Recombinant Human BCAT2 Protein, CF Summary
Product Specifications
Ala28-Val392
with an N-terminal Met and 6-His tag
Analysis
Product Datasheets
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
9537-BA
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution in Tris, NaCl, DTT and Glycerol. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Assay Procedure
- Assay Buffer: 50 mM Tris, 0.05% Tween-20, pH 8.0
- Recombinant Human BCAT2 (rhBCAT) (Catalog # 9537-BA)
- Recombinant Human NQO-1 (rhNQO-1) (Catalog # 7567-DH)
- Glutamate dehydrogenase (GIDH) (Sigma, Catalog # G7882), 200 U/mL sock in 50 mM Tris, 0.05% Tween-20, pH 8.0
- Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide ( beta -NAD) (Sigma, Catalog # N6522), 100 mM stock in deionized water
- Resazurin (Catalog # AR002)
- alpha -Ketoglutaric Acid (Sigma, Catalog # K2010), 1 M stock in deionized water
- L-Leucine (EMD Biosciences, Inc., Catalog # 4330), 100 mM stock in deionized water
- F16 Black Maxisorp Plate (Nunc, Catalog # 475515)
- Fluorescent Plate Reader (Model: SpectraMax Gemini EM by Molecular Devices) or equivalent
- Dilute rhBCAT2 to 0.1 µg/mL in Assay Buffer.
- Dilute alpha -Ketoglutaric Acid to 100 mM in Assay Buffer.
- Prepare Substrate Mixture containing 100 U/mL GIDH, 2 mM beta -NAD, 40 µM Resazurin, 1 mM alpha -Ketoglutaric Acid, 4 mM L-Leucine, and 4 µg/mL rhNQO-1 in Assay Buffer.
- Load 50 µL of 0.1 µg/mL rhBCAT2 in a plate, and start the reaction by adding 50 µL of Substrate Mixture. Include a Substrate Blank containing 50 µL Assay Buffer and 50 µL of Substrate Mixture.
- Read at excitation and emission wavelengths of 540 nm and 585 nm (top read), respectively, in kinetic mode for 8 minutes with a three minute lag time in kinetic mode.
- Calculate specific activity:
Specific Activity (pmol/min/µg) = | Adjusted Vmax* (RFU/min) x Conversion Factor** (pmol/RFU) |
| amount of enzyme (µg) |
*Adjusted for Substrate Blank.
**Derived using calibration standard Resorufin (Sigma, Catalog # R3257).
- rhBCAT2: 0.005 µg
- GIDH: 5 U
- beta -NAD: 1 mM
- rhNQO-1: 0.2 µg
- Resazurin: 0.02 mM
- alpha -Ketoglutaric Acid: 0.5 mM
- L-Leucine: 2 mM
Scientific Data
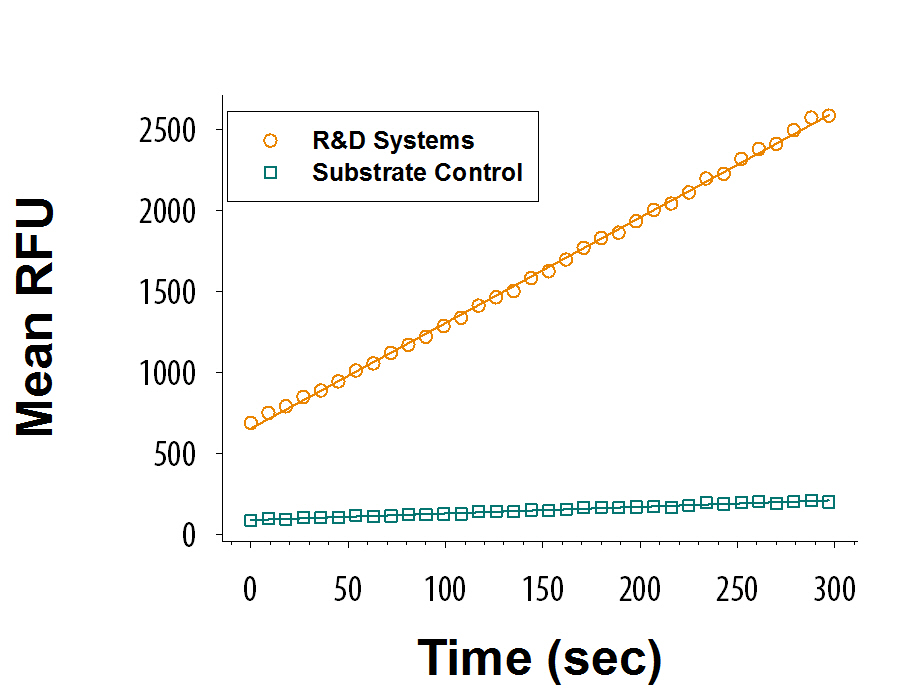 View Larger
View Larger
Recombinant Human BCAT2 (Catalog # 9537-BA) is measured by its ability to convert leucine and alpha-ketoglutarate to alpha-ketoisocaproate and glutamate.
Reconstitution Calculator
Background: BCAT2
Branched-chain-amino-acid aminotransferases (BCATs) are enzymes that catalyze the first reaction in the catabolism of the essential branched-chain amino acids leucine, isoleucine, and valine to their respective keto-acids while concurrently producing glutamate. BCATs belong to the class-IV pyridoxal-phosphate-dependent (PLP-dependent) aminotransferase family of enzymes (1). There are two BCAT isozymes in humans and mammals, a mitochondrial form known as BCATm or BCAT2 and a cytosolic form known as BCATc or BCAT1 that share 55% sequence identity. In humans and rodents, BCATc is almost exclusively present in the nervous system (2,3) while BCATm is constitutively expressed in most tissues and is generally thought to be important in body nitrogen metabolism (1,2). The 41 kDa human BCATm exists as an active homodimer and has a unique CXXC active site near the dimerization domain (4). Knockouts display decreased adiposity and obesity through alterations of leucine-dependent mTOR signaling making it a potential therapeutic target for obesity (5). BCATm can be regulated by oxidative stress, interfering with its ability to interact with protein disulfide isomerase (6). BCATm overexpression in the brain is detectable in Alzheimers disease and dementia (7,8) suggesting it plays an important role in glutamate toxicity, a key pathogenic feature of these diseases.
- Hutson, S. (2001) Prog. Nucleic. Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 70:175.
- Suryawan, A. et al. (1998) Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 68:72.
- Hall, T.R. et al. (1993) J. Biol. Chem. 268:3092.
- Yennawar, N. H. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281:39660. (BCATm)
- She, P. et al. (2007) Cell Metab. 6:181.
- El Hindy, M. et al. (2014) Antioxid. Redox Signal 20:2497.
- Ashby, E.L. et al. (2017) Neurochem. Res. 42:306.
- Hull, J. et al. (2015) J. Alzheimers Dis. 45:891.
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsReviews for Recombinant Human BCAT2 Protein, CF
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Recombinant Human BCAT2 Protein, CF and earn rewards!
Have you used Recombinant Human BCAT2 Protein, CF?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥1250 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
