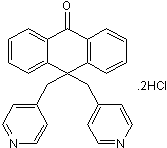
XE 991 dihydrochloride
Chemical Name: 10,10-bis(4-Pyridinylmethyl)-9(10H)-anthracenone dihydrochloride
Purity: ≥99%
Biological Activity
XE 991 dihydrochloride is a potent and selective blocker of KV7 (KCNQ) voltage-gated potassium channels. Blocks KV7.2+7.3 (KCNQ2+3) / M-currents (IC50 = 0.6 - 0.98 μM) and KV7.1 (KCNQ1) homomeric channels (IC50 = 0.75 μM) but is less potent against KV7.1/minK channels (IC50 = 11.1 μM). Augments hippocampal ACh release and is a cognitive enhancer following oral administration in vivo.Technical Data
The technical data provided above is for guidance only.
For batch specific data refer to the Certificate of Analysis.
Tocris products are intended for laboratory research use only, unless stated otherwise.
Background References
-
KCNQ2 and KCNQ3 potassium channel subunits: molecular correlates of the M-channel.
Wang et al.
Science, 1998;282:1890 -
Two new potent neurotransmitter release enhancers, 10,10-bis(4-pyridinylmethyl)-9(10H)-anthracenone and 10,10-bis(2-fluoro-4-pyridinylmethyl)-9(10H)-anthracenone: comparison to linopirdine.
Zaczek et al.
J.Pharmacol.Exp.Ther., 1998;285:724 -
Molecular basis for differential sensitivity of KCNQ and IKs channels to the cognitive enhancer XE991.
Wang et al.
Mol.Pharmacol., 2000;57:1218 -
KCNQ/M currents in sensory neurons: significance for pain therapy.
Passmore et al.
J.Neurosci., 2003;23:7227
Product Datasheets
Reconstitution Calculator
Molarity Calculator
Citations for XE 991 dihydrochloride
The citations listed below are publications that use Tocris products. Selected citations for XE 991 dihydrochloride include:
34 Citations: Showing 1 - 10
-
How Gastrin-Releasing Peptide Opens the Spinal Gate for Itch.
Authors: Pagani Et al.
Neuron 2019;
-
PTBP1-Mediated Alternative Splicing Regulates the Inflammatory Secretome and the Pro-tumorigenic Effects of Senescent Cells.
Authors: Georgilis Et al.
Cancer Cell 2018;34:85
-
XE991 and Linopirdine are state-dependent inhibitors for Kv7/KCNQ channels that favor activated single subunits.
Authors: Greene Et al.
J.Pharmacol.Exp.Ther. 2017;362:177
-
M-current inhibition rapidly induces a unique CK2-dependent plasticity of the axon initial segment.
Authors: Lezmy
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2017;114(47):E10234
-
Control of sensory neuron excitability by serotonin involves 5HT2C receptors and Ca2+-activated chloride channels.
Authors: Salzer Et al.
Neuropharmacology 2016;110 (A):277
-
Kv1 channels and neural processing in vestibular calyx afferents.
Authors: Meredith Et al.
Mol Pharmacol 2015;9:85
-
Cholinergic and ghrelinergic receptors and KCNQ channels in the medial PFC regulate the expression of palatability.
Authors: Parent Et al.
Front Syst Neurosci 2015;9:284
-
The M-current contributes to high threshold membrane potential oscillations in a cell type-specific way in the pedunculopontine nucleus of mice.
Authors: Bordas Et al.
Mol Brain 2015;9:121
-
N-MthD.-aspartate receptors mediate activity-dependent down-regulation of potassium channel genes during the expression of homeostatic intrinsic plasticity.
Authors: Lee Et al.
J Neurosci 2015;8:4
-
Loss of Local Astrocyte Support Disrupts Action Potential Propagation and Glutamate Release Synchrony from Unmyelinated Hippocampal Axon Terminals In Vitro.
Authors: Sobieski Et al.
Front Behav Neurosci 2015;35:11105
-
KV7 Channels Regulate Firing during Synaptic Integration in GABAergic Striatal Neurons.
Authors: Pérez-Ramírez Et al.
PLoS One 2015;2015:472676
-
Effects of KCNQ2 gene truncation on M-type Kv7 potassium currents.
Authors: Robbins Et al.
PLoS One 2013;8:e71809
-
Triple cysteine module within M-type K+ channels mediates reciprocal channel modulation by nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species.
Authors: Ooi Et al.
Neural Plast 2013;33:6041
-
Raised activity of L-type calcium channels renders neurons prone to form paroxysmal depolarization shifts.
Authors: Rubi Et al.
Neuromolecular Med 2013;15:476
-
Contribution of near-threshold currents to intrinsic oscillatory activity in rat medial entorhinal cortex layer II stellate cells.
Authors: Boehlen Et al.
J Neurophysiol 2013;109:445
-
Differential effects of cystathionine-γ-lyase-dependent vasodilatory H2S in periadventitial vasoregulation of rat and mouse aortas.
Authors: Köhn Et al.
J Physiol 2012;7:e41951
-
Functional significance of M-type potassium channels in nociceptive cutaneous sensory endings.
Authors: Passmore Et al.
Front Mol Neurosci 2012;5:63
-
Increased Kv1 channel expression may contribute to decreased sIPSC frequency following chronic inhibition of NR2B-containing NMDAR.
Authors: He Et al.
Neuropsychopharmacology 2012;37:1338
-
Restoration of ion channel function in deafness-causing KCNQ4 mutants by synthetic channel openers.
Authors: Leitner Et al.
Br J Pharmacol 2012;165:2244
-
Visceral hyperalgesia induced by forebrain-specific suppression of native Kv7/KCNQ/M-current in mice.
Authors: Bi Et al.
Mol Pain 2011;7:84
-
KV7 channels regulate muscle tone and nonadrenergic noncholinergic relaxation of the rat gastric fundus.
Authors: Ipavec Et al.
Pharmacol Res 2011;64:397
-
AKAP79/150 signal complexes in G-protein modulation of neuronal ion channels.
Authors: Zhang Et al.
J Neurosci 2011;31:7199
-
Dynamic interplay of excitatory and inhibitory coupling modes of neuronal L-type calcium channels.
Authors: Geier Et al.
Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2011;300:C937
-
The contribution of Kv7 channels to pregnant mouse and human myometrial contractility.
Authors: McCallum Et al.
J Neurosci 2011;15:577
-
NE causes a biphasic change in mammalian pinealocye membrane potential: role of alpha1B-adrenoreceptors, phospholipase C, and Ca2+.
Authors: Zemkova Et al.
Endocrinology 2011;152:3842
-
MinK-dependent internalization of the IKs potassium channel.
Authors: Xu Et al.
Cardiovasc Res 2009;82:430
-
KCNQ modulators reveal a key role for KCNQ potassium channels in regulating the tone of rat pulmonary artery smooth muscle.
Authors: Joshi Et al.
J Neurosci 2009;329:368
-
Endolymphatic sodium homeostasis by extramacular epithelium of the saccule.
Authors: Kim and Marcus
J Neurosci 2009;29:15851
-
Regulation of ENaC-mediated sodium transport by glucocorticoids in Reissner's membrane epithelium.
Authors: Kim Et al.
Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2009;296:C544
-
KCNQ currents and their contribution to resting membrane potential and the excitability of interstitial cells of Cajal from the guinea pig bladder.
Authors: Anderson Et al.
J.Urol. 2009;182:330
-
The KCNQ/M-current modulates arterial baroreceptor function at the sensory terminal in rats.
Authors: Wladyka Et al.
J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2008;586:795
-
Inhibition of M current in sensory neurons by exogenous proteases: a signaling pathway mediating inflammatory nociception.
Authors: Linley Et al.
Br J Pharmacol 2008;28:11240
-
Inhibitory gating modulation of small conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels by the synthetic compound (R)-N-(benzimidazol-2-yl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1-naphtylamine (NS8593) reduces afterhyperpolarizing current in hippocampal CA1 neurons.
Authors: Strøbaek Et al.
J Cell Mol Med 2006;70:1771
-
Electrophysiological and functional effects of the KCNQ channel blocker XE991 on murine portal vein smooth muscle cells.
Authors: Yeung and Greenwood
J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2005;146:585
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Small Molecule FAQsReviews for XE 991 dihydrochloride
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review XE 991 dihydrochloride and earn rewards!
Have you used XE 991 dihydrochloride?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image