Human PSGL-1/CD162 Antibody Summary
Gln42-Gly295
Accession # Q14242
Applications
This antibody functions as an ELISA capture antibody when paired with Sheep Anti-Human PSGL‑1/CD162 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody(Catalog # AF3345).
This product is intended for assay development on various assay platforms requiring antibody pairs. We recommend the Human PSGL-1/CD162 DuoSet ELISA (Catalog # DY3345-05) for convenient development of a sandwich ELISA.
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
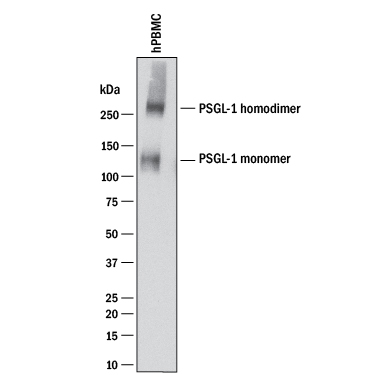
Detection of Human PSGL‑1/CD162 by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). PVDF membrane was probed with 2 µg/mL of Mouse Anti-Human PSGL-1/CD162 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB9962) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF018). A specific band was detected for PSGL-1/CD162 monomer at approximately 110-120 and PSGL-1/CD162 homodimer at approximately 250-260 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.
 View Larger
View Larger
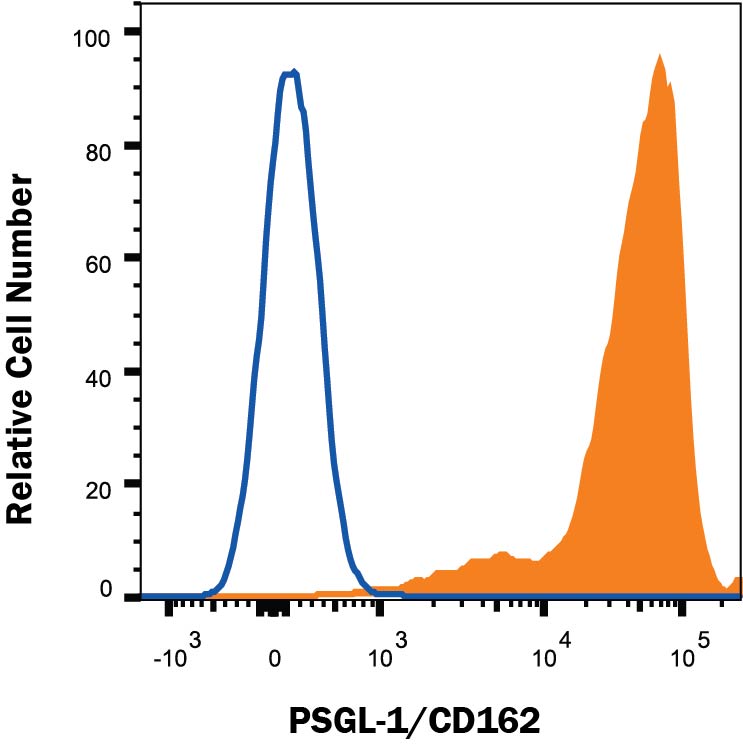
Detection of PSGL-1/CD162 in Human Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes by Flow Cytometry. Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with Mouse Anti-Human PSGL-1/CD162 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB9962, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # MAB0041, open histogram) followed by anti-Mouse IgG PE-conjugates secondary antibody (Catalog # F0102B). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.
 View Larger
View Larger
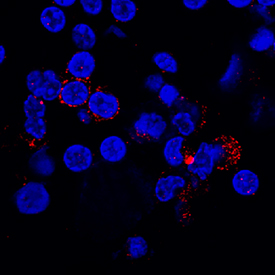
PSGL‑1/CD162 in Human PBMCs. PSGL-1/CD162 was detected in immersion fixed human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) using Mouse Anti-Human PSGL-1/CD162 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB9962) at 5 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL007) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Non-adherent Cells.
 View Larger
View Larger
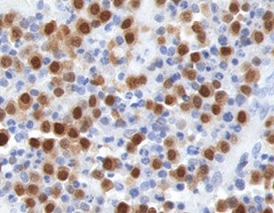
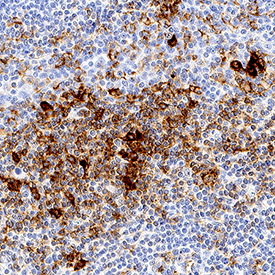
PSGL‑1/CD162 in Human Tonsil. PSGL-1/CD162 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human tonsil using Mouse Anti-Human PSGL-1/CD162 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB9962) at 5 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Mouse IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (Catalog # VC001). Tissue was stained using DAB (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to lymphocytes. View our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.
 View Larger
View Larger
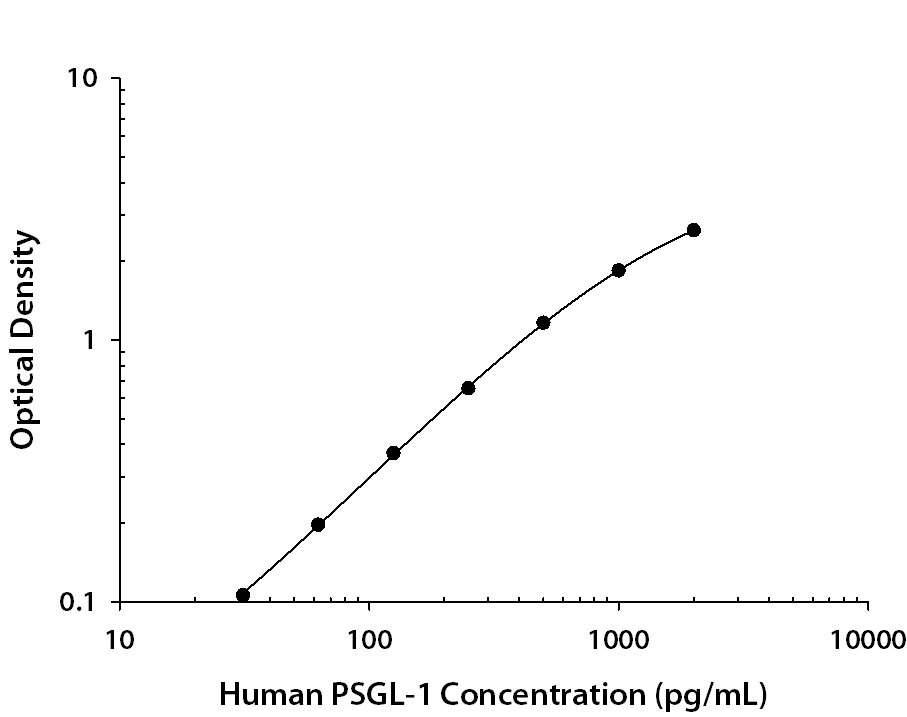
Human PSGL‑1/CD162 ELISA Standard Curve. Recombinant Human PSGL-1/CD162 protein was serially diluted 2-fold and captured by Mouse Anti-Human PSGL-1/CD162 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB9962) coated on a Clear Polystyrene Microplate (Catalog # DY990). Sheep Anti-Human PSGL-1/CD162 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody(Catalog # AF3345) was biotinylated and incubated with the protein captured on the plate. Detection of the standard curve was achieved by incubating Streptavidin-HRP (Catalog # DY998) followed by Substrate Solution (Catalog # DY999) and stopping the enzymatic reaction with Stop Solution (Catalog # DY994).
 View Larger
View Larger
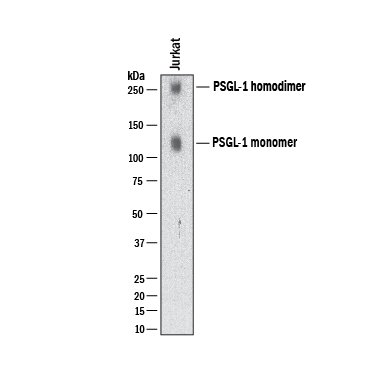
Detection of Human PSGL‑1/CD162 by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of Jurkat human acute T cell leukemia cell line and Ramos human Burkitt's lymphoma cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 2 µg/mL of Mouse Anti-Human PSGL‑1/CD162 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB9962) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (HAF018). Specific bands were detected for PSGL‑1/CD162 at approximately 120, 250 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Western Blot Buffer Group 1.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: PSGL-1/CD162
Human PSGL-1 (P-Selectin Glycoprotein Ligand-1; also CD162), is a 120 kDa mucin-type glycoprotein that plays a key role in leukocyte adhesion (1-3). It is synthesized as a 412 amino acid (aa) preproprecursor that contains a 17 aa signal sequence, a 24 aa propeptide, a 279 aa extracellular domain (ECD), a 21 aa transmembrane segment and a 71 aa cytoplasmic region (4, 5). Following cleavage of the pre- and prosegments, it is expressed as a 240 kDa disulfide-linked homodimer. The extreme N-terminus (aa 1-16 of the mature molecule) contains one threonine (aa 16) and three tyrosines (aa 5, 7, and 10) that are involved in ligand binding. The Thr residue allows for O-linked glycosylation in the form of a core-2 structure (GalNAc-Gal) linked in a beta 1,6 bond to a sialylated Lewis X motif (GlcNAc linked to both Fuc and Gal with a terminal sialic acid residue) (1, 2, 5, 6, 7). The three tyrosine residues allow for sulfation (8, 9). When binding to P-selectin, Tyr sulfation and glycosylation are essential. Tyr7 provides the most efficient sulfate moiety, while Fuc and sialic acid are essentially mandatory (7). When binding to E-selectin, only carbohydrate is needed, while both carbohydrate and Tyr10 are used for L-selectin binding (6, 8). There are 16 decameric aa repeats in the ECD of the longform of PSGL-1. This form is referred to as the A allele, and represents 65 - 80% of the population. Alleles B and C show deletions of decameric repeats #2 (aa 132-141) plus #9 and 10 (aa 222-241), respectively. Shorter forms may show weaker binding to P-selectin (9, 10). Soluble forms of PSGL-1 are also known. Neutrophil elastase will cleave somewhere within repeats #5-9, while cathepsin G cleaves after Tyr7 (11). The loss of Tyr5 and 7 should impact binding affinity. PSGL-1 is found on virtually all leukocytes and macrophages/DC’s (1). Although there is similarity in the organization of the ECD between species, there is little aa identity. Human PSGL-1 ECD shares 51%, 52% and 43% aa sequence identity with equine, canine and mouse ECD, respectively.
- Yang, J. et al. (1999) Thromb. Haemost. 81:1.
- Cummings, R.D. (1999) Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 32:519.
- McEver, R.P. and R.D. Cummings (1997) J. Clin. Invest. 100:485.
- Sako, D. et al. (1993) Cell 75:1179.
- Veldman, G.M. et al. (1995) J. Biol. Chem. 270:16470.
- Bernimoulin, M.P. et al. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278:37.
- Leppanen, A. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275:39569.
- Sako, D. et al. (1995) Cell 83:323.
- Afshar-Kharghan, V. et al. (2001) Blood 97:3306.
- Lozano, M.L. et al. (2001) Br. J. Haematol. 115:969.
- Gardiner, E.E. et al. (2001) Blood 98:1440.
Product Datasheets
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human PSGL-1/CD162 Antibody
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 1 Review)
Have you used Human PSGL-1/CD162 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by: