Human CD44v6 Antibody Summary
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
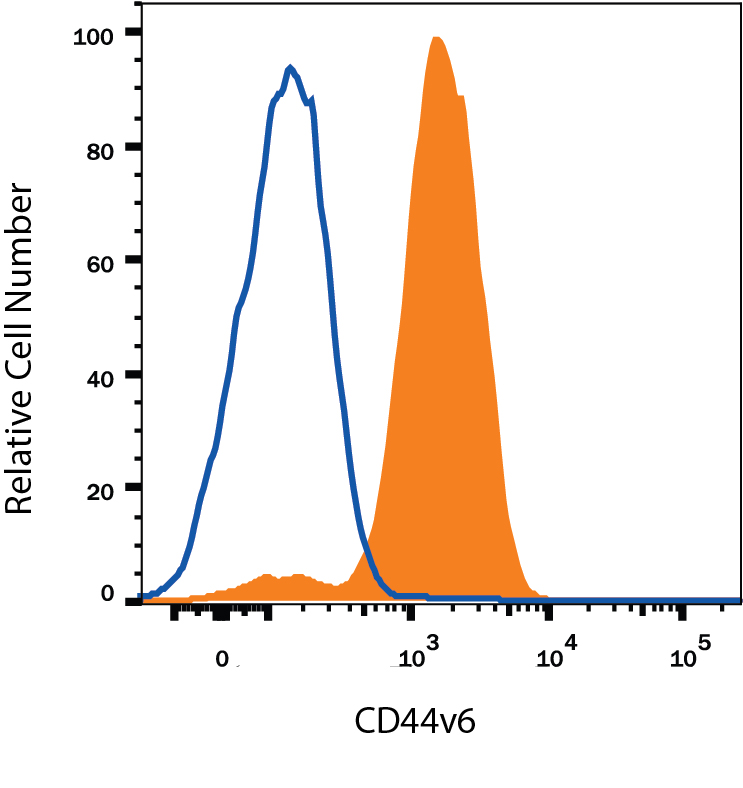
Detection of CD44 in Human Blood Monocytes by Flow Cytometry. Human peripheral blood monocytes were stained with Mouse Anti-Human CD44 v6 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # BBA13, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (MAB002, open histogram), followed by Allophycocyanin-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (F0101B).
 View Larger
View Larger
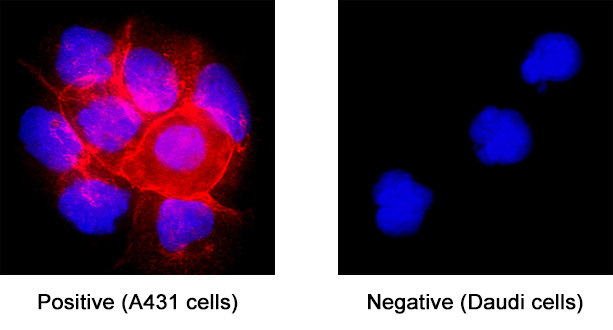
CD44 in A431 Human Cell Line. CD44 was detected in immersion fixed A431 human epithelial carcinoma cell line (positive staining) and Daudi human Burkitt's lymphoma cell line (negative staining) using Mouse Anti-Human CD44 v6 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # BBA13) at 25 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (red; NL007) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cell surface. Staining was performed using our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Non-adherent Cells.
 View Larger
View Larger
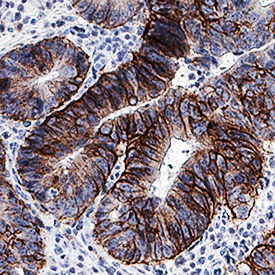
CD44 in Human Colon Adenocarcinoma Tissue. CD44 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human colon adenocarcinoma tissue using Mouse Anti-Human CD44 v6 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # BBA13) at 1.7 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Mouse IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (VC001). Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (CTS013). Tissue was stained using DAB (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to plasma membrane. View our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: CD44
CD44 is a ubiquitously expressed protein that is the major receptor for hyaluronan and exerts control over cell growth and migration (1‑3). Human CD44 has a 20 amino acid (aa) signal sequence, an extracellular domain (ECD) with a 100 aa hyaluronan‑binding disulfide‑stabilized link region and a 325‑530 aa stem region, a 21 aa transmembrane domain, and a 72 aa cytoplasmic domain. Within the stem, ten variably spliced exons (v1‑10, exons 6‑15) produce multiple protein isoforms (1‑3). The standard or hematopoietic form, CD44H, does not include the variable segments (1‑3). Cancer aggressiveness and T cell activation have been correlated with expression of specific isoforms (1, 3). CD44v6 contains exon 10 and is associated with tumor progression and metastasis in many types of cancer including breast, colon, lung, renal, skin, and ovarian tumors. With variable N‑ and O‑glycosylation and splicing within the stalk, CD44 can range from 80 to 200 kDa (1). Within the N‑terminal invariant portion of the ECD (aa 21‑220), human CD44 shares 76%, 76%, 86%, 83% and 79% identity with corresponding mouse, rat, equine, canine and bovine CD44, respectively. The many reported functions of CD44 fall within three categories (1). First, CD44 binds hyaluronan and other ligands within the extracellular matrix and can function as a “platform” for growth factors and metalloproteinases. Second, CD44 can function as a co‑receptor that modifies activity of receptors including MET and the ERBB family of tyrosine kinases. Third, the CD44 intracellular domain links the plasma membrane to the actin cytoskeleton via the ERM proteins, ezrin, radixin and moesin. CD44 can be synthesized in a soluble form (4) or may be cleaved at multiple sites by either membrane‑type matrix metalloproteinases, or ADAM proteases to produce soluble ectodomains (5, 6). The cellular portion may then undergo gamma secretase‑dependent intramembrane cleavage to form an A beta ‑like transmembrane portion and a cytoplasmic signaling portion that affects gene expression (7, 8). These cleavage events are thought to promote metastasis by enhancing tumor cell motility and growth (1, 5).
- Ponta, H. et al. (2003) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4:33.
- Screaton, G.R. et al. (1992) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:12160.
- Lynch, K.W. (2004) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4:931.
- Yu, Q. and B.P. Toole (1996) J. Biol. Chem. 271:20603.
- Nagano, O. and H. Saya (2004) Cancer Sci. 95:930.
- Nakamura, H. et al. (2004) Cancer Res. 64:876.
- Murakami, D. et al. (2003) Oncogene 22:1511.
- Lammich, S. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277:44754.
- Fox, S.B. et al. (1994) Cancer Res. 54:4539.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human CD44v6 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
25
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Negative regulation of CD44st by miR-138-5p affects the invasive ability of breast cancer cells and patient prognosis after breast cancer surgery
Authors: FX Jian, PX Bao, WF Li, YH Cui, HG Hong
BMC Cancer, 2023-03-24;23(1):269.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
EZH2/hSULF1 axis mediates receptor tyrosine kinase signaling to shape cartilage tumor progression
Authors: ZS Lin, CC Chung, YC Liu, CH Chang, HC Liu, YY Liang, TL Huang, TM Chen, CH Lee, CH Tang, MC Hung, YH Chen
Elife, 2023-01-09;12(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Immunoprecipitation, Western Blot -
Adipose stem cell niche reprograms the colorectal cancer stem cell metastatic machinery
Authors: S Di Franco, P Bianca, DS Sardina, A Turdo, M Gaggianesi, V Veschi, A Nicotra, LR Mangiapane, M Lo Iacono, I Pillitteri, S van Hooff, F Martorana, G Motta, E Gulotta, VL Lentini, E Martorana, ME Fiori, S Vieni, MR Bongiorno, G Giannone, D Giuffrida, L Memeo, L Colarossi, M Mare, P Vigneri, M Todaro, R De Maria, JP Medema, G Stassi
Nature Communications, 2021-08-18;12(1):5006.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells, Whole Tissue
Applications: Flow Cytometry, ICC, IHC -
Control of replication stress and mitosis in colorectal cancer stem cells through the interplay of PARP1, MRE11 and RAD51
Authors: G Manic, M Musella, F Corradi, A Sistigu, S Vitale, S Soliman Ab, L Mattiello, E Malacaria, C Galassi, M Signore, M Pallocca, S Scalera, F Goeman, F De Nicola, A Guarracino, R Pennisi, F Antonangel, F Sperati, M Baiocchi, M Biffoni, M Fanciulli, M Maugeri-Sa, A Franchitto, P Pichierri, R De Maria, I Vitale
Cell Death and Differentiation, 2021-02-02;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
CD44v6 Targeted by miR-193b-5p in the Coding Region Modulates the Migration and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cells
Authors: S Hu, M Cao, Y He, G Zhang, Y Liu, Y Du, C Yang, F Gao
J Cancer, 2020-01-01;11(1):260-271.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Targeting chemoresistant colorectal cancer via systemic administration of a BMP7 variant
Authors: V Veschi, LR Mangiapane, A Nicotra, S Di Franco, E Scavo, T Apuzzo, DS Sardina, M Fiori, A Benfante, ML Colorito, G Cocorullo, F Giuliante, C Cipolla, G Pistone, MR Bongiorno, A Rizzo, CM Tate, X Wu, S Rowlinson, LF Stancato, M Todaro, R De Maria, G Stassi
Oncogene, 2019-10-07;0(0):.
Species: Human, Xenograft
Sample Types: Whole Cells, Whole Tissue
Applications: ICC, IHC-P -
PPARdelta mediates the effect of dietary fat in promoting colorectal cancer metastasis
Authors: D Wang, L Fu, J Wei, Y Xiong, RN DuBois
Cancer Res., 2019-06-25;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Clinical impact of different exosomes' protein expression in pancreatic ductal carcinoma patients treated with standard first line palliative chemotherapy
Authors: R Giampieri, F Piva, G Occhipinti, A Bittoni, A Righetti, S Pagliarett, A Murrone, F Bianchi, C Amantini, M Giulietti, G Ricci, G Principato, G Santoni, R Berardi, S Cascinu
PLoS ONE, 2019-05-02;14(5):e0215990.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
Applications: ELISA Detection -
CD44 targeted delivery of siRNA by using HA-decorated nanotechnologies for KRAS silencing in cancer treatment
Authors: A Tirella, K Kloc-Munia, L Good, J Ridden, M Ashford, S Puri, N Tirelli
Int J Pharm, 2019-02-26;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: IHC -
Novel antibody reagents for characterization of drug- and tumor microenvironment-induced changes in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cells
Authors: T Navas, TD Pfister, S Colantonio, A Aziz, L Dieckman, RG Saul, J Kaczmarczy, S Borgel, SY Alcoser, MG Hollingshe, YH Lee, DP Bottaro, T Hiltke, G Whiteley, N Takebe, RJ Kinders, RE Parchment, JE Tomaszewsk, JH Doroshow
PLoS ONE, 2018-06-21;13(6):e0199361.
Species: Xenograft
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Musashi-1 promotes a cancer stem cell lineage and chemoresistance in colorectal cancer cells
Authors: GY Chiou, TW Yang, CC Huang, CY Tang, JY Yen, MC Tsai, HY Chen, N Fadhilah, CC Lin, YJ Jong
Sci Rep, 2017-05-19;7(1):2172.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Autophagy supports generation of cells with high CD44 expression via modulation of oxidative stress and Parkin-mediated mitochondrial clearance
Authors: KA Whelan, PM Chandramou, K Tanaka, M Natsuizaka, M Guha, S Srinivasan, DS Darling, Y Kita, S Natsugoe, JD Winkler, AJ Klein-Szan, RK Amaravadi, NG Avadhani, AK Rustgi, H Nakagawa
Oncogene, 2017-04-17;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC, Western Blot -
CD44 mediates the Catch-Bond Activated Rolling of HEPG2 Epithelial Cancer Cells on Hyaluronan
Authors: Axel Rosenhahn
Cell Adh Migr, 2017-02-01;0(0):0.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
MIF allele-dependent regulation of the MIF coreceptor CD44 and role in rheumatoid arthritis
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2016-11-21;113(49):E7917-E7926.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Isolation of All CD44 Transcripts in Human Epidermis and Regulation of Their Expression by Various Agents
PLoS ONE, 2016-08-09;11(8):e0160952.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Nomogram Incorporating CD44v6 and Clinicopathological Factors to Predict Lymph Node Metastasis for Early Gastric Cancer
PLoS ONE, 2016-08-02;11(8):e0159424.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Dynamic regulation of the cancer stem cell compartment by Cripto-1 in colorectal cancer.
Authors: Francescangeli F, Contavalli P, De Angelis M, Baiocchi M, Gambara G, Pagliuca A, Fiorenzano A, Prezioso C, Boe A, Todaro M, Stassi G, Castro N, Watanabe K, Salomon D, De Maria R, Minchiotti G, Zeuner A
Cell Death Differ, 2015-03-20;22(10):1700-13.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Overexpression of progelatinase B/proMMP-9 affects migration regulatory pathways and impairs chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell homing to bone marrow and spleen.
Authors: Bailon E, Ugarte-Berzal E, Amigo-Jimenez I, Van den Steen P, Opdenakker G, Garcia-Marco J, Garcia-Pardo A
J Leukoc Biol, 2014-08-01;96(2):185-99.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Establishment of highly tumorigenic human colorectal cancer cell line (CR4) with properties of putative cancer stem cells.
Authors: Rowehl, Rebecca, Burke, Stephani, Bialkowska, Agnieszk, Pettet, Donald W, Rowehl, Leahana, Li, Ellen, Antoniou, Eric, Zhang, Yuanhao, Bergamaschi, Roberto, Shroyer, Kenneth, Ojima, Iwao, Botchkina, Galina I
PLoS ONE, 2014-06-12;9(6):e99091.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Evaluation of protein biomarkers of prostate cancer aggressiveness.
Authors: Rizzardi A, Rosener N, Koopmeiners J, Isaksson Vogel R, Metzger G, Forster C, Marston L, Tiffany J, McCarthy J, Turley E, Warlick C, Henriksen J, Schmechel S
BMC Cancer, 2014-04-05;14(0):244.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
CD44v6 is a marker of constitutive and reprogrammed cancer stem cells driving colon cancer metastasis.
Authors: Todaro M, Gaggianesi M, Catalano V, Benfante A, Iovino F, Biffoni M, Apuzzo T, Sperduti I, Volpe S, Cocorullo G, Gulotta G, Dieli F, De Maria R, Stassi G
Cell Stem Cell, 2014-03-06;14(3):342-56.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells, Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC, Neutralization -
Identification of a population of blood circulating tumor cells from breast cancer patients that initiates metastasis in a xenograft assay.
Authors: Baccelli I, Schneeweiss A, Riethdorf S, Stenzinger A, Schillert A, Vogel V, Klein C, Saini M, Bauerle T, Wallwiener M, Holland-Letz T, Hofner T, Sprick M, Scharpff M, Marme F, Sinn H, Pantel K, Weichert W, Trumpp A
Nat Biotechnol, 2013-04-21;31(6):539-44.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Expression of the CD44v2-10 isoform confers a metastatic phenotype: importance of the heparan sulfate attachment site CD44v3.
Authors: Barbour AP, Reeder JA, Walsh MD, Fawcett J, Antalis TM, Gotley DC
Cancer Res., 2003-02-15;63(4):887-92.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Effect of hyaluronan on xenotransplanted breast cancer.
Authors: Herrera-Gayol A, Jothy S
Exp. Mol. Pathol., 2002-06-01;72(3):179-85.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
CD44 is exposed to the extracellular matrix at invasive sites in basal cell carcinomas.
Authors: Dingemans KP, Ramkema MD, Pals ST
Lab. Invest., 2002-03-01;82(3):313-22.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Electron Microscopy
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human CD44v6 Antibody
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 1 Review)
Have you used Human CD44v6 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:







