Recombinant Porcine ACE-2 His-tag Protein, CF
View Products
Recombinant Porcine ACE-2 His-tag Protein, CF Summary
Product Specifications
Gln18-Thr740
with a C-terminal 6-His tag
Analysis
Product Datasheets
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
10545-ZN
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution in Tris, NaCl, ZnCl2 and Glycerol. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
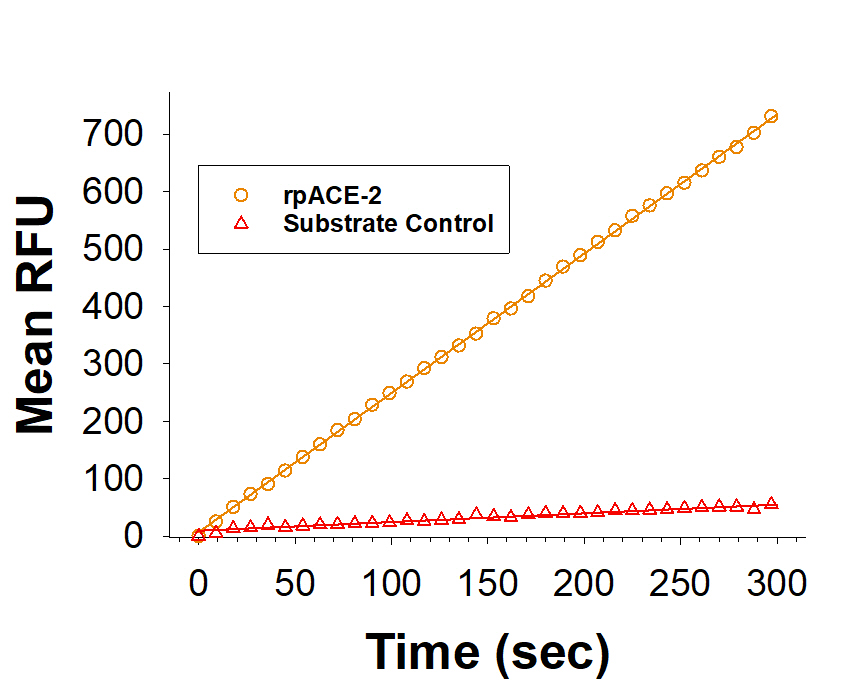
Assay Procedure
- Assay Buffer: 50 mM Tris, 1 M NaCl, pH 7.5
- Recombinant Porcine ACE-2 (rpACE-2) (Catalog # 10545-ZN)
- Substrate: Mca-Tyr-Val-Ala-Asp-Ala-Pro-Lys(Dnp)-OH (Catalog # ES007), 2 mM stock in DMSO
- F16 Black Maxisorp Plate (Nunc, Catalog # 475515)
- Plate Reader (Model: SpectraMax Gemini EM by Molecular Devices) or equivalent
- Dilute rpACE-2 to 5 µg/mL in Assay Buffer.
- Dilute Substrate to 80 µM in Assay Buffer.
- Load into a plate 50 µL of 5 µg/mL rpACE-2, and start the reaction by adding 50 µL of 80 µM Substrate. Include a Substrate Blank containing 50 µL of Assay Buffer and 50 µL of 80 µM Substrate.
- Read at excitation and emission wavelengths of 320 nm and 405 nm (top read), respectively in kinetic mode for 5 minutes.
- Calculate specific activity:
Specific Activity (pmol/min/µg) = | Adjusted Vmax* (RFU/min) x Conversion Factor** (pmol/RFU) |
| amount of enzyme (µg) |
*Adjusted for Substrate Blank
**Derived using calibration standard MCA-Pro-Leu-OH (Bachem, Catalog # M-1975). Per Well:
- rpACE-2: 0.25 µg
- Substrate: 40 µM
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
 View Larger
View Larger
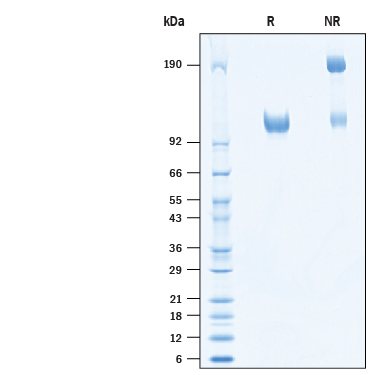
2 μg/lane of Recombinant Porcine ACE-2 His-tag (10545-ZN) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at ~111 kDa under reducing conditions.
Reconstitution Calculator
Background: ACE-2
Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme (ACE-2), also called ACEH (ACE homologue), is a dimeric, zinc-dependent metalloprotease of the ACE family that also includes somatic and germinal ACE (1, 2). ACE-2 mRNA is found at high levels in heart, testis, and kidney and at lower levels in a wide variety of tissues (1, 3). ACE-2 is the SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV2 Spike protein receptor in vivo (4-6), functions catalytically as a carboxypeptidase to cleave several substrates including angiotensins I and II, and acts as a partner for B0AT1-family amino acid transporters (1, 2). Through these functions, ACE-2 has been shown to be involved in several diseases including SARS, COVID19, acute lung injury (4, 7), heart disease (8), liver and lung fibrosis (9), inflammatory lung disease (10), and cardiopulmonary disease (11). Full length ACE-2 protein includes an extracellular region composed of a single N-terminal peptidase domain and C-terminal collectrin-like domain (CLD), a transmembrane domain, and a short cytoplasmic tail (12). The N-terminal peptidase region is required for binding to SARS-CoV and SARSCoV2 spike proteins, while the CLD contains a region that promotes dimerization and association with amino acid transporters (2). The peptidase domain contains a long deep cleft that undergoes a large hinge-bending movement at substrate and inhibitor binding (12). Classical ACE inhibitors such as captopril and lisinopril do not inhibit ACE-2 activity and inhibitors of ACE-2 do not inhibit ACE activity (13). Porcine ACE-2 shares about 79% amino acid identity with human ACE-2.
- Kuba, K. et al. (2010) Pharmacol. Ther. 128:119.
- Yan, et al. (2020) Science 367:1444.
- Tipnis, S.R. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275:33238.
- Kuba, K. et al. (2005) Nature Med. 11:875.
- Hoffman, M. et al. (2020) Cell.181:1.
- Wrapp, et al. (2020) Science 367:1260.
- Imai, Y. et al. (2005) Nature 436:112.
- Huang, L. et al. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278:15532.
- Schrom, E. et al. (2017) Mol. Therapy Nuc. Acid 7:350.
- Jia, H. et al. (2016) Shock. 46:239.
- Cole-Jeffrey, C.T. et al. (2015) J. Cadiovasc. Pharmacol. 66:540.
- Towler, P. et al. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279:17996.
- Crackower, M.A. et al. (2002) Nature 417:822.
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsReviews for Recombinant Porcine ACE-2 His-tag Protein, CF
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Recombinant Porcine ACE-2 His-tag Protein, CF and earn rewards!
Have you used Recombinant Porcine ACE-2 His-tag Protein, CF?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥1250 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image


