Recombinant Human CD5 His-tag Avi-tag Protein, CF
Recombinant Human CD5 His-tag Avi-tag Protein, CF Summary
Product Specifications
| Human CD5 (Arg25-Asn371) Accession # P06127.2 | 6-His tag | Avi-tag |
| N-terminus | C-terminus | |
Analysis
Product Datasheets
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
AVI1636
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 500 μg/mL in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
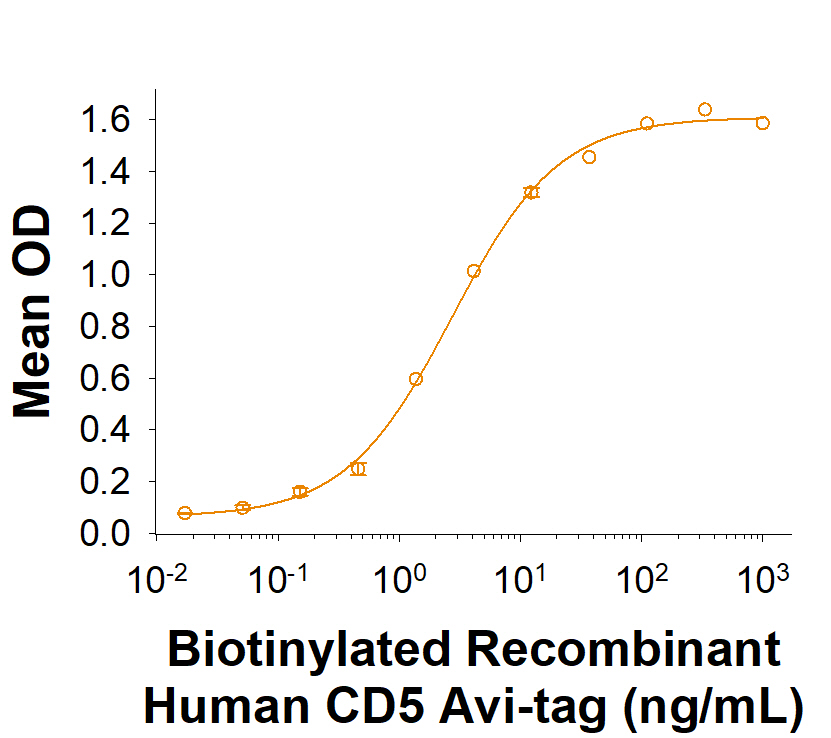
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. When Human CD5 Antibody (MAB16361) is immobilized at 0.500 µg/mL (100 µL/well), Biotinylated Recombinant Human CD5 His-tag Avi-tag Protein (Catalog # AVI1636) binds with an ED50 of 0.600-6.00 ng/mL.
 View Larger
View Larger
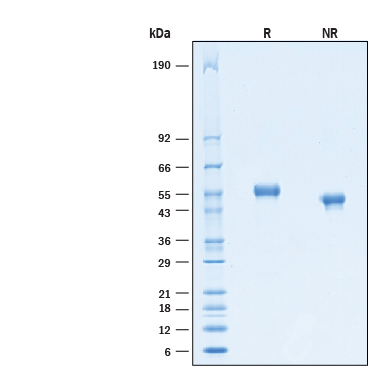
2 μg/lane of Biotinylated Recombinant Human CD5 His-tag Avi-tag Protein (Catalog # AVI1636) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at 50-59 kDa.
Reconstitution Calculator
Background: CD5
CD5, also known as Leu-1, Ly-1, and T1, is a 67 kDa transmembrane glycoprotein in the scavenger receptor superfamily (1). Mature human CD5 consists of a 348 amino acid (aa) extracellular domain (ECD) with three scavenger receptor cysteine-rich (SRCR) domains, a 30 aa transmembrane segment, and a 93 aa cytoplasmic domain (2). Within the ECD, human CD5 shares 55% aa sequence identity with mouse and rat CD5. The 52 kDa ECD can be cleaved from the cell surface and circulates in the serum (3). CD5 has been shown to interact homophilically, with CD72 on B cells, and with beta-glucan components of fungal cell walls (4‑6). CD5 expression on developing thymocytes is positively regulated by signaling through the T cell antigen receptor (TCR) and is up‑regulated on tolerized peripheral CD4+ cells (7, 8). It inhibits TCR signaling and promotes T cell nonresponsiveness and survival (8‑10). CD5 signaling inhibits the generation of regulatory T cells but promotes the development of Th17 cells (11, 12). Within the B cell lineage, CD5 is expressed on B-1a cells, anergic B cells, and IL-10 producing regulatory B cells (13‑16). Similarly to on T cells, it negatively regulates signaling through the B cell antigen receptor and supports peripheral B cell survival, anergy, and tolerance (13, 14, 16). B cells can produce an intracellularly-retained form of CD5 which lacks the signal peptide and a portion of the first SRCR domain (17). CD5 is also involved in the cellular entry of hepatitis C virus into T cells (18). Our Avi-tag Biotinylated Human CD5 His tag protein features biotinylation at a single site contained within the Avi-tag, a unique 15 amino acid peptide. Protein orientation will be uniform when bound to streptavidin-coated surface due to the precise control of biotinylation and the rest of the protein is unchanged so there is no interference in the protein's bioactivity.
- Soldevila, G. et al. (2011) Curr. Opin. Immunol. 23:310.
- Jones, N.H. et al. (1986) Nature 323:346.
- Calvo, J. et al. (1999) Tissue Antigens 54:128.
- Brown, M.H. and E. Lacey (2010) J. Immunol. 185:6068.
- Van de Velde, H. et al. (1991) Nature 351:662.
- Vera, J. et al. (2009) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 106:1506.
- Azzam, H.S. et al. (1998) J. Exp. Med. 188:2301.
- Hawiger, D. et al. (2004) Immunity 20:695.
- Tarakhovsky, A. et al. (1995) Science 269:535.
- Friedlein, G. et al. (2007) J. Immunol. 178:6821.
- Ordonez-Rueda, D. et al. (2009) Eur. J. Immunol. 39:2233.
- de Wit, J. et al. (2011) Blood 118:6107.
- Bikah, G. et al. (1996) Science 274:1906.
- Hippen, K.L. et al. (2000) J. Exp. Med. 191:883.
- Yanaba, K. et al. (2008) Immunity 28:639.
- Gary-Gouy, H. et al. (2002) Blood 100:4537.
- Renaudineau, Y. et al. (2005) Blood 106:2781.
- Sarhan, M.A. et al. (2012) J. Virol. Epub.
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsReviews for Recombinant Human CD5 His-tag Avi-tag Protein, CF
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Recombinant Human CD5 His-tag Avi-tag Protein, CF and earn rewards!
Have you used Recombinant Human CD5 His-tag Avi-tag Protein, CF?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image

