Recombinant Human FGF-23 Protein Summary
Product Specifications
Tyr25-Ile251 (Arg179Gln), with a C-terminal 6-His tag
Analysis
Product Datasheets
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
2604-FG
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in MOPS, Na2SO4, EDTA and DTT with BSA as a carrier protein. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in sterile PBS containing at least 0.1% human or bovine serum albumin. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
2604-FG/CF
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in MOPS, Na2SO4, EDTA and DTT. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in sterile PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Scientific Data
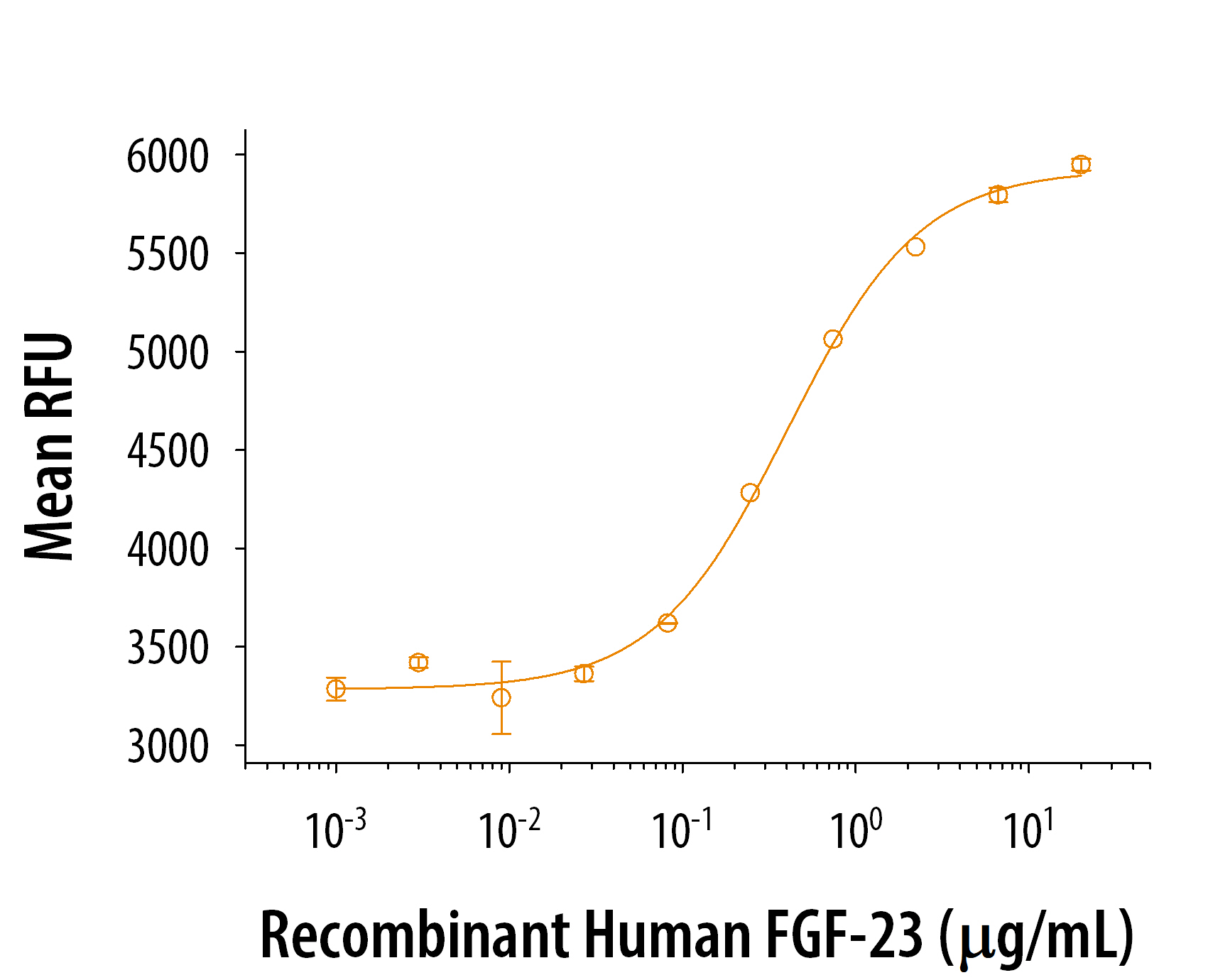 View Larger
View Larger
Reconstitution Calculator
Background: FGF-23
Fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF‑23) is a 30‑32 kDa member of the FGF family, within a subfamily that also includes FGF‑19 and FGF‑21. FGF proteins contain a 120 amino acid (aa) core FGF domain that exhibits a beta ‑trefoil structure (1, 2). FGF‑19 subfamily members are highly diffusible molecules owing to their poor ECM/heparin sulfate binding and plasma‑stabilizing intramolecular folds (2‑4). Mature human FGF‑23 contains an atypical (very low affinity) heparin binding site (aa 134‑162), a proteolytic cleavage site (Arg179‑Ser180), and multiple O‑linked glycosylation sites with Thr178 being of particular importance (4‑7). O‑linked glycosylation at Thr178 blocks the cleavage of FGF‑23, thereby preventing loss of FGF‑23 activity (7, 8). Mature human FGF‑23 shows 72% aa identity to mouse FGF‑23 and is active on mouse cells (6). FGF‑23 exerts its effects through a ternary complex that includes Klotho and an FGF receptor (FGF R4 or the "c" isoforms of FGF R1 or FGF R3). Klotho has a restricted distribution that limits FGF‑23 activity (9‑11). FGF‑23 is produced by osteocytes and osteoblasts in response to high circulating phosphate levels, elevated parathyroid hormone, and circulatory volume loading. It functions as an endocrine phosphatonin by suppressing circulating phosphate levels (12). FGF‑23 interaction with renal proximal tubular epithelium decreases the renal resorption of phosphate by down‑regulating phosphate transporters and by suppressing vitamin D production. It also decreases the intestinal absorption of phosphate (13).
- Mohammadi, M. et al. (2005) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 16:107.
- Fukumoto, S. (2007) Endocr. J. Sep 14; [Epub ahead of print].
- Goetz, R. et al. (2007) Mol. Cell. Biol. 27:3417.
- Harmer, N.J. et al. (2004) Biochemistry 43:629.
- Yamashita, T. et al. (2000) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 277:494.
- Shimada, T. et al. (2001) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:6500.
- Frishberg, Y. et al. (2007) J. Bone Miner. Res. 22:235.
- Kato, K. et al. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281:18370.
- Zhang, X. et al. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281:15694.
- Urakawa, I. et al. (2006) Nature 444:770.
- Kurosu, H. et al. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281:6120.
- Razzaque, M.S. and B. Lanske (2007) J. Endocrinol. 194:1.
- Kurosu, H. et. al. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282:26687.
Citations for Recombinant Human FGF-23 Protein
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
18
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Dynamic Single Cell Transcriptomics Defines Kidney FGF23/KL Bioactivity and Novel Segment-Specific Inflammatory Targets
Authors: Agoro, R;Myslinski, J;Marambio, YG;Janosevic, D;Jennings, KN;Liu, S;Hibbard, LM;Fang, F;Ni, P;Noonan, ML;Solis, E;Chu, X;Wang, Y;Dagher, PC;Liu, Y;Wan, J;Hato, T;White, KE;
bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: In vivo assay -
ERR?-inducible FGF23 promotes alcoholic liver injury through enhancing CYP2E1 mediated hepatic oxidative stress
Authors: Jung, YS;Radhakrishnan, K;Hammad, S;Müller, S;Müller, J;Noh, JR;Kim, J;Lee, IK;Cho, SJ;Kim, DK;Kim, YH;Lee, CH;Dooley, S;Choi, HS;
Redox biology
Species: Transgenic Mouse, Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: In vivo assay -
Mutations in an unrecognized internal NPT2A PDZ motif disrupt phosphate transport causing congenital hypophosphatemia
Authors: WB Sneddon, PA Friedman, T Mamonova
bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology, 2023-03-07;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
RGS14 regulates hormone-sensitive NPT2A-mediated renal phosphate uptake via binding to the NHERF1 scaffolding protein
Authors: PA Friedman, WB Sneddon, T Mamonova, C Montanez-M, S Ramineni, NH Harbin, KE Squires, JV Gefter, CE Magyar, DR Emlet, JR Hepler
The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2022-03-17;0(0):101836.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Bone marrow sinusoidal endothelium controls terminal erythroid differentiation and reticulocyte maturation
Authors: J Heil, V Olsavszky, K Busch, K Klapproth, C de la Torr, C Sticht, K Sandorski, J Hoffmann, H Schönhaber, J Zierow, M Winkler, CD Schmid, T Staniczek, DE Daniels, J Frayne, G Metzgeroth, D Nowak, S Schneider, M Neumaier, V Weyer, C Groden, HJ Gröne, K Richter, C Mogler, MM Taketo, K Schledzews, C Géraud, S Goerdt, PS Koch
Nature Communications, 2021-11-29;12(1):6963.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Structure-function relationships of the soluble form of the antiaging protein Klotho have therapeutic implications for managing kidney disease
Authors: X Zhong, S Jagarlapud, Y Weng, M Ly, JC Rouse, K McClure, T Ishino, Y Zhang, E Sousa, J Cohen, B Tzvetkova, K Cote, JJ Scarcelli, K Johnson, J Palandra, JR Apgar, S Yaddanapud, RG Villalobos, AC Opsahl, K Lam, Q Yao, W Duan, A Sievers, J Zhou, D Ferguson, A D'Antona, R Zollner, HL Zhu, R Kriz, L Lin, V Clerin
J. Biol. Chem., 2020-01-31;0(0):.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Cell Culture -
FGF23-Mediated Activation of Local RAAS Promotes Cardiac Hypertrophy and Fibrosis
Authors: I Böckmann, J Lischka, B Richter, J Deppe, A Rahn, DC Fischer, J Heineke, D Haffner, M Leifheit-N
Int J Mol Sci, 2019-09-18;20(18):.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Prolonged exposure to 1,25(OH)2D3 and high ionized calcium induces FGF-23 production in intestinal epithelium-like Caco-2 monolayer: A local negative feedback for preventing excessive calcium transport
Authors: M Rodrat, K Wongdee, N Panupinthu, J Thongbunch, J Teerapornp, N Krishnamra, N Charoenpha
Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 2018-01-06;640(0):10-16.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Fibroblast growth factor 23 weakens chemotaxis of human blood neutrophils in microfluidic devices
Authors: K Yang, H Peretz-Sor, J Wu, L Zhu, X Cui, M Zhang, C Rigatto, Y Liu, F Lin
Sci Rep, 2017-06-08;7(1):3100.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
?-Klotho expression determines nitric oxide synthesis in response to FGF-23 in human aortic endothelial cells
Authors: CP Chung, YC Chang, Y Ding, K Lim, Q Liu, L Zhu, W Zhang, TS Lu, G Molostvov, D Zehnder, LL Hsiao
PLoS ONE, 2017-05-02;12(5):e0176817.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Convergent Signaling Pathways Regulate Parathyroid Hormone and Fibroblast Growth Factor-23 Action on NPT2A-mediated Phosphate Transport
J Biol Chem, 2016-07-18;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Regulation of CYP27B1 mRNA Expression in Primary Human Osteoblasts
Authors: K van der Me, HW van Essen, FW Bloemers, EA Schulten, P Lips, N Bravenboer
Calcif Tissue Int, 2016-03-25;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Direct, acute effects of Klotho and FGF23 on vascular smooth muscle and endothelium.
Authors: Six I, Okazaki H, Gross P, Cagnard J, Boudot C, Maizel J, Drueke T, Massy Z
PLoS ONE, 2014-04-02;9(4):e93423.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
FGF-23 is a negative regulator of prenatal and postnatal erythropoiesis.
Authors: Coe, Lindsay, Madathil, Sangeeth, Casu, Carla, Lanske, Beate, Rivella, Stefano, Sitara, Despina
J Biol Chem, 2014-02-07;289(14):9795-810.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo, Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay, In Vivo -
Rational design of a fibroblast growth factor 21-based clinical candidate, LY2405319.
Authors: Kharitonenkov, Alexei, Beals, John M, Micanovic, Radmila, Strifler, Beth A, Rathnachalam, Radhakri, Wroblewski, Victor J, Li, Shun, Koester, Anja, Ford, Amy M, Coskun, Tamer, Dunbar, James D, Cheng, Christin, Frye, Christop, Bumol, Thomas F, Moller, David E
PLoS ONE, 2013-03-11;8(3):e58575.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Antibody-mediated activation of FGFR1 induces FGF23 production and hypophosphatemia.
Authors: Wu, Ai-Luen, Feng, Bo, Chen, Mark Z, Kolumam, Ganesh, Zavala-Solorio, Jose, Wyatt, Shelby K, Gandham, Vineela, Carano, Richard, Sonoda, Junichir
PLoS ONE, 2013-02-22;8(2):e57322.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Circulating alphaKlotho influences phosphate handling by controlling FGF23 production.
Authors: Smith R
J. Clin. Invest., 2012-11-26;122(12):4710-5.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Altered splicing of FGFR1 is associated with high tumor grade and stage and leads to increased sensitivity to FGF1 in bladder cancer.
Authors: Tomlinson DC, Knowles MA
Am. J. Pathol., 2010-10-01;177(5):2379-86.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsReviews for Recombinant Human FGF-23 Protein
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Recombinant Human FGF-23 Protein and earn rewards!
Have you used Recombinant Human FGF-23 Protein?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
