Recombinant Human ST2/IL-33R Fc Chimera Avi-tag Protein, CF
Recombinant Human ST2/IL-33R Fc Chimera Avi-tag Protein, CF Summary
Learn more about Avi-tag Biotinylated ProteinsProduct Specifications
When Recombinant Human IL-33 (Catalog # 3625-IL) is immobilized at 2 µg/mL (100 µL/well), Biotinylated Recombinant Human ST2/IL-33R Fc Chimera Avi-tag (Catalog # AVI11066) binds with an ED50 of 90.0-720 ng/mL.
| Human ST-2 (Lys19-Ser328) Accession # Q01638.4 | IEGRMD | Human IgG1 (Pro100-Lys330) | Avi-tag |
| N-terminus | C-terminus | ||
Analysis
Product Datasheets
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
AVI11066
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 500 μg/mL in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Scientific Data
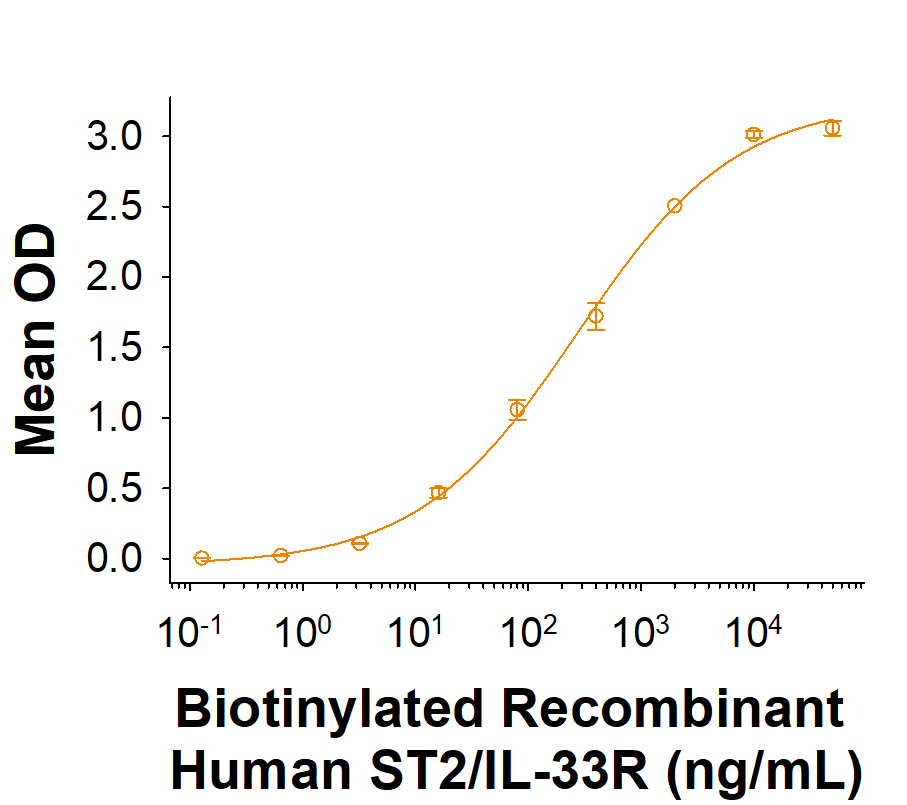 View Larger
View Larger
When Recombinant Human IL-33 (3625-IL) is immobilized at 2 µg/mL (100 µL/well), Biotinylated Recombinant Human ST2/IL-33R Fc Chimera Avi-tag Protein (Catalog # AVI11066) binds with an ED50 of 90.0-720 ng/mL.
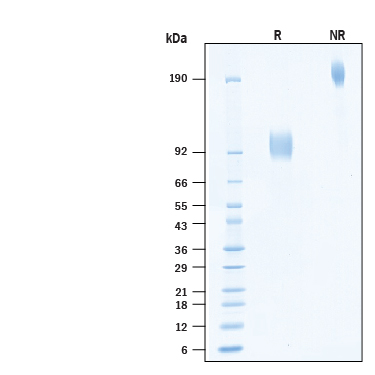 View Larger
View Larger
2 μg/lane of Biotinylated Recombinant Human ST2/IL-33R Fc Chimera Avi-tag Protein (Catalog # AVI11066) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at 90-105 kDa and 180-210 kDa, respectively.
Reconstitution Calculator
Background: ST2/IL-33R
Serum stimulation-2 (ST2), also known as Interleukin receptor like-1 (IL1RL1) and T1, is a member of the Interleukin-1 receptor superfamily family glycoprotein that contributes to Th2 immune responses (1, 2). Human ST2 consists of an extracellular domain (ECD) with three Ig-like domains, a transmembrane segment, and a cytoplasmic domain with an intracellular Toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domain (3, 4). Within the ECD, human ST2 shares 68% and 64% amino acid sequence identity with mouse and rat ST2, respectively. Alternate splicing of human ST2 generates a soluble isoform that lacks the transmembrane and cytoplasmic regions as well as an isoform that additionally lacks the third Ig‑like domain (4). ST2 is expressed on the surface of mast cells, activated Th2 cells, macrophages, and cardiac myocytes (5-8). It binds IL33, a cytokine that is upregulated by inflammation or mechanical strain in smooth muscle cells, airway epithelia, keratinocytes, and cardiac fibroblasts (5, 9). IL-33 binding induces the association of ST2 with IL1R AcP, a shared signaling subunit that also associates with IL1RI and IL1R rp2 (1, 10, 11). In macrophages, ST2 interferes with signaling from IL1RI and TLR4 by sequestering the adaptor proteins MyD88 and Mal (7). In addition to its role in promoting mast cell and Th2 dependent inflammation, ST2 activation enhances antigen induced hypernociception and protects from atherosclerosis and cardiac hypertrophy (5, 12-14). The soluble ST2 isoform is released by activated Th2 cells and strained cardiac myocytes and is elevated in the serum in allergic asthma (6, 8, 15). Soluble ST2 functions as a decoy receptor that blocks IL33 signaling by full-length ST2 (10, 13‑15). Our Avi-tag Biotinylated ST2 features biotinylation at a single site contained within the Avi-tag, a unique 15 amino acid peptide. Protein orientation will be uniform when bound to streptavidin-coated surface due to the precise control of biotinylation and the rest of the protein is unchanged so there is no interference in the protein's bioactivity.
- Barksby, H.E. et al. (2007) Clin. Exp. Immunol. 149:217.
- Gadina, M. and C.A. Jefferies (2007) Science STKE 2007:pe31.
- Tominaga, S. et al. (1992) Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1171:215.
- Li, H. et al. (2000) Genomics 67:284.
- Schmitz, J. et al. (2005) Immunity 23:479.
- Lecart, S. et al. (2002) Eur. J. Immunol. 32:2979.
- Brint, E.K. et al. (2004) Nat. Immunol. 5:373.
- Weinberg, E.O. et al. (2002) Circulation 106:2961.
- Sanada S. et al. (2007) J. Clin. Invest. 117:1538.
- Palmer, G. et al. (2008) Cytokine 42:358.
- Chackerian, A.A. et al. (2007) J. Immunol. 179:2551.
- Allakhverdi, Z. et al. (2007) J. Immunol. 179:2051.
- Verri, Jr. W.A. et al. (2008) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 105:2723.
- Miller, A.M. et al. (2008) J. Exp. Med. 205:339.
- Hayakawa, H. et al. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282:26369.
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsReviews for Recombinant Human ST2/IL-33R Fc Chimera Avi-tag Protein, CF
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Recombinant Human ST2/IL-33R Fc Chimera Avi-tag Protein, CF and earn rewards!
Have you used Recombinant Human ST2/IL-33R Fc Chimera Avi-tag Protein, CF?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥1250 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image



