PF 573228
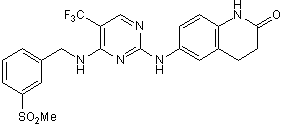
Chemical Name: 3,4-Dihydro-6-[[4-[[[3-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl]methyl]amino]-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]-2(1H)-quinolinone
Purity: ≥98%
Biological Activity
PF 573228 is a potent and selective inhibitor of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) (IC50 = 4 nM). Displays 50 - 250-fold selectivity for FAK over other protein kinases. Blocks serum and fibronectin-directed migration and decreases focal adhesion turnover in vitro.Technical Data
The technical data provided above is for guidance only.
For batch specific data refer to the Certificate of Analysis.
Tocris products are intended for laboratory research use only, unless stated otherwise.
Additional Information
Background References
-
Cellular characterization of a novel focal adhesion kinase inhibitor.
Slack-Davis et al.
J.Biol.Chem., 2007;282:14845 -
FAK-heterozygous mice display enhanced tumour angiogenesis.
Kostourou et al.
Nat.Commun., 2013;5:2020
Product Datasheets
Reconstitution Calculator
Molarity Calculator
Citations for PF 573228
The citations listed below are publications that use Tocris products. Selected citations for PF 573228 include:
48 Citations: Showing 1 - 10
-
Vaccinia virus hijacks EGFR signalling to enhance virus spread through rapid and directed infected cell motility.
Authors: Beerli Et al.
Nat Microbiol 2019;4:216
-
The increased adhesion of tumor cells to endothelial cells after irradiation can be reduced by FAK-inhibition.
Authors: Kouam Et al.
Radiat Oncol 2019;14:25
-
The protein tyrosine phosphatase Shp2 regulates oligodendrocyte differentiation and early myelination and contributes to timely remyelination.
Authors: Ahrendsen Et al.
J Neurosci 2018;38:787
-
Matrix stiffness modulates infection of endothelial cells by Listeria monocytogenes via expression of cell surface vimentin.
Authors: Bastounis Et al.
Mol Biol Cell 2018;29:1571
-
Blood vitronectin is a major activator of LIF and IL-6 in the brain through integrin-FAK and uPAR signaling.
Authors: Keasey Et al.
J Cell Sci 2018;131
-
Multiparametric Analysis of Cell Shape Demonstrates that β-PIX Directly Couples YAP Activation to Extracellular Matrix Adhesion.
Authors: Sero and Bakal
Cell Syst 2017;4:84
-
Tenascin-C Is a Major Component of the Fibrogenic Niche in Kidney Fibrosis.
Authors: Fu Et al.
J Am Soc Nephrol 2017;28:785
-
Disruption of outer blood-retinal barrier by Toxoplasma gondii-infected monocytes is mediated by paracrinely activated FAK signaling
Authors: Song
PLoS One 2017;12(4):e0175159
-
Imatinib and nilo. increase glioblastoma cell invasion via Abl-independent stimulation of p130Cas and FAK signalling.
Authors: Frolov Et al.
Sci Rep 2016;6:27378
-
Extracellular matrix stiffness dictates Wnt expression through integrin pathway.
Authors: Du Et al.
Sci Rep 2016;6:20395
-
Topographic confinement of epithelial clusters induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in compliant matrices.
Authors: Nasrollahi and Pathak
PLoS One 2016;6:18831
-
Focal adhesion kinase is required for actin polymerization and remodeling of the cytoskeleton during sperm capacitation.
Authors: Roa-Espitia Et al.
Biol Open 2016;5:1189
-
LEFTY2 Controls Migration of Human Endometrial Cancer Cells via Focal Adhesion Kinase Activity (FAK) and miRNA-200a
Authors: Alowayed Et al.
Cell Physiol Biochem 2016;39:815
-
Smooth muscle contraction and growth of stromal cells in the human prostate are both inhibited by the Src family kinase inhibitors, AZM475271 and PP2.
Authors: Wang Et al.
Br J Pharmacol 2016;173:3342
-
Eosinophil peroxidase activates cells by HER2 receptor engagement and β1-integrin clustering with downstream MAPK cell signaling
Authors: Hennigan Et al.
Clinical Immunology 2016;171:1
-
Endothelial Cells Use a Formin-Dependent Phagocytosis-Like Process to Internalize the Bacterium Listeria monocytogenes.
Authors: Rengarajan Et al.
Sci Rep 2016;12:e1005603
-
Thrombin-induced reactive oxygen species generation in platelets: A novel role for protease-activated receptor 4 and GPIbα.
Authors: Carrim Et al.
J Exp Med 2015;6:640
-
GABAB receptor upregulates fragile X mental retardation protein expression in neurons.
Authors: Zhang Et al.
Redox Biol 2015;5:10468
-
Defective apical extrusion signaling contributes to aggressive tumor hallmarks.
Authors: Gu Et al.
Elife 2015;4:e04069
-
Combination of heat shock protein 90 and focal adhesion kinase inhibitors synergistically inhibits the growth of non-small cell lung cancer cells.
Authors: Webber Et al.
Oncoscience 2015;2:765
-
IgE-activated basophils regulate eosinophil tissue entry by modulating endothelial function.
Authors: Cheng Et al.
Sci Rep 2015;212:513
-
WISP-2 in human gastric cancer and its potential metastatic suppressor role in gastric cancer cells mediated by JNK and PLC-γ pathways.
Authors: Ji Et al.
Br J Cancer 2015;113:921
-
Segmentation of Image Data from Complex Organotypic 3D Models of Cancer Tissues with Markov Random Fields.
Authors: Robinson Et al.
PLoS One 2015;10:e0143798
-
Astroglial-derived periostin promotes axonal regeneration after spinal cord injury.
Authors: Shih Et al.
J Biol Chem 2014;34:2438
-
The phosphatidylserine receptor TIM4 utilizes integrins as coreceptors to effect phagocytosis.
Authors: Flannagan Et al.
Mol Biol Cell 2014;25:1511
-
Essential function for PDLIM2 in cell polarization in three-dimensional cultures by feedback regulation of the β1-integrin-RhoA signaling axis.
Authors: Deevi Et al.
Neoplasia 2014;16:422
-
Selective inhibition of RET mediated cell proliferation in vitro by the kinase inhibitor SPP86.
Authors: Alao Et al.
BMC Cancer 2014;14:853
-
Signals from the surface modulate differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells through glycosaminoglycans and integrins.
Authors: Wrighton Et al.
PLoS Pathog 2014;111:18126
-
Periostin links mechanical strain to inflammation in abdominal aortic aneurysm.
Authors: Yamashita Et al.
J Neurosci 2013;8:e79753
-
Lysyl oxidase activity regulates oncogenic stress response and tumorigenesis.
Authors: Wiel Et al.
Cell Death Dis 2013;4:e855
-
Reversal of myofibroblast differentiation by prostaglandin E(2).
Authors: Garrison Et al.
Mol Cancer Ther 2013;48:550
-
Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) receptors 1 and 2 coordinately induce mesenchymal cell migration through S1P activation of complementary kinase pathways.
Authors: Quint Et al.
PLoS One 2013;288:5398
-
Pathogenic NPHP5 mutations impair protein interaction with Cep290, a prerequisite for ciliogenesis.
Authors: Barbelanne Et al.
Hum Mol Genet 2013;22:2482
-
Focal adhesion kinase negatively regulates Lck function downstream of the T cell antigen receptor.
Authors: Chapman Et al.
J Immunol 2013;191:6208
-
Microdomain heterogeneity in 3D affects the mechanics of neonatal cardiac myocyte contraction.
Authors: Curtis Et al.
Biomech Model Mechanobiol 2013;12:95
-
Inhibition of a novel specific neuroglial integrin signaling pathway increases STAT3-mediated CNTF expression.
Authors: Keasey Et al.
Cell Commun Signal 2013;11:35
-
Contractile Activity Regulates Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Expression and NO(i) Production in Cardiomyocytes via a FAK-Dependent Signaling Pathway.
Authors: Chu Et al.
J Signal Transduct 2012;2012:473410
-
Focal adhesion kinase links mechanical force to skin fibrosis via inflammatory signaling.
Authors: Wong Et al.
Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2012;18:148
-
Integrin/Fak/Src-mediated regulation of cell survival and anoikis in human intestinal epithelial crypt cells: selective engagement and roles of PI3-K isoform complexes.
Authors: Beauséjour Et al.
Apoptosis 2012;17:566
-
Cooperation between c-Met and focal adhesion kinase family members in medulloblastoma and implications for therapy.
Authors: Guessous Et al.
Mol Cancer 2012;11:288
-
Saccharomyces boulardii improves intestinal cell restitution through activation of the α2β1 integrin collagen receptor.
Authors: Canonici Et al.
Hepatology 2011;6:e18427
-
Matrix stiffness modulates proliferation, chemotherapeutic response, and dormancy in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
Authors: Schrader Et al.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2011;53:1192
-
A focal adhesion protein-based mechanochemical checkpoint regulates cleft progression during branching morphogenesis.
Authors: Daley Et al.
Dev Dyn 2011;240:2069
-
β1 integrin mediates an alternative survival pathway in breast cancer cells resistant to lapa.
Authors: Huang Et al.
Breast Cancer Res 2011;13:R84
-
GABAB receptor activation protects neurons from apoptosis via IGF-1 receptor transactivation.
Authors: Tu Et al.
J Neurosci 2010;30:749
-
DNA copy number aberrations in small-cell lung cancer reveal activation of the focal adhesion pathway.
Authors: Ocak Et al.
Oncogene 2010;29:6331
-
tPA is a potent mitogen for renal interstitial fibroblasts: role of beta1 integrin/focal adhesion kinase signaling.
Authors: Hao Et al.
Am J Pathol 2010;177:1164
-
Characterization of a novel focal adhesion kinase inhibitor in human platelets.
Authors: Jones Et al.
Nat Med 2009;389:198
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Small Molecule FAQsReviews for PF 573228
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review PF 573228 and earn rewards!
Have you used PF 573228?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image