Recombinant F. heparinum Heparinase I Protein, CF
View Terms and Conditions
Recombinant F. heparinum Heparinase I Protein, CF Summary
Learn more about Fluorescent Glycan Labeling and DetectionProduct Specifications
Gln22-Arg384, with an N-terminal Met and 6-His tag
Analysis
Product Datasheets
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
7897-GH
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution in Tris, NaCl and DTT. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with dry ice or equivalent. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Assay Procedure
- Assay Buffer: 50 mM Tris, 100 mM NaCl, 2 mM CaCl2, pH 7.5
- Recombinant F. heparinum Heparinase I (rFhHeparinase I) (Catalog # 7897-GH)
- Substrate: Heparin (Tocris, Catalog # 2812), 20 mg/mL stock in deionized water
- 96-well Clear UV Plate (Costar, Catalog # 3635)
- Plate Reader (Model: SpectraMax Plus by Molecular Devices) or equivalent
- Dilute rFhHeparinase I to 0.5 µg/mL in Assay Buffer.
- Dilute Substrate to 0.75 mg/mL in Assay Buffer.
- Load 100 µL of diluted rFhHeparinase I into a UV plate, and start the reaction by adding 200 µL of 0.75 mg/mL Substrate. Include a Substrate Blank containing 100 µL of Assay Buffer and 200 µL of 0.75 mg/mL Substrate.
- Read plate in kinetic mode for 5 minutes at an absorbance of 232 nm.
- Calculate specific activity:
|
Specific Activity (pmol/min/µg) = |
Adjusted Vmax* (OD/min) x well volume (L) x 1012 pmol/mol |
| ext. coeff** (M-1cm-1) x path corr.*** (cm) x amount of enzyme (µg) |
*Adjusted for Substrate Blank
**Using the extinction coefficient 3800 M-1cm-1
***Using the path correction 0.92 cm
Note: the output of many spectrophotometers is in mOD Per Reaction:
- rFhHeparinase I: 0.05 µg
- Substrate: 0.5 mg/mL
Scientific Data
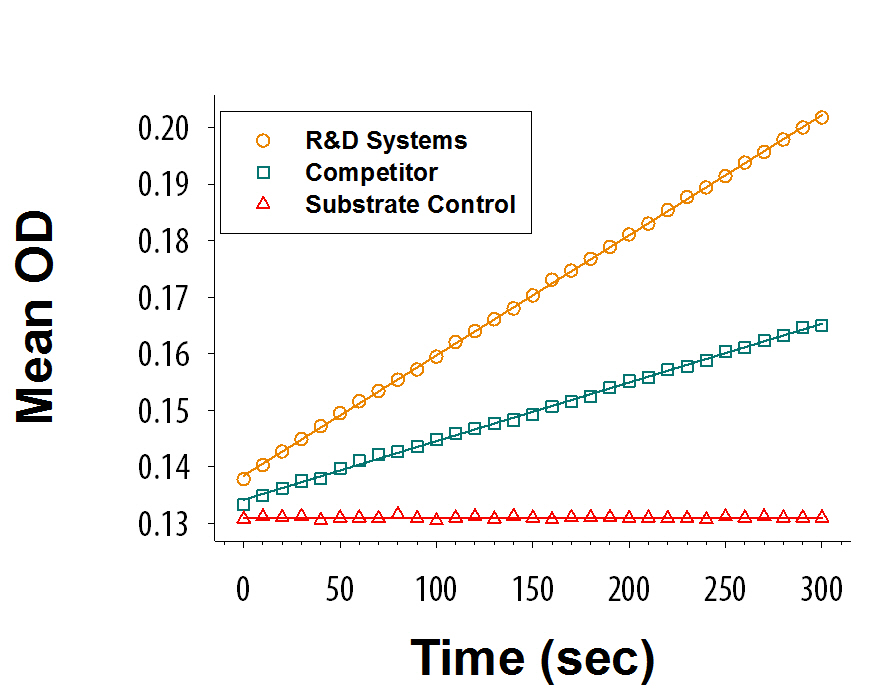 View Larger
View Larger
Heparinase I digestion of Heparin Sulfate (200 μg) is assessed in a 5-minute kinetic assay at room temperature by monitoring absorbance at 232 nm. R&D Systems RecombinantF. heparinumHeparinase I (Catalog # 6145-GH) (orange) exhibits greater activity than theBacteroidesHeparinase I from the competition (green).
Reconstitution Calculator
Background: Heparinase I
Heparin and heparan sulfate are sulfated glycosaminoglycans that share basic carbohydrate backbone structure with alternating uronic acid and N-acetylglucosamine residues (1, 2). Heparin is found in mast cells and has strong anticoagulation properties. Heparan sulfate is found on cell membrane and extracellular matrix and is involved in various biological events from cell growth, adhesion and migration to lipid metabolism. Heparin has a much higher degree of sulfation than heparan sulfate, which can be considered as a polysaccharide with regions similar to heparin interspaced with much less sulfated regions. Both heparin and heparan sulfate can be digested by heparinases, a group of bacterial lyases that are widely used as tools for processing and analyze these polysaccharides. Heparinases degrade heparin and heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycans through an eliminative mechanism (3). Heparinase I from Flavobacterium heparinum is highly active on heparin and has no activity against chondroitin sulfate and keratan sulfate (4). The enzyme readily releases highly sulfated oligosaccharides from heparin (5).
- MacArthur, J. M. et al. (2007) J. Clin. Invest. 117:153.
- Esko, J. D. and Selleck, S. B. (2002) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 71:435.
- Linhardt, R. J. et al. (1986) Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 12:135.
- Wu, Z.L. et al. (2011) Glycobiology 21:625.
- Ernst, S. et al. (1996) Biochem. J. 315:589.
Citations for Recombinant F. heparinum Heparinase I Protein, CF
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
2
Citations: Showing 1 - 2
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Enzymatic synthesis of low molecular weight heparins from N-sulfo heparosan depolymerized by heparanase or heparin lyase
Authors: Y Yu, L Fu, P He, K Xia, S Varghese, J Dordick, H Wang, F Zhang, RJ Linhardt
Carbohydrate polymers, 2022-07-05;295(0):119825.
Species: N/A
Sample Types: N/A
Applications: Enzyme Activity -
Systematic analysis of SARS-CoV-2 infection of an ACE2-negative human airway cell
Authors: M Puray-Chav, KM LaPak, TP Schrank, JL Elliott, DP Bhatt, MJ Agajanian, R Jasuja, DQ Lawson, K Davis, PW Rothlauf, Z Liu, H Jo, N Lee, K Tenneti, JE Eschbach, C Shema Mugi, EM Cousins, EW Cloer, HR Vuong, LA VanBlargan, AL Bailey, P Gilchuk, JE Crowe, MS Diamond, DN Hayes, SPJ Whelan, A Horani, SL Brody, D Goldfarb, MB Major, SB Kutluay
Cell Reports, 2021-06-23;0(0):109364.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsReviews for Recombinant F. heparinum Heparinase I Protein, CF
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Recombinant F. heparinum Heparinase I Protein, CF and earn rewards!
Have you used Recombinant F. heparinum Heparinase I Protein, CF?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
