Recombinant Mouse Sonic Hedgehog/Shh, N-Terminus Protein
Recombinant Mouse Sonic Hedgehog/Shh, N-Terminus Protein Summary
Product Specifications
Cys25-Gly198, with a C-terminal 6-His tag
Analysis
Product Datasheets
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
461-SH
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS, Trehalose and with BSA as a carrier protein. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in sterile PBS containing at least 0.1% human or bovine serum albumin. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
461-SH/CF
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in sterile PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Scientific Data
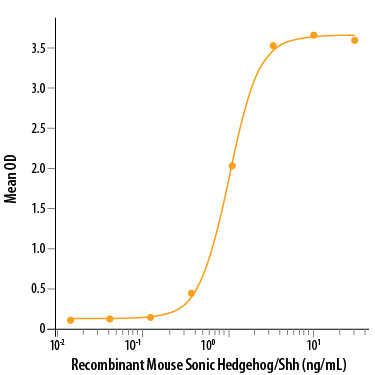 View Larger
View Larger
Recombinant Mouse Sonic Hedgehog/Shh, N-Terminus (Catalog # 461-SH) induces alkaline phosphatase production by the C3H10T1/2 mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line. The ED50 for this effect is 0.6-3 μg/mL.
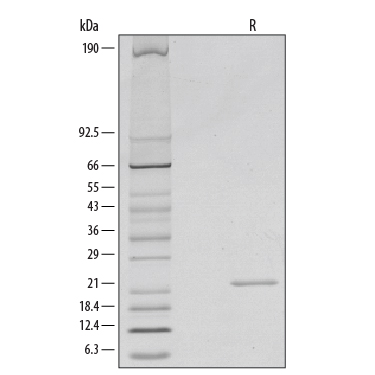 View Larger
View Larger
1 μg/lane of Recombinant Mouse Sonic Hedgehog/Shh, N-Terminus was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) conditions and visualized by silver staining, showing a single band at 23 kDa.
Reconstitution Calculator
Background: Sonic Hedgehog/Shh
Sonic Hedgehog (Shh) is expressed in embryonic tissues that are critical for the patterning of the developing central nervous system, somite, and limb. It is also involved in whisker, hair, foregut, tooth, and bone development. Shh regulates neural and hematopoietic stem cell fate and is important for thymocyte differentiation and proliferation as well as T cell determination. In adult tissue Shh is associated with cancer development and tissue remodeling following injury (1-3). Mouse Shh encodes a 437 amino acid (aa) precursor protein that is autocatalytically processed to yield a non-glycosylated 19 kDa N-terminal fragment (Shh-N) and a glycosylated 25 kDa C-terminal protein (Shh-C) (4). Shh-C, which is responsible for the intramolecular processing of Shh, is rapidly degraded following Shh proteolysis (5). Shh-N is highly conserved, sharing >98% aa identity between mouse, human, rat, canine, porcine, and chicken Shh-N. Shh-N can be palmitoylated at its
N-terminal cysteine and modified by cholesterol addition at its C-terminus (6). These modifications contribute to the membrane tethering of Shh as well as its assembly into various sized multimers (6-9). Lipid modification and multimerization greatly increase Shh-N receptor binding affinity and signaling potency (5, 6, 8, 9). Monomeric and multimeric Shh can be released from the plasma membrane by the cooperative action of DISP1, SCUBE2, and TACE/ADAM17 (10-12). Modifications also extend the effective range of Shh functionality and are required for the development of protein gradients important in tissue morphogenesis (9, 13). Canonical signaling of Shh is mediated by a multicomponent receptor complex that includes Patched (PTCH1, PTCH2) and Smoothened (SMO) (14). The binding of Shh to PTCH releases the basal repression of SMO by PTCH. Shh activity can also be regulated through interactions with heparin, glypicans, and membrane-associated Hip (hedgehog interacting protein) (13, 15, 16).
- Briscoe, J. and P.P. Therond (2013) Mol. Cell. Biol. 14:416.
- Aviles, E.C. et al. (2013) Front. Cell. Neurosci. 7:86.
- Xie, J. et al. (2013) OncoTargets Ther. 6:1425.
- Echelard, Y. et al. (1993) Cell 75:1417.
- Zeng, X. et al. (2001) Nature 411:716.
- Feng, J. et al. (2004) Development 131:4357.
- Goetz, J.A. et al. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281:4087.
- Pepinsky, R.B. et al. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273:14037.
- Chen, M.-H. et al. (2004) Genes Dev. 18:641.
- Etheridge, L.A. et al. (2010) Development 137:133.
- Jakobs, P. et al. (2014) J. Cell Sci. 127:1726.
- Dierker, T. et al. (2009) J. Biol. Chem. 284:8013.
- Lewis, P.M. et al. (2001) Cell 105:599.
- Carpenter, D. et al. (1998) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95:13630.
- Filmus, J. and M. Capurro (2014) Matrix Biol. 35:248.
- Chuang, P.-T. and A.P. McMahon (1999) Nature 397:617.
Citations for Recombinant Mouse Sonic Hedgehog/Shh, N-Terminus Protein
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
36
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Effect of Sonic Hedgehog on the Regeneration of Epidermal Texture Patterns
Authors: K Takaya, N Aramaki-Ha, S Sakai, K Okabe, K Kishi
Biomedicines, 2022-12-01;10(12):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: In Vivo -
Forebrain Shh overexpression improves cognitive function and locomotor hyperactivity in an aneuploid mouse model of Down syndrome and its euploid littermates
Authors: FJ Gao, D Klinedinst, FX Fernandez, B Cheng, A Savonenko, B Devenney, Y Li, D Wu, MG Pomper, RH Reeves
Acta neuropathologica communications, 2021-08-16;9(1):137.
Applications: MALDI-TOF, Western Blot -
BMI1 regulates multiple myeloma-associated macrophage's pro-myeloma functions
Authors: D Zhang, J Huang, F Wang, H Ding, Y Cui, Y Yang, J Xu, H Luo, Y Gao, L Pan, Y Wu, Y Gong, L Xie, Z Liu, Y Qu, L Zhang, W Liu, W Zhang, S Zhao, Q Yi, T Niu, Y Zheng
Cell Death & Disease, 2021-05-15;12(5):495.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
PDGFRA in vascular adventitial MSCs promotes neointima formation in arteriovenous fistula in chronic kidney disease
Authors: K Song, Y Qing, Q Guo, EK Peden, C Chen, WE Mitch, L Truong, J Cheng
JCI Insight, 2020-11-05;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Virus
Applications: Bioassay -
SMO-M2 mutation does not support cell-autonomous Hedgehog activity in cerebellar granule cell precursors
Authors: M Petroni, M Sahùn Ronc, V Ramponi, F Fabretti, V Nicolis Di, M Moretti, V Alfano, A Corsi, S De Panfili, M Giubettini, S Di Giulio, C Capalbo, F Belardinil, A Coppa, F Sardina, V Colicchia, F Pedretti, P Infante, B Cardinali, A Tessitore, G Canettieri, E De Smaele, G Giannini
Sci Rep, 2019-12-23;9(1):19623.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Hedgehog signaling promotes tumor-associated macrophage polarization to suppress intratumoral CD8+ T cell recruitment
Authors: AJ Petty, A Li, X Wang, R Dai, B Heyman, D Hsu, X Huang, Y Yang
J. Clin. Invest., 2019-12-02;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Cell Culture -
Reprogramming of Fibroblasts to Oligodendrocyte Progenitor-like Cells Using CRISPR/Cas9-Based Synthetic Transcription Factors
Authors: M Matjusaiti, LJ Wagstaff, A Martella, B Baranowski, C Blin, S Gogolok, A Williams, SM Pollard
Stem Cell Reports, 2019-11-07;13(6):1053-1067.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Cell Culture -
Ciliary IFT80 regulates dental pulp stem cells differentiation by FGF/FGFR1 and Hh/BMP2 signaling
Authors: X Yuan, M Liu, X Cao, S Yang
Int. J. Biol. Sci., 2019-08-06;15(10):2087-2099.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
High expression of Sonic hedgehog in allergic airway epithelia contributes to goblet cell metaplasia
Authors: C Xu, C Zou, M Hussain, W Shi, Y Shao, Z Jiang, X Wu, M Lu, J Wu, Q Xie, Y Ke, F Long, L Tang, X Wu
Mucosal Immunol, 2018-06-04;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: In Vivo -
Directed transdifferentiation of M�ller glial cells to photoreceptors using the sonic hedgehog signaling pathway agonist purmorphamine
Authors: D Gu, S Wang, S Zhang, P Zhang, G Zhou
Mol Med Rep, 2017-09-28;0(0):.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
The transcription factor Gli3 promotes B cell development in fetal liver through repression of Shh
Authors: A Solanki, CI Lau, JI Saldaña, S Ross, T Crompton
J. Exp. Med., 2017-05-22;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Bioassay -
Deficiency of NOX1 or NOX4 Prevents Liver Inflammation and Fibrosis in Mice through Inhibition of Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation.
Authors: Lan T, Kisseleva T, Brenner D
PLoS ONE, 2015-07-29;10(7):e0129743.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Modulation of Ciliary Phosphoinositide Content Regulates Trafficking and Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Output.
Authors: Chavez M, Ena S, Van Sande J, de Kerchove d'Exaerde A, Schurmans S, Schiffmann S
Dev Cell, 2015-07-16;34(3):338-50.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Deletion of IFT80 Impairs Epiphyseal and Articular Cartilage Formation Due to Disruption of Chondrocyte Differentiation.
Authors: Yuan X, Yang S
PLoS ONE, 2015-06-22;10(6):e0130618.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
TGFbeta signaling in myeloid cells regulates mammary carcinoma cell invasion through fibroblast interactions.
Authors: Shaw A, Pickup M, Chytil A, Aakre M, Owens P, Moses H, Novitskiy S
PLoS ONE, 2015-01-28;10(1):e0117908.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Generation of rat-induced pluripotent stem cells from a new model of metabolic syndrome.
Authors: Takenaka-Ninagawa, Nana, Kawabata, Yuka, Watanabe, Shogo, Nagata, Kohzo, Torihashi, Shigeko
PLoS ONE, 2014-08-11;9(8):e104462.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
The fate of the primary cilium during myofibroblast transition.
Authors: Rozycki M, Lodyga M, Lam J, Miranda M, Fatyol K, Speight P, Kapus A
Mol Biol Cell, 2014-01-08;25(5):643-57.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
A modular gain-of-function approach to generate cortical interneuron subtypes from ES cells.
Authors: Au E, Ahmed T, Karayannis T, Biswas S, Gan L, Fishell G
Neuron, 2013-12-04;80(5):1145-58.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
The acid-secreting parietal cell as an endocrine source of Sonic Hedgehog during gastric repair.
Authors: Engevik A, Feng R, Yang L, Zavros Y
Endocrinology, 2013-10-03;154(12):4627-39.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
-
MicroRNA-17-92 cluster mediates the proliferation and survival of neural progenitor cells after stroke.
Authors: Liu, Xian Shu, Chopp, Michael, Wang, Xin Li, Zhang, Li, Hozeska-Solgot, Ann, Tang, Tao, Kassis, Haifa, Zhang, Rui Lan, Chen, Charles, Xu, Jennifer, Zhang, Zheng Ga
J Biol Chem, 2013-03-19;288(18):12478-88.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: In Vivo -
Loss of the transcription factor GLI1 identifies a signaling network in the tumor microenvironment mediating KRAS oncogene-induced transformation.
Authors: Mills, Lisa D, Zhang, Yaqing, Marler, Ronald J, Herreros-Villanueva, Marta, Zhang, Lizhi, Almada, Luciana, Couch, Fergus, Wetmore, Cynthia, Pasca di Magliano, Marina, Fernandez-Zapico, Martin E
J Biol Chem, 2013-03-12;288(17):11786-94.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
Applications: Bioassay -
Sonic hedgehog signaling is decoded by calcium spike activity in the developing spinal cord.
Authors: Belgacem YH, Borodinsky LN
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2011-02-28;108(11):4482-7.
Species: Xenopus
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Bioassay -
Notch and Wnt signaling mediated rod photoreceptor regeneration by Muller cells in adult mammalian retina.
Authors: Del Debbio CB, Balasubramanian S, Parameswaran S, Chaudhuri A, Qiu F, Ahmad I
PLoS ONE, 2010-08-26;5(8):e12425.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: In Vivo -
Establishment and characterization of immortalized Gli-null mouse embryonic fibroblast cell lines.
Authors: Lipinski RJ, Bijlsma MF, Gipp JJ, Podhaizer DJ, Bushman W
BMC Cell Biol., 2008-09-13;9(0):49.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Sonic hedgehog promotes stem-cell potential of Muller glia in the mammalian retina.
Authors: Wan J, Zheng H, Xiao HL, She ZJ, Zhou GM
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2007-09-10;363(2):347-54.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: In Vivo, Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay, In Vivo -
Differentiation of ES cells into cerebellar neurons.
Authors: Salero E, Hatten ME
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2007-02-09;104(8):2997-3002.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Regulation of cavernous nerve injury-induced apoptosis by sonic hedgehog.
Authors: Podlasek CA, Meroz CL, Tang Y, McKenna KE, McVary KT
Biol. Reprod., 2006-09-20;76(1):19-28.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: In Vivo -
An early role for sonic hedgehog from foregut endoderm in jaw development: ensuring neural crest cell survival.
Authors: Brito JM, Teillet MA, Le Douarin NM
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2006-07-25;103(31):11607-12.
Species: Avian - Quail, Chicken
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Bioassay -
Expression of the short stature homeobox gene Shox is restricted by proximal and distal signals in chick limb buds and affects the length of skeletal elements.
Authors: Tiecke E, Bangs F, Blaschke R, Farrell ER, Rappold G, Tickle C
Dev. Biol., 2006-07-12;298(2):585-96.
Species: Chicken
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: In Vivo -
Embryonic stem cell-derived neuron models of Parkinson's disease exhibit delayed neuronal death.
Authors: Yamashita H, Nakamura T, Takahashi T, Nagano Y, Hiji M, Hirabayashi T, Amano T, Yagi T, Sakai N, Kohriyama T, Matsumoto M
J. Neurochem., 2006-07-01;98(1):45-56.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Multipotentiality, homing properties, and pyramidal neurogenesis of CNS-derived LeX(ssea-1)+/CXCR4+ stem cells.
Authors: Corti S, Locatelli F, Papadimitriou D, Donadoni C, Del Bo R, Fortunato F, Strazzer S, Salani S, Bresolin N, Comi GP
FASEB J., 2005-09-08;19(13):1860-2.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Shh and Fgf8 act synergistically to drive cartilage outgrowth during cranial development.
Authors: Abzhanov A, Tabin CJ
Dev. Biol., 2004-09-01;273(1):134-48.
Species: Chicken
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Bioassay -
Derivation of midbrain dopamine neurons from human embryonic stem cells.
Authors: Perrier AL, Tabar V, Barberi T, Rubio ME, Bruses J, Topf N, Harrison NL, Studer L
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2004-08-13;101(34):12543-8.
Species: Human, Primate - Macaca mulatta (Rhesus Macaque)
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
FGF8 dose-dependent regulation of embryonic submandibular salivary gland morphogenesis.
Authors: Jaskoll T, Witcher D, Toreno L, Bringas P, Moon AM, Melnick M
Dev. Biol., 2004-04-15;268(2):457-69.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Wnt regulation of progenitor maturation in the cortex depends on Shh or fibroblast growth factor 2.
Authors: Viti J, Gulacsi A, Lillien L
J. Neurosci., 2003-07-02;23(13):5919-27.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Bioassay -
Cyclopamine and jervine in embryonic rat tongue cultures demonstrate a role for Shh signaling in taste papilla development and patterning: fungiform papillae double in number and form in novel locations in dorsal lingual epithelium.
Authors: Mistretta CM, Liu HX, Gaffield W, MacCallum DK
Dev. Biol., 2003-02-01;254(1):1-18.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay
FAQs
-
What is the difference between Recombinant Mouse Sonic Hedgehog Catalog # 464-SH and Catalog # 461-SH?
Recombinant Mouse Sonic Hedgehog, Catalog # 464-SH, possesses a N-terminal mutation that increases its potency in bioassay tests. The amino acid sequence is Cys25-Gly198 (Cys25Ile-Ile), accession number Q62226. The Cys25Ile-Ile mutation was created to match a publication that describes enhanced activity with these modifications: "http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11284692". Catalog # 461-SH does not possess this mutation.
Reviews for Recombinant Mouse Sonic Hedgehog/Shh, N-Terminus Protein
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Recombinant Mouse Sonic Hedgehog/Shh, N-Terminus Protein and earn rewards!
Have you used Recombinant Mouse Sonic Hedgehog/Shh, N-Terminus Protein?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image


