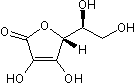
L-Ascorbic acid
Chemical Name: 3-Oxo-L-gulofuranolactone
Purity: ≥99%
Biological Activity
L-Ascorbic acid is an inhibitor of Cav3.2 channels (IC50 = 6.5 μM); displays no effect on Cav3.1 or Cav3.3 channels heterologously expressed in HEK 293 cells. Also enhances the generation of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) from mouse and human somatic cells by increasing reprogramming efficiency. Commonly used antifade reagent in live cell microscopy. Naturally occurring antioxidant.L-Ascorbic acid synthesized to Ancillary Material Grade also available.
For more information about how L-Ascorbic acid may be used, see our protocol: Highly Efficient Generation of CiPSCs from MEFs
Technical Data
The technical data provided above is for guidance only.
For batch specific data refer to the Certificate of Analysis.
Tocris products are intended for laboratory research use only, unless stated otherwise.
Background References
-
Vitamin C as an antioxidant: evaluation of its role in disease prevention.
Padayatty et al.
J.Am.Coll.Nutr., 2003;22:18 -
Molecular mechanisms of subtype-specific inhibition of neuronal T-type calcium channels by ascorbate.
Nelson et al.
J.Neurosci., 2007;27:12577 -
Vitamin C enhances the generation of mouse and human induced pluripotent stem cells.
Esteban et al.
Cell Stem Cell, 2010;6:71 -
Mechanisms and advancement of antifading agents for fluorescence microscopy and single-molecule spectroscopy.
Cordes et al.
Phys.Chem.Chem.Phys., 2011;13:6699
Product Datasheets
Reconstitution Calculator
Molarity Calculator
Citations for L-Ascorbic acid
The citations listed below are publications that use Tocris products. Selected citations for L-Ascorbic acid include:
16 Citations: Showing 1 - 10
-
Evidence of shared transcriptomic dysregulation of HNRNPU-related disorder between human organoids and embryonic mice.
Authors: Orly Et al.
iScience 2023;26:105797
-
High throughput 3D gel-based neural organotypic model for cellular assays using fluorescence biosensors.
Authors: Molly E Et al.
Commun Biol 2022;5:1236
-
Substantial somatic genomic variation and selection for BCOR mutations in human induced pluripotent stem cells.
Authors: Richard Et al.
Nat Genet 2022;54:1406-1416
-
Generation of human elongating multi-lineage organized cardiac gastruloids.
Authors: Janet L Et al.
STAR Protoc 2022;3:101898
-
The FDA-approved drug Auranofin has a dual inhibitory effect on SARS-CoV-2 entry and NF-κB signaling.
Authors: Philippe Et al.
iScience 2022;25:105066
-
A combined human gastruloid model of cardiogenesis and neurogenesis.
Authors: Janet L Et al.
iScience 2022;25:104486
-
Enhancement of Neuroglial Extracellular Matrix Formation and Physiological Activity of Dopaminergic Neural Cocultures by Macromolecular Crowding.
Authors: Marc Et al.
Cells 2022;11
-
Robotic high-throughput biomanufacturing and functional differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells.
Authors: Tristan Et al.
Stem Cell Rep. 2021;16:3076
-
Thioredoxin-1 distinctly promotes NF-κB target DNA binding and NLRP3 inflammasome activation independently of Txnip.
Authors: Qian Et al.
Elife 2020;9
-
Longitudinal assessment of tumor development using cancer avatars derived from genetically engineered pluripotent stem cells.
Authors: Jianhui Et al.
Nat Commun 2020;11:550
-
The COPII cargo adapter SEC24C is essential for neuronal homeostasis.
Authors: Wang Et al.
J Clin Invest 2018;128:3319
-
Direct Dopaminergic Projections from the SNc Modulate Visuomotor Transformation in the Lamprey Tectum.
Authors: Sten Et al.
Neuron 2017;96:910-924.e5
-
Anti-inflammatory activity of low molecular weight polysialic acid on human macrophages.
Authors: Shahraz Et al.
Cell Rep 2015;5:16800
-
Optimization of a cisp. model of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in mice: use of vitamin C and sodium bicarbonate pretreatments to reduce nephrotoxicity and improve animal health status.
Authors: Guindon Et al.
Mol Pain 2014;10:56
-
Generation of integration-free and region-specific neural progenitors from primate fibroblasts.
Authors: Lu Et al.
BMC Dev Biol 2013;3:1580
-
Ethanol-induced expression of ET-1 and ET-BR in liver sinusoidal endothelial cells and human endothelial cells involves hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and microrNA-199.
Authors: Yeligar Et al.
J Immunol 2009;183:5232
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Small Molecule FAQsReviews for L-Ascorbic acid
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review L-Ascorbic acid and earn rewards!
Have you used L-Ascorbic acid?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image