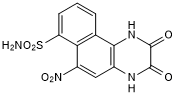
NBQX
Chemical Name: 2,3-Dioxo-6-nitro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrobenzo[f]quinoxaline-7-sulfonamide
Purity: ≥98%
Biological Activity
NBQX is a selective and competitive AMPA and kainate receptor antagonist (IC50 = 0.15 μM and 4.8 μM, respectively). NBQX blocks the antidepressant effects of 8-Hydroxy-DPAT hydrobromide (Cat. No. 0529), decreases mTOR and BDNF levels. NBQX is neuroprotective, anticonvulsant, antinociceptive and active in vivo.NBQX disodium salt, a more water-soluble form of NBQX, also available.
Technical Data
The technical data provided above is for guidance only.
For batch specific data refer to the Certificate of Analysis.
Tocris products are intended for laboratory research use only, unless stated otherwise.
Additional Information
Background References
-
The neuroprotective actions of 2,3-dihydroxy-6-nitro-7-sulfamoylbenzo(f)quinoxaline (NBQX) in a rat focal ischaemia model.
Gill et al.
Brain Res., 1992;580:35 -
Antiepileptogenic and anticonvulsant effects of NBQX, a selective AMPA receptor antagonist, in the rat kindling model of epilepsy.
Namba et al.
Brain Res., 1994;638:36 -
The pharmacology of AMPA receptors and their antagonists.
Sheardown et al.
Stroke, 1993;24:146 -
Pharmacological characterization of non-NMDA subtypes of glutamate receptors in the neonatal rat hemisected spinal cord in vitro.
Zeman and Lodg
Br.J.Pharmacol., 1992;106:367
Product Datasheets
Reconstitution Calculator
Molarity Calculator
Citations for NBQX
The citations listed below are publications that use Tocris products. Selected citations for NBQX include:
180 Citations: Showing 1 - 10
-
Pharmacological analysis of ionotropic glutamate receptor function in neuronal circuits of the zebrafish olfactory bulb.
Authors: Tabor and Friedrich
PLoS One ;3:e1416
-
Voltage-gated potassium channels ensure action potential shape fidelity in distal axons.
Authors: Sabater Et al.
J Neurosci 2021;41:5372
-
Polysynaptic inhibition between striatal cholinergic interneurons shapes their network activity patterns in a dopamine-dependent manner
Authors: Dorst Et al.
Nat Comms 2020;11:5113
-
Homeostatic Intrinsic Plasticity Is Functionally Altered in Fmr1 KO Cortical Neurons.
Authors: Bülow Et al.
Cell Rep 2019;26:1378
-
Kilohertz frame-rate two-photon tomography.
Authors: Kazemipour Et al.
Nature Methods 2019;16:778
-
Simultaneous voltage and calcium imaging and optogenetic stimulation with high sensitivity and a wide field of view.
Authors: Nguyen Et al.
Biomed Opt Express 2019;10:789
-
AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Is Essential for the Maintenance of Energy Levels during Synaptic Activation.
Authors: Marinangeli Et al.
iScience 2018;9:1
-
Drd3 Signaling in the Lateral Septum Mediates Early Life Stress-Induced Social Dysfunction.
Authors: Shin Et al.
Neuron 2018;97:195
-
Cocaine Inhibition of Synaptic Transmission in the Ventral Pallidum Is Pathway-Specific and Mediated by Serotonin.
Authors: Matsui and Alvarez Et al.
Cell Rep 2018;23(13):3852
-
DA D4 receptor activation restores CA1 LTP in hippocampal slices from aged mice.
Authors: Guo
Aging Cell 2017;16(6):1323
-
Striatopallidal dysfunction underlies repetitive behavior in Shank3-deficient model of autism.
Authors: Wang Et al.
J Clin Invest 2017;127:1978
-
Using c-kit to genetically target cerebellar molecular layer interneurons in adult mice.
Authors: Amat
PLoS One 2017;12(6):e0179347
-
Toll-like receptor 4 deficiency alters nucleus accumbens synaptic physiology and drug reward behavior.
Authors: Kashima and Grueter
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114(33):8865
-
Presynaptic GABAB receptors reduce transmission at parabrachial synapses in the lateral central amygdala by inhibiting N-type calcium channels.
Authors: Delaney and Crane
Sci Rep 2016;6:19255
-
Activation of Muscarinic M1 Acetylcholine Receptors Induces Long-Term Potentiation in the Hippocampus.
Authors: Dennis Et al.
J Neurosci 2016;26:414
-
NE Modulates Pyramidal Cell Synaptic Properties in the Anterior Piriform Cortex of Mice: Age-Dependent Effects of β-adrenoceptors.
Authors: Ghosh Et al.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2015;9:450
-
AMPA Receptor-mTOR Activation is Required for the Antidepressant-Like Effects of Sarcosine during the Forced Swim Test in Rats: Insertion of AMPA Receptor may Play a Role.
Authors: Chen Et al.
Front Behav Neurosci 2015;9:162
-
Calcium current homeostasis and synaptic deficits in hippocampal neurons from Kelch-like 1 knockout mice.
Authors: Perissinotti Et al.
Elife 2015;8:444
-
Co-release of glutamate and GABA from single vesicles in GABAergic neurons exogenously expressing VGLUT3.
Authors: Zimmermann Et al.
J Neurosci 2015;7:16
-
Optical control of NMDA receptors with a diffusible photoswitch.
Authors: Laprell Et al.
Front Cell Neurosci 2015;6:8076
-
R-KA: a rapid-onset and sustained antidepressant without psychotomimetic side effects.
Authors: Yang Et al.
Transl Psychiatry 2015;5:e632
-
The Chemokine MIP-1α/CCL3 impairs mouse hippocampal synaptic transmission, plasticity and memory.
Authors: Marciniak Et al.
Front Synaptic Neurosci 2015;5:15862
-
Corelease of acetylcholine and GABA from cholinergic forebrain neurons.
Authors: Saunders Et al.
Cereb Cortex 2015;4
-
A simple retinal mechanism contributes to perceptual interactions between rod- and cone-mediated responses in primates.
Authors: Grimes Et al.
Elife 2015;4
-
Involvement of adrenoceptors, DA receptors and AMPA receptors in antidepressant-like action of 7-O-ethylfangchinoline in mice.
Authors: Sheng Et al.
Acta Pharmacol Sin 2015;36:949
-
BK Channels Localize to the Paranodal Junction and Regulate Action Potentials in Myelinated Axons of Cerebellar Purkinje Cells.
Authors: Hirono Et al.
Brain Res 2015;35:7082
-
Activation of corticostriatal circuitry relieves chronic neuropathic pain.
Authors: Lee Et al.
Physiol Rep 2015;35:5247
-
Dual-channel circuit mapping reveals sensorimotor convergence in the primary motor cortex.
Authors: Hooks Et al.
Front Cell Neurosci 2015;35:4418
-
Loss of Local Astrocyte Support Disrupts Action Potential Propagation and Glutamate Release Synchrony from Unmyelinated Hippocampal Axon Terminals In Vitro.
Authors: Sobieski Et al.
PLoS One 2015;35:11105
-
Afterhyperpolarization (AHP) regulates the frequency and timing of action potentials in the mitral cells of the olfactory bulb: role of olfactory experience.
Authors: Duménieu Et al.
Sci Rep 2015;3
-
Impact of subanesthetic doses of KA on AMPA-mediated responses in rats: An in vivo electrophysiological study on monoaminergic and glutamatergic neurons.
Authors: Iskandrani Et al.
Stroke 2015;29:792
-
Functional α7 nicotinic receptors are expressed on immature granule cells of the postnatal dentate gyrus.
Authors: John Et al.
J Neurosci 2015;1601:15
-
Functional cortical neurons and astrocytes from human pluripotent stem cells in 3D culture.
Authors: Pasca Et al.
Front Cell Neurosci 2015;12:671
-
Tectal microcircuit generating visual selection commands on gaze-controlling neurons.
Authors: Kardamakis Et al.
J Neurosci 2015;112:E1956
-
The effect of Dflu. on neuronal communication at a central synapse.
Authors: Mapelli Et al.
Nat Commun 2015;10:e0123534
-
HSF1 transcriptional activity mediates alcohol induction of Vamp2 expression and GABA release.
Authors: Varodayan and Harrison
J Neurosci 2014;7:89
-
Imaging intraorganellar Ca2+ at subcellular resolution using CEPIA.
Authors: Suzuki Et al.
Nat Commun 2014;5:4153
-
Cross-synaptic synchrony and transmission of signal and noise across the mouse retina.
Authors: Grimes Et al.
Elife 2014;3:e03892
-
Fast retrieval and autonomous regulation of single spontaneously recycling synaptic vesicles.
Authors: Leitz and Kavalali
Elife 2014;3:e03658
-
Repeated binge-like ethanol drinking alters ethanol drinking patterns and depresses striatal GABAergic transmission.
Authors: Wilcox Et al.
Neuropsychopharmacology 2014;39:579
-
L-type Ca2+ currents at CA1 synapses, but not CA3 or dentate granule neuron synapses, are increased in 3xTgAD mice in an age-dependent manner.
Authors: Wang and Mattson
Neurobiol Aging 2014;35:88
-
Glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation in neurons and astrocytes during network activity in hippocampal slices.
Authors: Ivanov Et al.
J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2014;34:397
-
A novel mechanism for nicotinic potentiation of glutamatergic synapses.
Authors: Halff Et al.
J Neurosci 2014;34:2051
-
Modulation of neuronal microcircuit activities within the medial prefrontal cortex by mGluR5 positive allosteric modulator.
Authors: Pollard Et al.
J Psychopharmacol 2014;28:935
-
Rac1 and rac3 GTPases control synergistically the development of cortical and hippocampal GABAergic interneurons.
Authors: Vaghi Et al.
Cereb Cortex 2014;24:1247
-
CaMKII phosphorylation of neuroligin-1 regulates excitatory synapses.
Authors: Bemben Et al.
Nat Neurosci 2014;17:56
-
hPSC-derived maturing GABAergic interneurons ameliorate seizures and abnormal behavior in epileptic mice.
Authors: Cunningham Et al.
Cell Stem Cell 2014;15:559
-
Type 1 metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGlu1) trigger the gating of GluD2 δ glutamate receptors.
Authors: Ady Et al.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2014;15:103
-
Depressed GABA and glutamate synaptic signaling by 5-HT1A receptors in the nucleus tractus solitarii and their role in cardiorespiratory function.
Authors: Ostrowski Et al.
J Neurophysiol 2014;111:2493
-
Synaptic NMDA receptor-dependent Ca2+ entry drives membrane potential and Ca2+ oscillations in spinal ventral horn neurons.
Authors: Alpert and
PLoS One 2013;8:e63154
-
Contribution of NMDA receptor hypofunction in prefrontal and cortical excitatory neurons to schizophrenia-like phenotypes.
Authors: Rompala Et al.
J Neurosci 2013;8:e61278
-
Activation of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors potentiates heteromeric kainate receptors.
Authors: Rojas Et al.
Mol Pharmacol 2013;83:106
-
Different transporter systems regulate extracellular GABA from vesicular and non-vesicular sources.
Authors: Song Et al.
Front Cell Neurosci 2013;7:23
-
Intersecting circuits generate precisely patterned retinal waves.
Authors: Akrouh and Kerschensteiner
Neuron 2013;79:322
-
Impaired glutamate recycling and GluN2B-mediated neuronal calcium overload in mice lacking TGF-β1 in the CNS.
Authors: Koeglsperger Et al.
Glia 2013;61:985
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatase α in the dorsomedial striatum promotes excessive ethanol-drinking behaviors.
Authors: Hamida Et al.
Nat Neurosci 2013;33:14369
-
Moderate prenatal alcohol exposure reduces plasticity and alters NMDA receptor subunit composition in the dentate gyrus.
Authors: Brady Et al.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2013;33:1062
-
Activity-regulated somatostatin expression reduces dendritic spine density and lowers excitatory synaptic transmission via postsynaptic somatostatin receptor 4.
Authors: Hou and Yu
J Biol Chem 2013;288:2501
-
Behavioural and functional characterization of Kv10.1 (Eag1) knockout mice.
Authors: Ufartes Et al.
Hum Mol Genet 2013;22:2247
-
The adhesion protein IgSF9b is coupled to neuroligin 2 via S-SCAM to promote inhibitory synapse development.
Authors: Woo Et al.
J Cell Biol 2013;201:929
-
Genetic markers of a Munc13 protein family member, BAIAP3, are gender specifically associated with anxiety and benzodiazepine abuse in mice and humans.
Authors: Wojcik Et al.
Mol Med 2013;19:135
-
Physiological release of endogenous tau is stimulated by neuronal activity.
Authors: Pooler Et al.
J Neuroimmunol 2013;14:389
-
Neural progenitors organize in small-world networks to promote cell proliferation.
Authors: Malmersjö Et al.
J Neurosci 2013;110:E1524
-
S-nitrosylation of AMPA receptor GluA1 regulates phosphorylation, single-channel conductance, and endocytosis.
Authors: Selvakumar Et al.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2013;110:1077
-
AMPA/kainate glutamate receptors contribute to inflammation, degeneration and pain related behaviour in inflammatory stages of arthritis.
Authors: Bonnet Et al.
Ann Rheum Dis 2013;
-
Axon-glia synapses are highly vulnerable to white matter injury in the developing brain.
Authors: Shen Et al.
J Neurosci Res 2012;90:105
-
Differential requirement for protein synthesis in presynaptic unmuting and muting in hippocampal glutamate terminals.
Authors: Crawford Et al.
PLoS One 2012;7:e51930
-
Genetic inhibition of CaMKII in dorsal striatal medium spiny neurons reduces functional excitatory synapses and enhances intrinsic excitability.
Authors: Klug Et al.
PLoS One 2012;7:e45323
-
Olfactory bulb glomerular NMDA receptors mediate olfactory nerve potentiation and odor preference learning in the neonate rat.
Authors: Lethbridge Et al.
J Neurosci 2012;7:e35024
-
Consolidation of remote fear memories involves Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone (CRH) receptor type 1-mediated enhancement of AMPA receptor GluR1 signaling in the dentate gyrus.
Authors: Thoeringer Et al.
J Neuroimmunol 2012;37:787
-
β-OE unmasks metabotropic receptor-mediated metaplasticity of NMDA receptor transmission in the female rat dentate gyrus.
Authors: Nebieridze Et al.
Psychoneuroendocrinology 2012;37:1845
-
The role of inhibition in oscillatory wave dynamics in the cortex.
Authors: Xiao Et al.
Eur J Neurosci 2012;36:2201
-
Mixed electrical-chemical transmission between hippocampal mossy fibers and pyramidal cells.
Authors: Vivar Et al.
Eur J Neurosci 2012;35:76
-
Presynaptic Cav3.2 channels regulate excitatory neurotransmission in nociceptive dorsal horn neurons.
Authors: Jacus Et al.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2012;32:9374
-
Alteration of synaptic network dynamics by the intellectual disability protein PAK3.
Authors: Dubos Et al.
Eur J Neurosci 2012;32:519
-
Glutamate controls tPA recycling by astrocytes, which in turn influences glutamatergic signals.
Authors: Cassé Et al.
J Neurosci 2012;32:5186
-
Endocannabinoid-mediated long-term depression of afferent excitatory synapses in hippocampal pyramidal cells and GABAergic interneurons.
Authors: Peterfi Et al.
J Neurosci 2012;32:14448
-
Lack of kinase regulation of canonical transient receptor potential 3 (TRPC3) channel-dependent currents in cerebellar Purkinje cells.
Authors: Nelson and Glitsch
PLoS One 2012;287:6326
-
Essential role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the regulation of serotonin transmission in the basolateral amygdala.
Authors: Daftary Et al.
Neuroscience 2012;224:125
-
Heterogeneous reallocation of presynaptic efficacy in recurrent excitatory circuits adapting to inactivity.
Authors: Mitra Et al.
Nat Neurosci 2012;15:250
-
Focal adhesion kinase regulates actin nucleation and neuronal filopodia formation during axonal growth.
Authors: Chacón Et al.
Dev Neurobiol 2012;139:3200
-
Effect of prolonged R.zole exposure on cultured motoneurons in a mouse model of ALS.
Authors: Schuster Et al.
J Neurophysiol 2012;107:484
-
Development of NMDA NR2 subunits and their roles in critical period maturation of neocortical GABAergic interneurons.
Authors: Zhang and Sun
Neuropsychopharmacology 2011;71:221
-
CDK5 is essential for soluble amyloid β-induced degradation of GKAP and remodeling of the synaptic actin cytoskeleton.
Authors: Roselli Et al.
PLoS One 2011;6:e23097
-
Synaptic responses evoked by tactile stimuli in Purkinje cells in mouse cerebellar cortex Crus II in vivo.
Authors: Chu Et al.
PLoS One 2011;6:e22752
-
Cholinergic interneurons mediate fast VGluT3-dependent glutamatergic transmission in the striatum.
Authors: Higley Et al.
PLoS One 2011;6:e19155
-
Sleep-deprivation regulates α-2 adrenergic responses of rat hypocretin/orexin neurons.
Authors: Uschakov Et al.
PLoS One 2011;6:e16672
-
Cannabinoids attenuate hippocampal γ oscillations by suppressing excitatory synaptic input onto CA3 pyramidal neurons and fast spiking basket cells.
Authors: Holderith Et al.
Eur J Neurosci 2011;589:4921
-
Calcium-independent inhibitory G-protein signaling induces persistent presynaptic muting of hippocampal synapses.
Authors: Crawford Et al.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2011;31:979
-
NMDA receptor signaling in oligodendrocyte progenitors is not required for oligodendrogenesis and myelination.
Authors: Biase Et al.
J Neurophysiol 2011;31:12650
-
An autism-associated point mutation in the neuroligin cytoplasmic tail selectively impairs AMPA receptor-mediated synaptic transmission in hippocampus.
Authors: Etherton Et al.
EMBO J 2011;30:2908
-
Quantal amplitude at the cone ribbon synapse can be adjusted by changes in cytosolic glutamate.
Authors: Bartoletti and Thoreson
Mol Vis 2011;17:920
-
Developmental maturation of excitation and inhibition balance in principal neurons across four layers of somatosensory cortex.
Authors: Zhang Et al.
J Neurosci 2011;174:45931
-
Inflammation alters trafficking of extrasynaptic AMPA receptors in tonically firing lamina II neurons of the rat spinal dorsal horn.
Authors: Kopach Et al.
Pain 2011;152:912
-
Distinct functions of kainate receptors in the brain are determined by the auxiliary subunit Neto1.
Authors: Straub Et al.
Nat Neurosci 2011;14:866
-
Ca(2+)-dependent enhancement of release by subthreshold somatic depolarization.
Authors: Christie Et al.
Nat Neurosci 2011;14:62
-
The Etv1/Er81 transcription factor orchestrates activity-dependent gene regulation in the terminal maturation program of cerebellar granule cells.
Authors: Abe Et al.
Neuroscience 2011;108:12497
-
Endogenous N-acetylaspartylglutamate (NAAG) inhibits synaptic plasticity/transmission in the amygdala in a mouse inflammatory pain model.
Authors: Adedoyin Et al.
Mol Pain 2010;6:60
-
Nociceptive stimulation induces expression of Arc/Arg3.1 in the spinal cord with a preference for neurons containing enkephalin.
Authors: Hossaini Et al.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010;6:43
-
Facilitation of long-term potentiation by muscarinic M(1) receptors is mediated by inhibition of SK channels.
Authors: Buchanan Et al.
Neuron 2010;68:948
-
Control of cerebellar long-term potentiation by P-Rex-family guanine-nucleotide exchange factors and phosphoinositide 3-kinase.
Authors: Jackson Et al.
PLoS One 2010;5:e11962
-
High-Pass Filtering and Dynamic Gain Regulation Enhance Vertical Bursts Transmission along the Mossy Fiber Pathway of Cerebellum.
Authors: Mapelli Et al.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010;4:14
-
Selected SALM (synaptic adhesion-like molecule) family proteins regulate synapse formation.
Authors: Mah Et al.
J Physiol 2010;30:5559
-
Different relationship of N- and P/Q-type Ca2+ channels to channel-interacting slots in controlling neurotransmission at cultured hippocampal synapses.
Authors: Cao and Tsien
J Neurosci 2010;30:4536
-
Excitability and synaptic communication within the oligodendrocyte lineage.
Authors: Biase Et al.
J Neurosci 2010;30:3600
-
Calcium binding to PICK1 is essential for the intracellular retention of AMPA receptors underlying long-term depression.
Authors: Citri Et al.
J Neurosci 2010;30:16437
-
Postsynaptic spiking homeostatically induces cell-autonomous regulation of inhibitory inputs via retrograde signaling.
Authors: Peng Et al.
J Neurosci 2010;30:16220
-
Rapid activation of dormant presynaptic terminals by phorbol esters.
Authors: Chang Et al.
J Neurosci 2010;30:10048
-
Contribution of the d-Serine-Dependent Pathway to the Cellular Mechanisms Underlying Cognitive Aging.
Authors: Potier Et al.
Front Aging Neurosci 2010;2:1
-
Activation of native TRPC3 cation channels by phospholipase D.
Authors: Glitsch
FASEB J 2010;24:318
-
Effect of hypoxia on expiratory muscle activity in fetal sheep.
Authors: Bissonnette Et al.
Respir Physiol Neurobiol 2010;171:110
-
Competitive regulation of synaptic Ca2+ influx by D2 DA and A2A adenosine receptors.
Authors: Higley and Sabatini
Nat Neurosci 2010;13:958
-
A dynamic role for GABA receptors on the firing pattern of midbrain DArgic neurons.
Authors: Lobb Et al.
J Neurophysiol 2010;104:403
-
Dynamic modulation of phasic and asynchronous glutamate release in hippocampal synapses.
Authors: Chang
J Neurophysiol 2010;103:392
-
Combinatorial responses controlled by synaptic inhibition in the cerebellum granular layer.
Authors: Mapelli Et al.
Neuropharmacology 2010;103:250
-
Characterization of engineered channelrhodopsin variants with improved properties and kinetics.
Authors: Lin Et al.
Biophys J 2009;96:1803
-
Enhanced excitatory transmission at cortical synapses as the basis for facilitated spreading depression in Ca(v)2.1 knockin migraine mice.
Authors: Tottene Et al.
Neuron 2009;61:762
-
ATP-dependent infra-slow (0.1 Hz) oscillations in thalamic networks.
Authors: Lörincz Et al.
PLoS One 2009;4:e4447
-
Specific synapses develop preferentially among sister excitatory neurons in the neocortex.
Authors: Yu Et al.
EMBO Rep 2009;458:501
-
NMDA receptors regulate nicotine-enhanced brain reward function and intravenous nicotine self-administration: role of the ventral tegmental area and central nucleus of the amygdala.
Authors: Kenny Et al.
Neuropsychopharmacology 2009;34:266
-
N-MthD.-aspartate receptor- and metabotropic glutamate receptor-dependent long-term depression are differentially regulated by the ubiquitin-proteasome system.
Authors: Citri Et al.
J Neurophysiol 2009;30:1443
-
D1/D5 modulation of synaptic NMDA receptor currents.
Authors: Varela Et al.
J Neurosci 2009;29:3109
-
Millisecond timescale disinhibition mediates fast information transmission through an avian basal ganglia loop.
Authors: Leblois Et al.
J Neurosci 2009;29:15420
-
Chronic CXCL10 alters neuronal properties in rat hippocampal culture.
Authors: Cho Et al.
J Neurosci 2009;207:92
-
AMPA receptor trafficking and synaptic plasticity require SQSTM1/p62.
Authors: Jiang Et al.
Hippocampus 2009;19:392
-
Tamoxifen mediated estrogen receptor activation protects against early impairment of hippocampal neuron excitability in an oxygen/glucose deprivation brain slice ischemia model.
Authors: Zhang Et al.
Brain Res 2009;1247:196
-
Experience-dependent intrinsic plasticity in interneurons of barrel cortex layer IV.
Authors: Sun
J Neurosci 2009;102:2955
-
Co-transmission of DA and GABA in periglomerular cells.
Authors: Maher and Westbrook
J Neurophysiol 2008;99:1559
-
GABA actions in hippocampal area CA3 during postnatal development: differential shift from depolarizing to hyperpolarizing in somatic and dendritic compartments.
Authors: Romo-Parra Et al.
J Neurosci 2008;99:1523
-
Synapse-specific adaptations to inactivity in hippocampal circuits achieve homeostatic gain control while dampening network reverberation.
Authors: Kim and Tsien
Neuron 2008;58:925
-
Involvement of AMPA receptors in the antidepressant-like effects of Li in the mouse tail suspension test and forced swim test.
Authors: Gould Et al.
Neuropharmacology 2008;54:577
-
Cholecystokinin inhibits endocannabinoid-sensitive hippocampal IPSPs and stimulates others.
Authors: Karson Et al.
J Biol Chem 2008;54:117
-
Apoptosis induced by domoic acid in mouse cerebellar granule neurons involves activation of p38 and JNK MAP kinases.
Authors: Giordano Et al.
J Physiol 2008;52:1100
-
Cortical adenylyl cyclase 1 is required for thalamocortical synapse maturation and aspects of layer IV barrel development.
Authors: Iwasato Et al.
J Neurosci 2008;28:5931
-
Competition between calcium-activated K+ channels determines cholinergic action on firing properties of basolateral amygdala projection neurons.
Authors: Power and Sah
J Neurosci 2008;28:3209
-
White matter vulnerability to ischemic injury increases with age because of enhanced excitotoxicity.
Authors: Baltan Et al.
J Neurosci 2008;28:1479
-
Resveratrol attenuates early pyramidal neuron excitability impairment and death in acute rat hippocampal slices caused by oxygen-glucose deprivation.
Authors: Zhang Et al.
Exp Neurol 2008;212:44
-
The chemokine CCL2 activates p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in cultured rat hippocampal cells.
Authors: Cho and Gruol
J Neurosci 2008;199:94
-
Dendritic glutamate release produces autocrine activation of mGluR1 in cerebellar Purkinje cells.
Authors: Shin Et al.
Nature 2008;105:746
-
Long-lasting NMDA receptor-mediated EPSCs in mouse striatal medium spiny neurons.
Authors: Logan Et al.
J Neurophysiol 2007;98:2693
-
Increased thalamocortical synaptic response and decreased layer IV innervation in GAP-43 knockout mice.
Authors: Albright Et al.
J Neurophysiol 2007;98:1610
-
Endogenous D-serine contributes to NMDA-receptor-mediated light-evoked responses in the vertebrate retina.
Authors: Gustafson Et al.
J Neurophysiol 2007;98:122
-
Presynaptic plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase isoform 2a regulates excitatory synaptic transmission in rat hippocampal CA3.
Authors: Jensen Et al.
Chem Senses 2007;579:85
-
Long-term modifications in the strength of excitatory associative inputs in the piriform cortex.
Authors: Young and Sun
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007;32:783
-
Axon and dendrite geography predict the specificity of synaptic connections in a functioning spinal cord network.
Authors: Li Et al.
Neural Dev 2007;2:17
-
Plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase 2 contributes to short-term synapse plasticity at the parallel fiber to Purkinje neuron synapse.
Authors: Empson Et al.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007;27:3753
-
Disynaptic amplification of metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 responses in the olfactory bulb.
Authors: Jan and Westbrook
J Neurosci 2007;27:132
-
Somatodendritic release of glutamate regulates synaptic inhibition in cerebellar Purkinje cells via autocrine mGluR1 activation.
Authors: Duguid Et al.
J Neurosci 2007;27:12464
-
Potent and specific action of the mGlu1 antagonists YM-298198 and JNJ16259685 on synaptic transmission in rat cerebellar slices.
Authors: Fukunaga Et al.
Br J Pharmacol 2007;151:870
-
Vesicular release of glutamate from unmyelinated axons in white matter.
Authors: Ziskin Et al.
Front Integr Neurosci 2007;10:321
-
Properties of GluR3 receptors tagged with GFP at the amino or carboxyl terminus.
Authors: Limon Et al.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007;104:15526
-
Glutathione levels modulate domoic acid induced apoptosis in mouse cerebellar granule cells.
Authors: Giordano Et al.
Toxicol Sci 2007;100:433
-
Neurotoxicity of domoic Acid in cerebellar granule neurons in a genetic model of glutathione deficiency.
Authors: Giordano Et al.
Mol Pharmacol 2006;70:2116
-
Environment matters: synaptic properties of neurons born in the epileptic adult brain develop to reduce excitability.
Authors: Jakubs Et al.
Neuron 2006;52:1047
-
Ionotropic and metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonism attenuates cue-induced cocaine seeking.
Authors: Bäckström and Hyytiä
Neuropsychopharmacology 2006;31:778
-
Glial glutamate transporters maintain one-to-one relationship at the climbing fiber-Purkinje cell synapse by preventing glutamate spillover.
Authors: Takayasu Et al.
J Neurosci 2006;26:6563
-
Regulated expression of HCN channels and cAMP levels shape the properties of the h current in developing rat hippocampus.
Authors: Surges Et al.
Mol Pain 2006;24:94
-
Adaptation to synaptic inactivity in hippocampal neurons.
Authors: Thiagarajan Et al.
Neuron 2005;47:725
-
Activation of NR2A-containing NMDA receptors is not obligatory for NMDA receptor-dependent long-term potentiation.
Authors: Weitlauf Et al.
Neurochem Int 2005;25:8386
-
Programmed and induced phenotype of the hippocampal granule cells.
Authors: Gómez-Lira Et al.
J Neurosci 2005;25:6939
-
Calcium increases in retinal glial cells evoked by light-induced neuronal activity.
Authors: Newman
Nat Methods 2005;25:5502
-
Differences in transmission properties and susceptibility to long-term depression reveal functional specialization of ascending axon and parallel fiber synapses to Purkinje cells.
Authors: Sims and Hartell
EMBO Rep 2005;25:3246
-
Interactions between ephrin-B and metabotropic glutamate 1 receptors in brain tissue and cultured neurons.
Authors: Calò Et al.
J Neurosci 2005;25:2245
-
Antinociceptive interactions between intrathecal gabap. and MK801 or NBQX in rat formalin test.
Authors: Yoon Et al.
J Korean Med Sci 2005;20:307
-
Augmenting neurotransmitter release by enhancing the apparent Ca2+ affinity of synaptotagmin 1.
Authors: Rhee Et al.
J Neurosci 2005;102:18664
-
Endocannabinoid-mediated metaplasticity in the hippocampus.
Authors: Chevaleyre and Castillo
Neuron 2004;43:871
-
Glucose but not lactate in combination with acidosis aggravates ischemic neuronal death in vitro.
Authors: Cronberg Et al.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2004;35:753
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA and protein are targeted to discrete dendritic laminas by events that trigger epileptogenesis.
Authors: Tongiorgi Et al.
Development 2004;24:6842
-
Astrocyte glutamate transporters regulate metabotropic glutamate receptor-mediated excitation of hippocampal interneurons.
Authors: Huang Et al.
J Neurosci 2004;24:4551
-
Functional excitatory synapses in HEK293 cells expressing neuroligin and glutamate receptors.
Authors: Fu Et al.
J Neurophysiol 2003;90:3950
-
DA controls the firing pattern of DA neurons via a network feedback mechanism.
Authors: Paladini Et al.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2003;100:2866
-
A GDP/GTP exchange protein for the Rab3 small G protein family up-regulates a postdocking step of synaptic exocytosis in central synapses.
Authors: Yamaguchi Et al.
J Neurophysiol 2002;99:14536
-
The suppression of brain cold-stable microtubules in mice induces synaptic defects associated with neuroleptic-sensitive behavioral disorders.
Authors: Andrieux Et al.
Genes Dev 2002;16:2350
-
Glutamate antagonists limit tumor growth.
Authors: Rzeski Et al.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2001;98:6372
-
Kainate receptor-mediated synaptic currents in cerebellar Golgi cells are not shaped by diffusion of glutamate.
Authors: Bureau Et al.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2000;97:6838
-
Presynaptic N-MthD.-aspartate receptors at the parallel fiber-Purkinje cell synapse.
Authors: Casado Et al.
J Neurosci 2000;97:11593
-
Histamine depolarizes cholinergic interneurones in the rat striatum via a H(1)-receptor mediated action.
Authors: Bell Et al.
Br J Pharmacol 2000;131:1135
-
Calcium dynamics in single spines during coincident pre- and postsynaptic activity depend on relative timing of back-propagating action potentials and subthreshold excitatory postsynaptic potentials.
Authors: Koester and Sakmann
PLoS One 1998;95:9596
-
Spreading depression and focal brain ischemia induce cyclooxygenase-2 in cortical neurons through N-MthD.-aspartic acid-receptors and phospholipase A2.
Authors: Miettinen Et al.
J Psychopharmacol 1997;94:6500
-
Effect of chronic ethanol treatment in vivo on excitability in mouse cortical neurones in vitro.
Authors: Ibbotson Et al.
Br J Pharmacol 1997;122:956
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Small Molecule FAQsReviews for NBQX
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review NBQX and earn rewards!
Have you used NBQX?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image