Human/Mouse Follistatin Antibody Summary
Gly30-Asp329
Accession # P19883
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
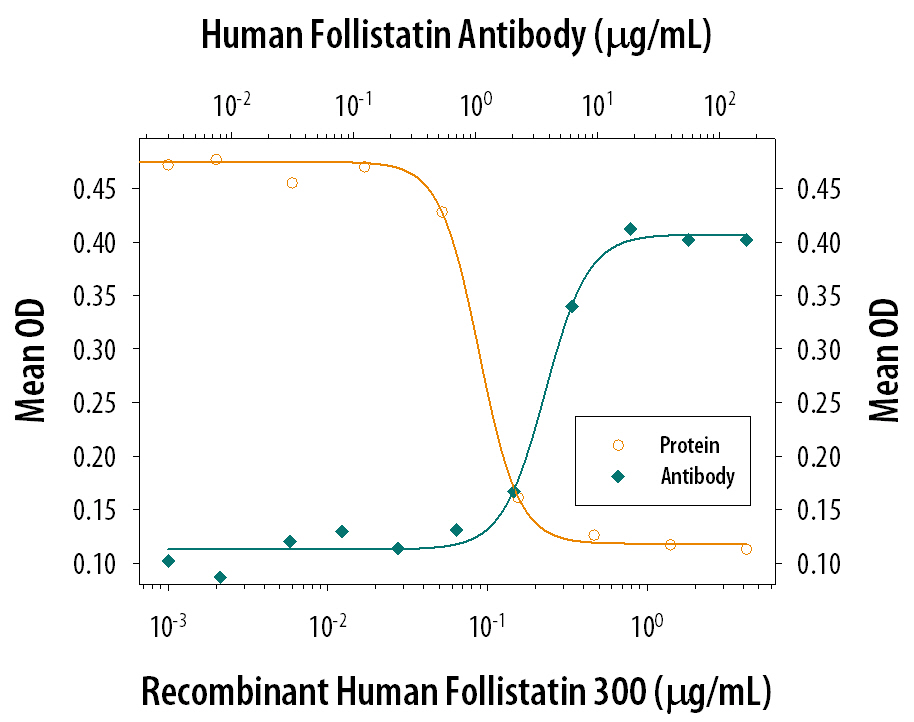 View Larger
View Larger
Follistatin Inhibition of Activin A-induced Hemo-globin Expression and Neutralization by Human Follistatin Antibody. Recombinant Human Follistatin 300 (Catalog # 669-FO) inhibits Recombinant Human/Mouse/Rat Activin A (Catalog # 338-AC) induced hemoglobin expression in the K562 human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line in a dose-dependent manner (orange line), as measured by psuedoperoxidase activity. Inhibition of Recombinant Human/Mouse/Rat Activin A (7.5 ng/mL) activity elicited by Recombinant Human Follistatin 300 (0.4 µg/mL) is neutralized (green line) by increasing concentrations of Goat Anti-Human/Mouse Follistatin Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF669). At 6 µg/mL, this antibody will neutralize > 60% of rhFollistatin 300 bioactivity.
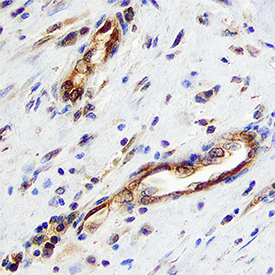 View Larger
View Larger
Follistatin in Human Breast. Follistatin was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human breast using Goat Anti-Human/Mouse Follistatin Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF669) at 10 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Goat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS008) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to epithelial cells. View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Follistatin
Follistatin (FS) was initially identified as a follicle-stimulating hormone inhibiting substance found in ovarian follicular fluid. It has since been shown that FS is a high‑affinity activin-binding protein that can act as an activin antagonist. Two alternatively spliced follistatin mRNAs, encoding mature FS with 288 amino acid (aa) residues (FS-288) and 315 aa residues (FS-315), exist. Natural FS purified from porcine ovaries is primarily a carboxy-terminal truncated form of FS-315 composed of 300 aa residues. The recombinant human FS-300 produced at R&D Systems contains 301 aa residues and represents a molecular form derived from human FS‑315 containing a truncation of 15 residues from the carboxy–terminus. FS-288 binds with high‑affinity to cell-surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans whereas FS-315 binds with low-affinity. The binding affinity of R&D Systems’ FS-300 to heparan sulfate has not been determined. Cell surface-associated FS has been suggested to play a role in the clearance and bioavailability of activin in vivo. Besides activin, FS has also been shown to bind with multiple BMPs and to inhibit BMP activity in early Xenopus embryos. FS deficient mice have been shown to have multiple embryonic defects that will result in death shortly after birth. Overexpression of FS can also cause reproductive defects in transgenic mice. Over aa 30-329, human Follistatin shares 97% aa identity with mouse Follistatin.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human/Mouse Follistatin Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
11
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Taste papilla cell differentiation requires tongue mesenchyme via ALK3-BMP signaling to regulate the production of secretory proteins
Authors: M Ishan, Z Wang, P Zhao, Y Yao, S Stice, L Wells, Y Mishina, HX Liu
bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology, 2023-04-04;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Myostatin Overexpression and Smad Pathway in Detrusor Derived from Pediatric Patients with End-Stage Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction
Authors: S Salemi, LJ Schori, T Gerwinn, M Horst, D Eberli
International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023-02-24;24(5):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Protein
Applications: Western Blot -
Gene therapy for follistatin mitigates systemic metabolic inflammation and post-traumatic arthritis in high-fat diet-induced obesity
Authors: R Tang, NS Harasymowi, CL Wu, KH Collins, YR Choi, SJ Oswald, F Guilak
Sci Adv, 2020-05-08;6(19):eaaz7492.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Myostatin and activin blockade by engineered follistatin results in hypertrophy and improves dystrophic pathology in mdx mouse more than myostatin blockade alone
Authors: A Iskenderia, N Liu, Q Deng, Y Huang, C Shen, K Palmieri, R Crooker, D Lundberg, N Kastrapeli, B Pescatore, A Romashko, J Dumas, R Comeau, A Norton, J Pan, H Rong, K Derakhchan, DE Ehmann
Skelet Muscle, 2018-10-27;8(1):34.
-
Inhibition of the Activin Receptor Type-2B Pathway Restores Regenerative Capacity in Satellite Cell-Depleted Skeletal Muscle
Authors: L Formicola, A Pannérec, RM Correra, B Gayraud-Mo, D Ollitrault, V Besson, S Tajbakhsh, J Lachey, JS Seehra, G Marazzi, DA Sassoon
Front Physiol, 2018-05-24;9(0):515.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Transcriptomic analysis comparing mouse strains with extreme total lung capacities identifies novel candidate genes for pulmonary function
Authors: L George, A Mitra, TA Thimraj, M Irmler, S Vishweswar, L Lunding, D Hühn, A Madurga, J Beckers, H Fehrenbach, S Upadhyay, H Schulz, GD Leikauf, K Ganguly
Respir. Res., 2017-08-09;18(1):152.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Follistatin is a metastasis suppressor in a mouse model of HER2-positive breast cancer
Authors: DD Seachrist, ST Sizemore, E Johnson, FW Abdul-Kari, KL Weber Bonk, RA Keri
Breast Cancer Res., 2017-06-05;19(1):66.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Differential Expression and Release of Activin A and Follistatin in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with and without Nasal Polyps.
Authors: Yang Y, Zhang N, Crombruggen K, Lan F, Hu G, Hong S, Bachert C
PLoS ONE, 2015-06-01;10(6):e0128564.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-Fr -
Dendritic cell regulation of NK-cell responses involves lymphotoxin-alpha, IL-12, and TGF-beta.
Authors: Sarhan D, Palma M, Mao Y, Adamson L, Kiessling R, Mellstedt H, Osterborg A, Lundqvist A
Eur J Immunol, 2015-04-17;45(6):1783-93.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Analysis of the effects of androgens and training on myostatin propeptide and follistatin concentrations in blood and skeletal muscle using highly sensitive Immuno PCR.
Authors: Diel P, Schiffer T, Geisler S, Hertrampf T, Mosler S, Schulz S, Wintgens KF, Adler M
Mol. Cell. Endocrinol., 2010-08-27;330(1):1-9.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Recombinant Protein, Serum
Applications: ELISA Development, Immuno-PCR, Western Blot -
Follistatin restricts bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-2 action on the differentiation of osteoblasts in fetal rat mandibular cells.
Authors: Abe Y, Abe T, Aida Y, Hara Y, Maeda K
J. Bone Miner. Res., 2004-05-03;19(8):1302-7.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human/Mouse Follistatin Antibody
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 1 Review)
Have you used Human/Mouse Follistatin Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:


