Human DLL1 APC-conjugated Antibody Summary
Ser22-Gly540
Accession # AAG09716
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
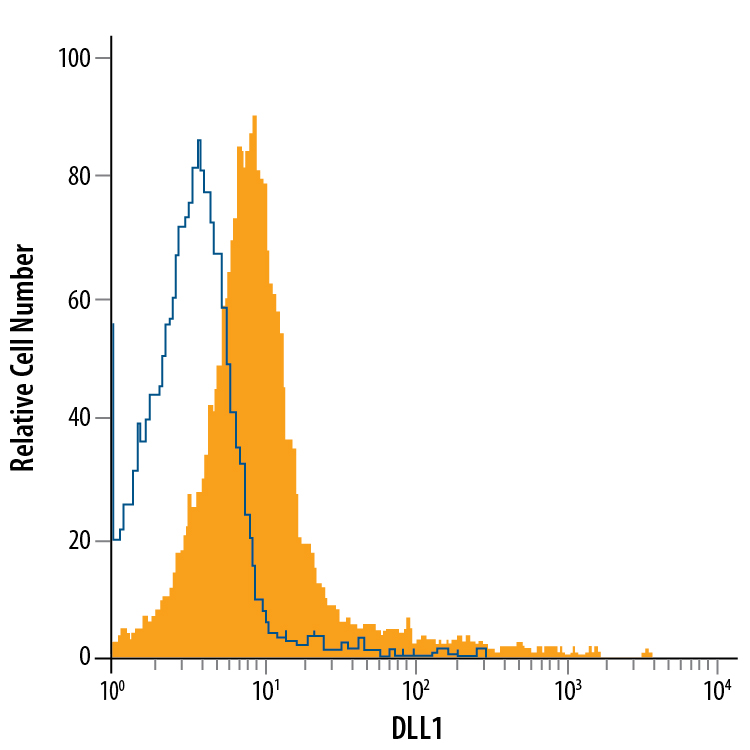 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of DLL1 in T98G Human Glioblastoma Cell Line by Flow Cytometry. T98G human glioblastoma cell line was stained with Mouse Anti-Human DLL1 APC-conjugated Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB1818A, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # IC0041A, open histogram). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, 2 to 8 °C as supplied.
Background: DLL1
Delta-like protein 1 (DLL1) is a 90-100 kDa type I transmembrane protein that belongs to the Delta/Serrate/Lag-2 (DSL) family of Notch ligands. Mature human DLL1 consists of a 528 amino acid (aa) extracellular domain (ECD) with one DSL domain and eight EGF-like repeats, a 23 aa transmembrane segment, and a 155 aa cytoplasmic domain (1). Within the ECD, human DLL1 shares 91% aa sequence identity with mouse and rat DLL1. It shares 26%, 37%, and 54% aa sequence identity with DLL2, 3, and 4, respectively. A 60 kDa ECD fragment released by ADAM9, 12, or 17 mediated proteolysis, promotes the proliferation of hematopoietic progenitor cells (2, 3). The residual membrane-bound portion of DLL1 can be cleaved by presenilin-dependent gamma -secretase, enabling the cytoplasmic domain to migrate to the nucleus (4). DLL1 localizes to adherens junctions on neuronal processes through its association with the scaffolding protein MAGI1 (5). DLL1 is widely expressed, and it plays an important role in embryonic somite formation, cochlear hair cell differentiation, plus B and T lymphocyte differentiation (6-11). The upregulation of DLL1 in arterial endothelial cells following injury or angiogenic stimulation is central to postnatal arteriogenesis (12). DLL1 is also overexpressed in cervical carcinoma and glioma and contributes to tumor progression (1, 13).
- Gray, G.E. et al. (1999) Am. J. Pathol. 154:785.
- Dyczynska, E. et al. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282:436.
- Karanu, F.N. et al. (2001) Blood 97:1960.
- Ikeuchi, T. and S.S. Sisodia (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278:7751.
- Mizuhara, E. et al. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280:26499.
- Takahashi, Y. et al. (2003) Development 130:4259.
- Teppner, I. et al. (2007) BMC Dev. Biol. 7:68.
- Kiernan, A.E. et al. (2005) Development 132:4353.
- Schmitt, T.M. and J.C. Zuniga-Pflucker (2002) Immunity 17:749.
- Hozumi, K. et al. (2004) Nat. Immunol. 5:638.
- Santos, M.A. et al. (2007) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 104:15454.
- Limbourg, A. et al. (2007) Circ. Res. 100:363.
- Purow, B.W. et al. (2005) Cancer Res. 65:2353.
Product Datasheets
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human DLL1 APC-conjugated Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Human DLL1 APC-conjugated Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Human DLL1 APC-conjugated Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image


