Recombinant Cynomolgus Integrin alpha 4 beta 1 Protein, CF
Recombinant Cynomolgus Integrin alpha 4 beta 1 Protein, CF Summary
Product Specifications
| Cynomolgus Monkey Integrin alpha 4
(Tyr34-Gln970)
Accession # XP_005573683.1 | HP + 2x GGGSGGGS | Acidic Tail | 6-His tag |
| Cynomolgus Monkey Integrin beta 1 (Gln21-Asp728) Accession # XP_005564991.1 | HP + 2x GGGSGGGS | Basic Tail | HA-tag |
N-terminus C-terminus
Analysis
Product Datasheets
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
10527-A4
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 250 μg/mL in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Scientific Data
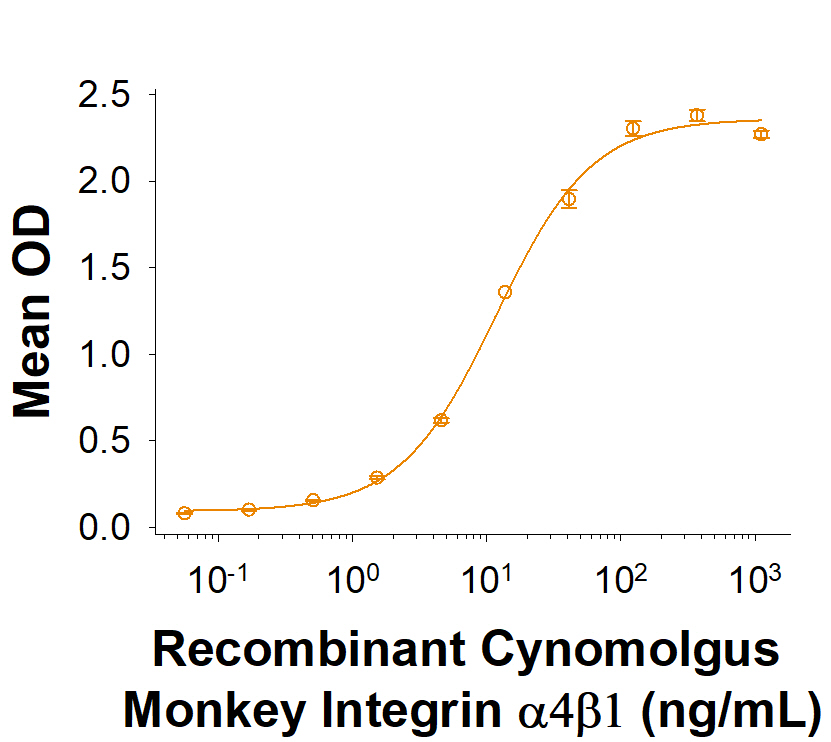 View Larger
View Larger
When Recombinant Human VCAM-1/CD106 Fc Chimera (862-VC) is immobilized at 1 µg/mL (100 µL/well), Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey Integrin alpha 4 beta 1 (Catalog # 10527-A4) binds with an ED50 of 4-40 ng/mL.
Reconstitution Calculator
Background: Integrin alpha 4 beta 1
Integrin alpha 4 beta 1, also called VLA4, is an integrin family adhesion receptor that shares the beta 1 subunit with eleven other family members and the alpha 4 subunit with integrin alpha 4 beta 7 (1-4). The non-covalent heterodimer of 150 kDa alpha 4/CD49d and 130 kDa beta 1/CD29 type I transmembrane glycoprotein subunits mediates cell adhesion to VCAM-1/CD106 on other cells and the CS-1 fragment of fibronectin in the extracellular matrix (2-4). The alpha 4 extracellular domain (ECD) contains an N-terminal beta -propeller structure, followed by domains termed thigh, calf-1 and calf-2 (1). The beta 1 ECD contains a vWFA domain, which interacts with the alpha 4 beta -propeller to form a binding domain when the dimer is in active, extended and open conformation. Each subunit has a transmembrane sequence and a short cytoplasmic tail. Within the ECD, cynomolgus alpha 4 shares 97% sequence idently with human alpha 4, while cynomolgus beta 1 shares 99.9% sequence identity with human beta 1 ECD. Five alternate splice forms of the human beta 1 cytoplasmic domain, including one antagonistic form, vary by 12 to 48 aa and show differential expression patterns (5). Leukocytes (except for neutrophils), erythroid precursors and some non-hematopoietic cells such as epicardial, endothelial and smooth muscle precursors, Schwann cells, and chorionic cells express alpha 4 beta 1 (6-10). Deletion is lethal in the mouse embryo due to faulty placentation and development of the epicardium and coronary vessels (7, 10). In the adult, alpha 4 beta 1 primarily regulates immune cell migration (11-13). Circulating leukocyte alpha 4 beta 1 is rapidly activated by inflamed endothelial cells that present VCAM-1 and chemokines such as SDF-1 (11). This activation facilitates rolling, firm adhesion, and extravasation. Interfering with leukocyte migration via the therapeutic alpha 4 beta 1antibody Natalizumab can reduce the severity of autoimmune disorders such as multiple sclerosis (12). Natalizumab can also mobilize hematopoietic precursors from the bone marrow by impeding their interaction with stromal cell VCAM-1 (8, 12). During immune cell activation, alpha 4 beta 1 can function as a costimulatory molecule (13, 14).
- Luo, B-H. et al. (2007) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 25:619.
- Takada, Y. et al. (1989) EMBO J. 8:1361.
- Argraves, W.S. et al. (1987) J. Cell Biol. 1025:1183.
- Takada, Y. et al. (2007) Genome Biol. 8:215.
- Svineng, G. et al. (1998) Biochem. J. 330:1255.
- Eshghi, S. et al. (2007) J. Cell Biol. 177:871.
- Yang, J.T. et al. (1995) Development 121:549.
- Sheppard, A.M. et al. (1994) Cell Adhes. Commun. 2:27.
- Haack, H. and R.O. Hynes (2001) Dev. Biol. 233:38.
- Grazioli, A. et al. (2006) Dev. Biol. 293:165.
- Alon, R. and K. Ley (2008) Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 20:525.
- Bauer, M. et al. (2009) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106:1920.
- Banerjee, E.R. et al. (2008) Exp. Hematol. 36:1004.
- Nguyen, K. et al. (2008) Immunity 28:810.
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsReviews for Recombinant Cynomolgus Integrin alpha 4 beta 1 Protein, CF
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Recombinant Cynomolgus Integrin alpha 4 beta 1 Protein, CF and earn rewards!
Have you used Recombinant Cynomolgus Integrin alpha 4 beta 1 Protein, CF?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image