Recombinant Cynomolgus/Rhesus EMMPRIN/CD147 Fc Protein, CF
Recombinant Cynomolgus/Rhesus EMMPRIN/CD147 Fc Protein, CF Summary
Product Specifications
| Cynomolgus/Rhesus EMMPRIN/CD147 (Glu138-Ala327) Accession # XP_005587353.1 | IEGRMD | Human IgG1 (Pro100-Lys330) |
| N-terminus | C-terminus | |
Analysis
Product Datasheets
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
10797-EM
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with dry ice or equivalent. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Scientific Data
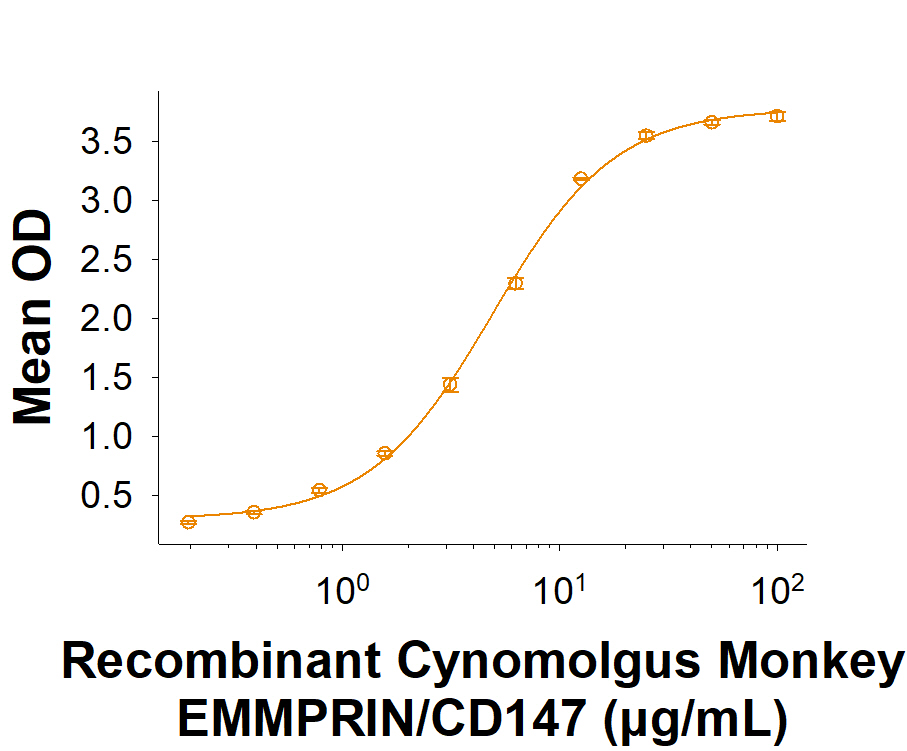 View Larger
View Larger
When Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD Fc Chimera (10499-CV) is immobilized at 1 µg/mL (100 µL/well), Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey EMMPRIN/CD147 Fc Chimera (Catalog # 10797-EM) binds with an ED50 of 1.50-12.0 µg/mL.
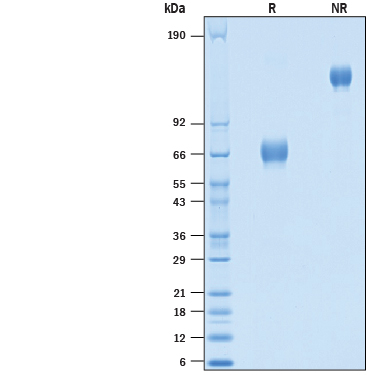 View Larger
View Larger
2 μg/lane of Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey EMMPRIN/CD147 Fc Chimera Protein (Catalog # 10797-EM) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at 63-72 kDa and 120-140 kDa, respectively.
Reconstitution Calculator
Background: EMMPRIN/CD147
Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) inducer (EMMPRIN), also known as basigin and CD147, is a 44‑66 kDa, variably N‑ and O‑glycosylated, type I transmembrane protein that belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily (1‑4). Based on its high homology with human EMMPRIN, cynomolgus EMMPRIN is predicted to contain a 24 aa signal sequence, a 190 aa extracellular domain (ECD), a 21 aa transmembrane (TM) segment and a 41 aa cytoplasmic tail. The ECD contains one C2‑type and one V‑type Ig‑like domain. There is one 385 aa human splice variant that contains an extra N‑terminal IgCAM domain and is found only in the retina (5). There are additional multiple potential isoform variants for EMMMPRIN. Two that have been characterized are 205 and 176 aa in length. The 176 aa isoform utilizes an alternative start site at Met94, while the 205 aa isoform contains an 11 aa substitution for aa 1‑75. Notably, the 176 aa isoform heterodimerizes with the standard EMMPRIN isoform and down‑modulates its activity. This is in contrast to EMMPRIN homodimers that show full biological activity (6). EMMPRIN is expressed in areas of tissue remodeling, including endometrium, placenta, skin, and regions undergoing angiogenesis (1, 2, 7‑10). It is also expressed on cells with high metabolic activity, such as lymphoblasts, macrophages and particularly tumor cells (2, 11). On such cells, EMMPRIN is often co‑expressed with the amino acid transporter CD98h (12). EMMPRIN also interacts with caveolin-1 (via its C2‑like domain), and this reduces the level of EMMPRIN glycosylation and subsequent EMMPRIN multimerization and activity (13). In addition, EMMMPRIN is reported to complex with both annexin II and beta 1 integrins alpha 3 and alpha 6, an interaction that contributes to tumor growth and metastasis (14‑16). Finally, the soluble calcium‑binding protein S100A9 has now been identified as a ligand for EMMPRIN, and may mediate many of the tumorigenic activities attributed to EMMPRIN (17). EMMPRIN’s TM sequence contains a charged aa (Glu), and a Pro important for intracellular interactions with cyclophilins (CyP) (3, 18, 19). CyPA (cyclosporin A receptor) and CyP60 interactions with the TM segment promote leukocyte inflammatory chemotaxis and surface expression of EMMPRIN, respectively (18, 19). An active 22 kDa fragment can be shed from tumor cells by MT1‑MMP (1). Tumor cells can also release active, full‑length EMMPRIN in microvesicles (20, 21). Functionally, EMMPRIN is known to induce urokinase‑type plasminogen activator (uPA), VEGF, hyaluronan and multiple MMPs (1, 2, 8‑10). Cynomolgus EMMPRIN (269 aa) shows 78% aa identity with human EMMPRIN.
- Gabison, E. E. et al. (2005) Biochimie 87:361.
- Yurchenko, V. et al. (2006) Immunology 117:301.
- Kasinrerk, W. et al. (1992) J. Immunol. 149:847.
- Iacono, K.T. et al. (2007) Exp. Mol. Pathol. 83:283.
- Hanna, S. M. et al. (2003) BMC Biochem. 4:17.
- Liao, C-G. et al. (2011) Mol. Cell. Biol. 31:2591.
- Riethdorf, S. et al. (2006) Int. J. Cancer 119:1800.
- Braundmeier, A. G. et al. (2006) J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 91:2358.
- Tang, Y. et al. (2006) Mol. Cancer Res. 4:371.
- Quemener, C. et al. (2007) Cancer Res. 67:9.
- Wilson, M. C. et al. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280:27213.
- Xu, D. and M. E. Hemler, (2005) Mol. Cell. Proteomics 4:1061.
- Tang, W. et al. (2004) Mol. Biol. Cell 15:4043.
- Zhao, P. et al. (2010) Cancer Sci. 101:387.
- Dai, J. et al. (2009) BMC Cancer 9:337.
- Li, Y. et al. (2012) J. Biol. Chem. 287:4759.
- Hibino, T. et al. (2013) Cancer Res. 73:172.
- Arora, K. et al. (2005) J. Immunol. 175:517.
- Pushkarsky, T. et al. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280:27866.
- Egawa, N. et al. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281:37576.
- Sidhu, S. S. et al. (2004) Oncogene 23:956.
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsReviews for Recombinant Cynomolgus/Rhesus EMMPRIN/CD147 Fc Protein, CF
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Recombinant Cynomolgus/Rhesus EMMPRIN/CD147 Fc Protein, CF and earn rewards!
Have you used Recombinant Cynomolgus/Rhesus EMMPRIN/CD147 Fc Protein, CF?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥1250 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
