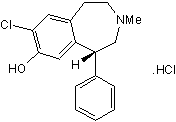
SCH 23390 hydrochloride
Chemical Name: (R)-(+)-7-Chloro-8-hydroxy-3-methyl-1-phenyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-3-benzazepine hydrochloride
Purity: ≥98%
Biological Activity
SCH 23390 hydrochloride is a potent dopamine receptor antagonist (Ki values are 0.2 nM and 0.3 nM at D1 and D5 receptor sub-types, respectively). Also an agonist at 5-HT2C receptors in vitro (Ki values are 6.3 - 9.3 nM). Blocks quinpirole-induced Kir3 (GIRK) currents (EC50 = 268 nM) independently of receptors.Technical Data
The technical data provided above is for guidance only.
For batch specific data refer to the Certificate of Analysis.
Tocris products are intended for laboratory research use only, unless stated otherwise.
Background References
-
Classic D1 DA receptor antagonist R-(+)-7-chloro-8-hydroxy-3-methyl-1-phenyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-3-benzazepine hydrochloride (SCH23390) directly inhibits G protein-coupled inwardly rectifying potassium channels.
Kuzhikandathil and Oxford
Mol.Pharmacol., 2002;62:119 -
Activation of the 5-HT1C receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes by the benzazepines SCH 23390 and SKF 38393.
Briggs et al.
Br.J.Pharmacol., 1991;104:1038 -
SCH 23390: The first selective DA D1-like receptor antagonist.
Bourne et al.
CNS Drug Rev., 2001;7:399 -
The "selective" DA D1 receptor antagonist, SCH23390, is a potent and high efficacy agonist against cloned human serotonin2C receptors.
Millan et al.
Psychopharmacology, 2001;156:58
Product Datasheets
Reconstitution Calculator
Molarity Calculator
Citations for SCH 23390 hydrochloride
The citations listed below are publications that use Tocris products. Selected citations for SCH 23390 hydrochloride include:
59 Citations: Showing 1 - 10
-
Cell-type-specific optogenetic stimulation of the locus coeruleus induces slow-onset potentiation and enhances everyday memory in rats.
Authors: Tsea Et al.
Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.U.S.A. 2023;120:e2307275120
-
Polysynaptic inhibition between striatal cholinergic interneurons shapes their network activity patterns in a dopamine-dependent manner
Authors: Dorst Et al.
Nat Commun 2020;11:5113
-
DA Receptor Subtypes Mediate Opposing Effects on Form Deprivation Myopia in Pigmented Guinea Pigs.
Authors: Zhang Et al.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2018;59(11):4441
-
Selective blockade of spinal D2DR by levo-corydalmine attenuates MOR tolerance via suppressing PI3K/Akt-MAPK signaling in a MOR-dependent manner.
Authors: Dai Et al.
Exp Mol Med 2018;50:148
-
Altered Baseline and Nicotine-Mediated Behavioral and Cholinergic Profiles in ChAT-Cre Mouse Lines.
Authors: Chen Et al.
J Neurosci 2018;38:2177
-
DA Cells Differentially Regulate Striatal Cholinergic Transmission across Regions through Corelease of DA and Glutamate.
Authors: Cai and Ford
Cell Rep 2018;25:3148
-
The small molecule CA140 inhibits the neuroinflammatory response in wild-type mice and a mouse model of AD.
Authors: Lee Et al.
J Neuroinflammation 2018;15:286
-
Fasting biases μ-opioid receptors toward β-arrestin2 dependent signaling in the accumbens shell.
Authors: Scheggi
Neuroscience 2017;352:19
-
DA D4 receptor activation restores CA1 LTP in hippocampal slices from aged mice.
Authors: Guo
Aging Cell 2017;16(6):1323
-
Nicotinic and opioid receptor regulation of striatal DA D2-receptor mediated transmission
Authors: Mamaligas Et al.
Scientific Reports 2016;6:37834
-
The First Alcohol Drink Triggers mTORC1-Dependent Synaptic Plasticity in Nucleus Accumbens DA D1 Receptor Neurons.
Authors: Beckley Et al.
J Neurosci 2016;36:701
-
The σ1 receptor regulates accumulation of GM1 ganglioside-enriched autophagosomes in astrocytes
Authors: Kasaharaa Et al.
Neuroscience 2016;340:176
-
Prostaglandin-dependent modulation of DArgic neurotransmission elicits inflammation-induced aversion in mice.
Authors: Fritz Et al.
J Clin Invest 2016;126:695
-
Endogenous 17β-OE is required for activity-dependent long-term potentiation in the striatum: interaction with the DArgic system.
Authors: Tozzi Et al.
Front Cell Neurosci 2015;9:192
-
L-Stepholidine rescues memory deficit and synaptic plasticity in models of Alzheimer's disease via activating DA D1 receptor/PKA signaling pathway.
Authors: Hao Et al.
Cell Death Dis 2015;6:e1965
-
Retroactive modulation of spike timing-dependent plasticity by DA.
Authors: Brzosko Et al.
Elife 2015;4
-
Incubation of metha. craving is associated with selective increases in expression of Bdnf and trkb, glutamate receptors, and epigenetic enzymes in cue-activated fos-expressing dorsal striatal neurons.
Authors: Li Et al.
Learn Mem 2015;35:8232
-
Spinal DArgic projections control the transition to pathological pain plasticity via a D1/D5-mediated mechanism.
Authors: Kim Et al.
J Neurosci 2015;35:6307
-
Evaluation of AaDOP2 receptor antagonists reveals antidepressants and antipsychotics as novel lead molecules for control of the yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti.
Authors: Conley Et al.
PLoS One 2015;352:53
-
DArgic modulation of appetitive trace conditioning: the role of D1 receptors in medial prefrontal cortex.
Authors: Pezze Et al.
Behav Neurosci 2015;232:2669
-
Regionally selective requirement for D1/D5 DArgic neurotransmission in the medial prefrontal cortex in object-in-place associative recognition memory.
Authors: Savalli Et al.
PLoS One 2015;22:69
-
A critical role of nucleus accumbens DA D1-family receptors in renewal of alcohol seeking after punishment-imposed abstinence.
Authors: Marchant and Kaganovsky
PLoS One 2015;129:281
-
Pharmacological Characterization of 5-HT1A Autoreceptor-Coupled GIRK Channels in Rat Dorsal Raphe 5-HT Neurons.
Authors: Montalbano Et al.
J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2015;10:e0140369
-
Blocking DArgic Signaling Soon after Learning Impairs Memory Consolidation in Guinea Pigs.
Authors: Lee and Chirwa
Nat Neurosci 2015;10:e0135578
-
DA Promotes Motor Cortex Plasticity and Motor Skill Learning via PLC Activation.
Authors: Rioult-Pedotti Et al.
PLoS One 2015;10:e0124986
-
Effect of DArgic D1 receptors on plasticity is dependent of serotoninergic 5-HT1A receptors in L5-pyramidal neurons of the prefrontal cortex.
Authors: Meunier Et al.
PLoS One 2015;10:e0120286
-
Phasic DA release drives rapid activation of striatal D2-receptors.
Authors: Marcott Et al.
Neuron 2014;84:164
-
Characterization of the guinea pig animal model and subsequent comparison of the behavioral effects of selective DArgic drugs and metha.
Authors: Lee Et al.
Synapse 2014;68:221
-
Differential role of D1 and D2 receptors in the perifornical lateral hypothalamus in controlling ethanol drinking and food intake: possible interaction with local orexin neurons.
Authors: Chen Et al.
Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2014;38:777
-
Korean Red Ginseng attenuates anxiety-like behavior during ethanol withdrawal in rats.
Authors: Zhao Et al.
Br J Pharmacol 2014;38:256
-
DArgic modulation of GABAergic transmission in the entorhinal cortex: concerted roles of α1 adrenoreceptors, inward rectifier K+, and T-type Ca2+ channels.
Authors: Cilz Et al.
Cereb Cortex 2014;24:3195
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 knockout promotes motor and biochemical alterations in a mouse model of Huntington's disease.
Authors: Ribeiro Et al.
J Neurosci 2014;23:2030
-
DA D1 and corticotrophin-releasing hormone type-2α receptors assemble into functionally interacting complexes in living cells.
Authors: Fuenzalida Et al.
J Clin Invest 2014;171:5650
-
Extinction of remotely acquired fear depends on an inhibitory NR2B/PKA pathway in the retrosplenial cortex.
Authors: Corcoran Et al.
J Neurosci 2013;33:19492
-
Age-dependent regulation of synaptic connections by DA D2 receptors.
Authors: Jia Et al.
Nat Neurosci 2013;16:1627
-
Sucrose produces withdrawal and DA-sensitive reinforcing effects in planarians.
Authors: Zhang Et al.
Physiol Behav 2013;112-113:8
-
SKF83959, an agonist of phosphatidylinositol-linked D(1)-like receptors, promotes ERK1/2 activation and cell migration in cultured rat astrocytes.
Authors: Huang Et al.
Neuroscience 2012;7:e49954
-
Stimulation of DA receptor D5 expressed on dendritic cells potentiates Th17-mediated immunity.
Authors: Prado Et al.
Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2012;188:3062
-
Mephedrone ('bath salt') elicits conditioned place preference and DA-sensitive motor activation.
Authors: Lisek Et al.
Drug Alcohol Depend 2012;126:257
-
Synergistic activation of DA D1 and TrkB receptors mediate gain control of synaptic plasticity in the basolateral amygdala.
Authors: Li Et al.
PLoS One 2011;6:e26065
-
DA-induced plasticity, phospholipase D (PLD) activity and cocaine-cue behavior depend on PLD-linked metabotropic glutamate receptors in amygdala.
Authors: Krishnan Et al.
PLoS One. 2011;6:e25639
-
Exposure to extremely low frequency magnetic fields induces fos-related antigen-immunoreactivity via activation of DArgic d1 receptor.
Authors: Shin Et al.
Hum Mol Genet 2011;20:130
-
DA receptor mechanisms mediate corticotropin-releasing factor-induced long-term potentiation in the rat amygdala following cocaine withdrawal.
Authors: Krishnan Et al.
Eur J Neurosci 2010;31:1027
-
DA-dependent tuning of striatal inhibitory synaptogenesis.
Authors: Goffin Et al.
J Neurosci 2010;30:2935
-
Differential effects of selective adenosine antagonists on the effort-related impairments induced by DA D1 and D2 antagonism.
Authors: Nunes Et al.
Neuroscience 2010;170:268
-
Amphetamine up-regulates activator of G-protein signaling 1 mRNA and protein levels in rat frontal cortex: the role of DA and glucocorticoid receptors.
Authors: Schwendt and McGinty
J Neurosci 2010;168:96
-
MeCP2 in the nucleus accumbens contributes to neural and behavioral responses to psychostimulants.
Authors: Deng Et al.
J Ginseng Res 2010;13:1128
-
Amphetamine modulation of long-term potentiation in the prefrontal cortex: dose dependency, monoaminergic contributions, and paradoxical rescue in hyperDArgic mutant.
Authors: Xu Et al.
Exp Neurobiol 2010;115:1643
-
Post-translational modification of glutamic acid decarboxylase 67 by intermittent hypoxia: evidence for the involvement of DA D1 receptor signaling.
Authors: Raghuraman Et al.
J Neurochem 2010;115:1568
-
HyperDArgic tone erodes prefrontal long-term potential via a D2 receptor-operated protein phosphatase gate.
Authors: Xu Et al.
J Immunol 2009;29:14086
-
DA neuron glutamate cotransmission: frequency-dependent modulation in the mesoventromedial projection.
Authors: Chuhma Et al.
Neuroscience 2009;164:1068
-
Activation of phosphatidylinositol-linked novel D1 DA receptors inhibits high-voltage-activated Ca2+ currents in primary cultured striatal neurons.
Authors: Ma Et al.
J Neurophysiol 2009;101:2230
-
Electrophysiology and pharmacology of striatal neuronal dysfunction induced by mitochondrial complex I inhibition.
Authors: Costa Et al.
J Neurosci 2008;28:8040
-
DA enhances fast excitatory synaptic transmission in the extended amygdala by a CRF-R1-dependent process.
Authors: Kash Et al.
J Neurochem 2008;28:13856
-
Coregulation of natively expressed pertussis toxin-sensitive muscarinic receptors with G-protein-activated potassium channels.
Authors: Clancy Et al.
PLoS One 2007;27:6388
-
Cellular localization and function of DARPP-32 in the rodent retina.
Authors: Witkovsky Et al.
Eur J Neurosci 2007;25:3233
-
Catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibition increases pain sensitivity through activation of both beta2- and beta3-adrenergic receptors.
Authors: Nackley Et al.
Pain 2007;128:199
-
Prolonged wakefulness induces experience-dependent synaptic plasticity in mouse hypocretin/orexin neurons.
Authors: Rao Et al.
J Neurosci 2007;117:4022
-
DA targets cycling B cells independent of receptors/transporter for oxidative attack: Implications for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Authors: Meredith Et al.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006;103:13485
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Small Molecule FAQsReviews for SCH 23390 hydrochloride
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review SCH 23390 hydrochloride and earn rewards!
Have you used SCH 23390 hydrochloride?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image