Human Endoglin/CD105 Antibody Summary
Glu26-Gly586
Accession # Q5T9B9
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
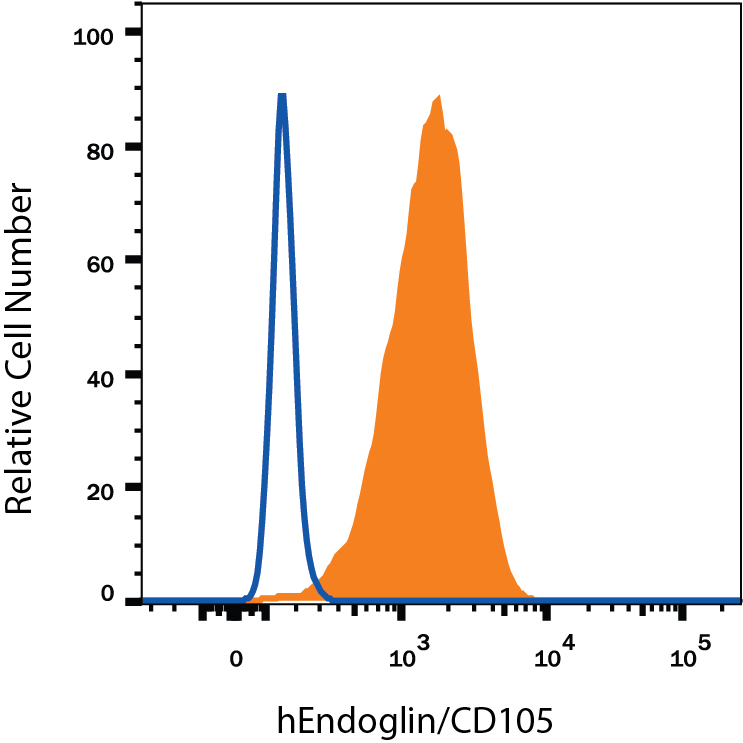 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Endoglin/CD105 in U937 Human Cell Line by Flow Cytometry. U937 human histiocytic lymphoma cell line was stained with Mouse Anti-Human Endoglin/CD105 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB10971, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # MAB002, open histogram), followed by Phycoerythrin-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # F0102B). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Endoglin/CD105
Endoglin (CD105) is a 90 kDa type I transmembrane glycoprotein of the zona pellucida (ZP) family of proteins (1‑3). Endoglin and betaglycan/T beta RIII are type III receptors for TGF beta superfamily ligands, sharing 71% aa identity in the transmembrane (TM) and cytoplasmic domains. Endoglin is highly expressed on proliferating vascular endothelial cells, chondrocytes, and syncytiotrophoblasts of term placenta, with lower amounts on hematopoietic, mesenchymal and neural crest stem cells, activated monocytes, and lymphoid and myeloid leukemic cells (2‑5). Human Endoglin cDNA encodes 658 amino acids (aa) including a 25 aa signal sequence, a 561 aa extracellular domain (ECD) with an orphan domain and a two-part ZP domain, a TM domain and a 47 aa cytoplasmic domain (1‑3). An isoform with a 14 aa cytoplasmic domain (S-endoglin) can oppose effects of long (L) Endoglin (6, 7). The human Endoglin ECD shares 65-72% aa identity with mouse, rat, bovine, porcine and canine Endoglin. Endoglin homodimers interact with TGF-beta 1 and TGF-beta 3 (but not TGF-beta 2), but only after binding T beta RII (8). Similarly, they interact with activin-A and BMP-7 via activin type IIA or B receptors, and with BMP-2 via BMPR-1A/ALK-3 or BMPR-1B/ALK-6 (9). BMP-9, however, is reported to bind Endoglin directly (10). Endoglin modifies ligand-induced signaling in multiple ways. For example, expression of Endoglin can inhibit TGF-beta 1 signals but enhance BMP7 signals in the same myoblast cell line (11). In endothelial cells, Endoglin inhibits T beta RI/ALK5, but enhances ALK1-mediated activation (12). Deletion of mouse Endoglin causes lethal vascular and cardiovascular defects, and human Endoglin haploinsufficiency can a cause the vascular disorder, hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia type I (13, 14). These abnormalities confirm the essential function of Endoglin in differentiation of smooth muscle, angiogenesis, and neovascularization (2‑4, 12‑14). In preeclampsia of pregnancy, high levels of proteolytically generated soluble Endoglin and VEGF R1 (sFLT1), along with low placental growth factor (PlGF), are pathogenic due to antiangiogenic activity (15).
- Gougos, A. and Letarte, M. (1990) J. Biol. Chem. 265:8361.
- ten Dijke, P. et al. (2008) Angiogenesis 11:79.
- Bernabeu, C. et al. (2007) J. Cell. Biochem. 102:1375.
- Mancini, M.L. et al. (2007) Dev. Biol. 308:520.
- Moody, J.L. et al. (2007) Stem Cells 25:2809.
- Velasco, S. et al. (2008) J. Cell Sci. 121:913.
- Perez-Gomez, E. et al. (2005) Oncogene 24:4450.
- Cheifetz, S, et al. (1992) J. Biol. Chem. 267:19027.
- Barbara, N.P. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274:584.
- Scharpfenecker, M. et al. (2007) J. Cell Sci. 120:964.
- Scherner, O. et al. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282:13934.
- Pece-Barbara, N. et al. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280:27800.
- Arthur, H.M. et al. (2000) Dev. Biol. 217:42.
- Lebrin, F. and C.L. Mummery (2008) Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 18:25.
- Venkatesha, S. et al. (2006) Nat. Med. 12:642.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human Endoglin/CD105 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
8
Citations: Showing 1 - 8
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
The self-renewal dental pulp stem cell microtissues challenged by a toxic dental monomer
Authors: G Kaufman, NM Kiburi, D Skrtic
Biosci. Rep., 2020-06-26;40(6):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
CD105 (Endoglin) as negative prognostic factor in AML
Authors: J Kauer, K Schwartz, C Tandler, C Hinterleit, M Roerden, G Jung, HR Salih, JS Heitmann, M Märklin
Sci Rep, 2019-12-04;9(1):18337.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Fluoxetine induces direct inhibitory effects on mesenchymal stem cell?derived osteoprogenitor cells independent of serotonin concentration
Authors: SM Koura, M Salama, M El-Hussiny, MEA Khalil, A Lotfy, SA Hassan, SA Gad Elhak, MA Sobh
Mol Med Rep, 2019-02-01;0(0):.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Feasibility and Efficiency of Human Bone Marrow Stromal Cell Culture with Allogeneic Platelet Lysate-Supplementation for Cell Therapy against Stroke
Stem Cells Int, 2016-10-20;2016(0):6104780.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Human dermis harbors distinct mesenchymal stromal cell subsets.
Authors: Vaculik C, Schuster C, Bauer W, Iram N, Pfisterer K, Kramer G, Reinisch A, Strunk D, Elbe-Burger A
J. Invest. Dermatol., 2011-11-03;132(3):563-74.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Validation of the cardiosphere method to culture cardiac progenitor cells from myocardial tissue.
Authors: Davis D, Zhang Y, Smith R, Cheng K, Terrovitis J, Malliaras K, Li T, White A, Makkar R, Marban E
PLoS ONE, 2009-09-25;4(9):e7195.
Species: Mouse, Rat
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Characterization of human skin-derived mesenchymal stem cell proliferation rate in different growth conditions.
Authors: Riekstina U, Muceniece R, Cakstina I, Muiznieks I, Ancans J
Cytotechnology, 2009-02-14;58(3):153-62.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Therapeutic action of tranexamic acid in hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT): regulation of ALK-1/endoglin pathway in endothelial cells.
Authors: Fernandez-L A, Garrido-Martin EM, Sanz-Rodriguez F, Ramirez JR, Morales-Angulo C, Zarrabeitia R, Perez-Molino A, Bernabeu C, Botella LM
Thromb. Haemost., 2007-02-01;97(2):254-62.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human Endoglin/CD105 Antibody
Average Rating: 4 (Based on 3 Reviews)
Have you used Human Endoglin/CD105 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:






