Mouse LBP Antibody Summary
Gly25-Val481 (Ser102Arg, Tyr284His)
Accession # NP_032515
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
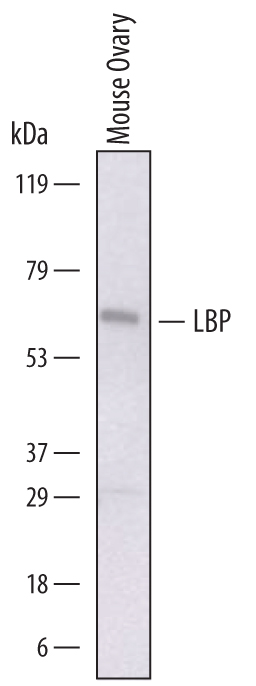
Detection of Mouse LBP by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of mouse ovary tissue. PVDF membrane was probed with 1 µg/mL of Sheep Anti-Mouse LBP Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF6635) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Sheep IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF016). A specific band was detected for LBP at approximately 65 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: LBP
LBP (Lipopolysaccharide binding protein) is a 58‑62 kDa, single-chain glycoprotein member of the BPI/LBP family, BPI/PLUNC/PSP superfamily of lipid-binding proteins (1-3). It is secreted by a number of mammalian cell types, including hepatocytes (4), gingival keratinocytes (5), intestinal Paneth cells (6), and type II Greater alveolar cells (7). LBP is considered to be a class 1 APR (acute phase reactant) that is induced upon exposure to both IL-1 and IL-6 (8). These two cytokines appear upon immune cell exposure to pathogenic microbes. Following its synthesis and release, LBP is known to interact with bacterial wall components, lipopolysaccharide/LPS/Lipid A from Gram- (Gm-) bacteria, and lipoteichoic acid/LTA from Gm+ bacteria (9-13). In the case of LPS, this interaction appears to occur both in the bacterial cell wall, and within the intercellular space, where LPS micelles naturally form following bacterial death and cell wall dissolution (14-17). LBP is posited to induce disassembly of LPS micelles, allowing for LPS binding to LBP, and a heparin-mediated transfer of LPS from LBP to membrane-bound CD14 on the surface of monocytes/macrophages (15, 18). This CD14:LPS complex activates a TLR4:MD2 membrane complex, resulting in the production of NO and TNF-alpha (19). TNF-alpha serves as a chemoattractant for PMNs, and an initiator of coagulation that helps to wall-off and localize microbial elements (16). Notably, increased concentrations of LBP are also associated with parasitic infections (Trypanosoma), and may contribute to the immune response towards parasites (20). In addition to the above, LBP is also reported to transfer LPS to lipoproteins, particularly HDL and LDL (19, 21-23). For LDL, this transfer appears to be inhibitory to monocyte activation; for HDL, the effect may be either stimulatory or inhibitory, depending upon the circumstances (19). Mouse LBP is synthesized as a 481 amino acids (aa) precursor that contains a 25 aa signal sequence and a 456 aa mature region (aa 26-481) (24). It contains an N‑terminal LPS binding region plus a likely C-terminal LPS transfer region (24, 25). Mature mouse LBP shares 68% and 88% aa identity with human and rat LBP, respectively (11, 25).
- Beamer, L.J. et al. (1998) Protein Sci. 7:906.
- Schroder, N.W.J. & R.R. Schumann (2005) J. Endotoxin Res. 11:237.
- Miyake, K. (2006) J. Endotoxin Res. 12:195.
- Grube, B.J. et al. (1994) J. Biol. Chem. 269:8477.
- Ren, L. et al. (2004) J. Periodont. Res. 39:242.
- Hansen, G.H. et al. (2009) Histochem. Cell Biol. 131:727.
- Dentener, M.A. et al. (2000) Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 23:146.
- Schumann, R.R. et al. (1996) Mol. Cell. Biol. 16:3490.
- Weber, J.R. et. al. (2003) Immunity 19:269.
- Schroder, N.W.J. et al. (2004) J. Immunol. 173:2683.
- Su, G.L. et al. (1994) J. Immunol. 153:743.
- Schroder, N.W.J. et al. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 178:15587.
- Wright, S.D. et al. (1989) J. Exp. Med. 170:1231.
- Hallatschek, W. et al. (2004) Eur. J. Immunol. 34:1441.
- Schumann, R.R. & E. Latz (2000) Chem. Immunol. 74:42.
- Mannel, D.N. & B. Echtenacher (2000) Chem. Immunol. 74:141.
- Tsukamoto, H. et al. (2010) Int. Immunol. 22:271.
- Heinzelmann, M. & H. Bosshart (2005) J. Immunol. 174:2280.
- Gallay, P. et al. (1993) Infect. Immun. 61:378.
- Ngure, R.M. et al. (2009) Res. Vet. Sci. 86:394.
- Levels, J.H.M. et al. (2005) Infect. Immun. 73:2321.
- Hubacek, J.A. et al. (1997) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 236:427.
- Thompson, P.A. & R.L. Kitchens (2006) J. Immunol. 177:4880.
- Lengacher, S. et al. (1995-1996) J. Inflamm. 47:165.
- Schumann, R.R. et al. (1990) Science 249:1429.
Product Datasheets
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Mouse LBP Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Mouse LBP Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Mouse LBP Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥1250 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image

