PBMCs. The PBMCs can be frozen in DMEM containing 10% FBS and 10% DMSO.
-
Is lot-specific information on viscosity available for Methyl Cellulose Stock Solution (Catalog # HSC001)?
Methyl cellulose Stock Solution is prepared using Methyl cellulose with an estimated viscosity of 1500 CPS. Because of our stringent quality control assays, we don’t expect large variations in viscosity from lot to lot.
-
Why is there color difference observed sometimes between two bottles of Methylcellulose Stock Solution (Catalog # HSC001)?
The difference in color can be because of dry ice added to the shipment. Dry ice can cause minor pH changes and slight changes in color, but this will not affect performance.
-
What is the molecular weight of Methylcellulose used in Catalog # HSC001?
The Methylcellulose in Catalog # HSC001 has a molecular weight range of 208272 - 219639 g/mol.
-
Why does the Human, Mouse and Rat colony forming assay protocol (CFC assay protocol) recommed use of non-tissue culture treated petri dishes?
The CFC assay promotes the growth of cells as colonies suspended in methylcellulose. However, if you use tissue culture treated dishes, the cells will also adhere and grow out on the bottom of the plate. Sometimes this appears as a round colony that is sticking and growing out on the edges (like an egg) and sometimes you can see patches of a monolayer. This makes it difficult to see the suspended colonies.
-
Burst Forming Unit-Erythroid (BFU-E ) colonies representing erythorid progenitors appear to be low in frequency. Is there a strategy to count these colonies and visualize them?
It is true that BFU-E colonies are low in frequency. To count and see good BFU-E colonies, the CFC assay is set up at two cell densities. For counting BFU-E colonies, a 10X cell concentration of 1.5-3x105 cells/mL is used. For properly visualizing the BFU-E colonies, an assay at half that cell density is used.
-
How many freeze-thaws cycles can Methylcellulose stock solution, Catalog # HSC001, undergo?
We recommend keeping freeze-thaw cycles to a minimum. In our experience, two freeze-thaw cycles of the material received is acceptable, but after that, the viscosity of the product may be affected.
Reviews for Methylcellulose Stock Solution
Average Rating: 4.3 (Based on 3 Reviews)
Have you used Methylcellulose Stock Solution?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:
We use to make stem cell spheres using methylcellulose.



