Recombinant Human FGFR4 His-tag Avi-tag Protein, CF
Recombinant Human FGFR4 His-tag Avi-tag Protein, CF Summary
Learn more about Avi-tag Biotinylated ProteinsProduct Specifications
| Human FGFR-4 (Leu22-Asp369) Accession # P22455.2 | 6-His tag | Avi-tag |
| N-terminus | C-terminus | |
Analysis
Product Datasheets
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
AVI11120
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 500 μg/mL in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Scientific Data
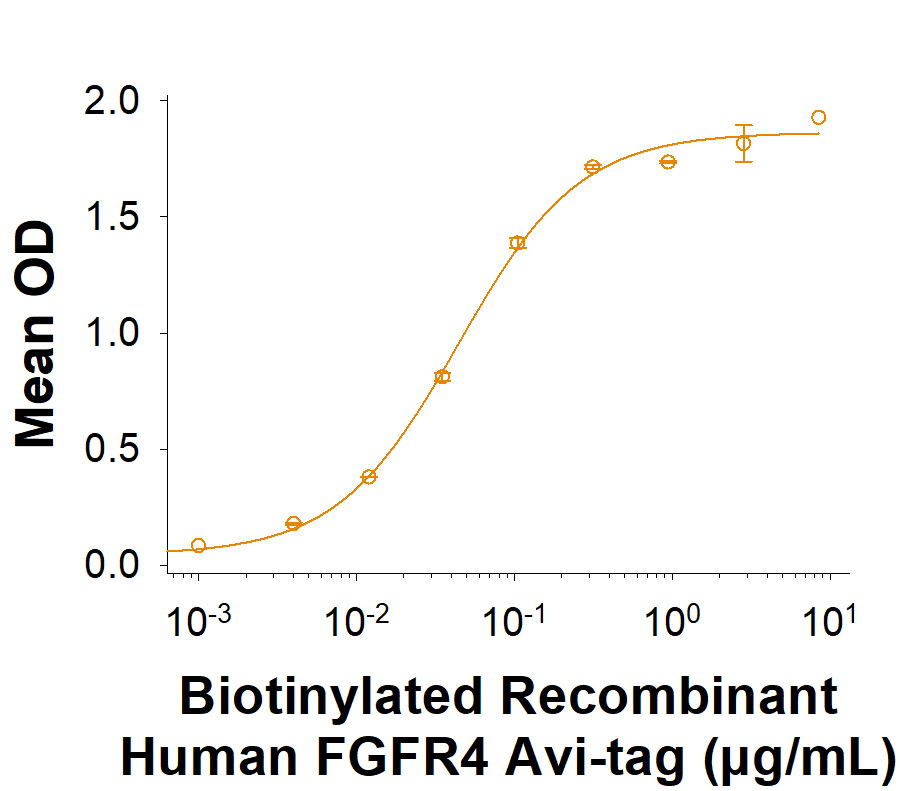 View Larger
View Larger
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. When recombinant human FGF acidic/FGF1 (232-FA/CF) is in the presence at 50.0 ng/mL, 100 μL/well, Recombinant Human FGFR4 His-tag Avi-tag Protein (Catalog # AVI11120) binds with an ED50 of 20.0-120 ng/mL.
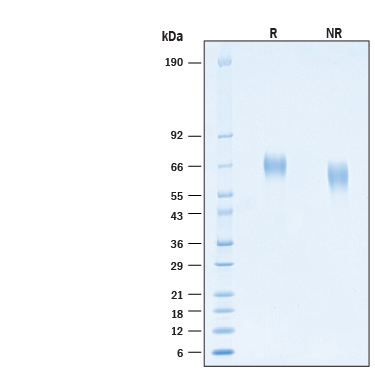 View Larger
View Larger
2 μg/lane of Biotinylated Recombinant Human FGFR4 His-tag Avi-tag Protein (Catalog # AVI11120) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at 60-75 kDa.
Reconstitution Calculator
Background: FGFR4
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4) belongs to a family of type I transmembrane tyrosine kinases which mediate the biological functions of FGFs that are involved in a multitude of physiological and pathological cellular processes (1). The FGFR family is comprised of 4 structurally conserved members (FGFR1-4) all possessing and extracellular domain (ECD) with three immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domains, an acid-box region containing a run of acidic residues between the IgI and IgII domains, a transmembrane domain and the split tyrosine-kinase domain (1, 2). The ECD of mature human FGFR4 shares 90% amino acid sequence identity with mouse FGFR4. Alternative splicing of the IgIII domain generates multiple forms of FGFR1-3, but FGFR4 does not have a splice variant (3, 4). FGFR4 exhibits distinct and varying binding affinities for different FGF ligands, with FGF1, FGF4, and FGF8 showing the highest affinity (4). FGFRs mediate the FGF signaling cascade which regulate developmental processes including cellular proliferation, differentiation, and migration, morphogenesis, and patterning (5). FGFRs transduce the signals through three dominant pathways including RAS/MAPK, PI3k/AKT, and PLC gamma (6). FGFR4 is expressed at high levels during embryonic development and is required for the maintenance of both lipid and glucose metabolism as well as an established role in cholesterol metabolism (7). Overexpression of the FGFR4 has been reported in several solid tumors including breast cancer, prostate cancer, pancreatic cancer, and renal cell carcinoma (4, 8). Further, FGFR4 expression is significantly upregulated in most liver cancer cases, and enhanced FGF19-FGFR4 signaling is linked to hepatocellular carcinoma progression, metastasis, and poor survival (8). FGFR4 is being explored as a potential therapeutic target for breast cancer and other solid tumors (9). Our Avi-tag Biotinylated human FGFR4 features biotinylation at a single site contained within the Avi-tag, a unique 15 amino acid peptide. Protein orientation will be uniform when bound to streptavidin-coated surface due to the precise control of biotinylation and the rest of the protein is unchanged so there is no interference in the protein's bioactivity.
- Ornitz, D.M. and Itoh, N. (2015) Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 4:215.
- Zhang, X. et al. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281:15694.
- Ferguson, H.R. et al. (2021) Signaling. Cells 10:1201.
- Lang, L. and Teng, Y. (2019) Cells. 8:31.
- Xie, Y. et al. (2020) Sig. Transduct. Target Ther. 5:181.
- Mossahebi-Mohammadi, M. et al. (2020) Front Cell Dev. Biol. 18:79.
- Huang, X. et al. (2007) Diabetes 56:2501.
- Liu, Y. et al. (2020) Front Cell Dev. Biol. 8:95.
- Levine, K.M. et al. (2020) Pharmacol. Ther. 214:107590.
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsReviews for Recombinant Human FGFR4 His-tag Avi-tag Protein, CF
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Recombinant Human FGFR4 His-tag Avi-tag Protein, CF and earn rewards!
Have you used Recombinant Human FGFR4 His-tag Avi-tag Protein, CF?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image




