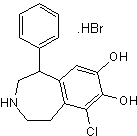
SKF 81297 hydrobromide
Chemical Name: (±)-6-Chloro-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1-phenyl-1H-3-benzazepine hydrobromide
Purity: ≥98%
Biological Activity
SKF 81297 hydrobromide is a dopamine D1-like receptor agonist. Centrally active following systemic administration in vivo.Technical Data
The technical data provided above is for guidance only.
For batch specific data refer to the Certificate of Analysis.
Tocris products are intended for laboratory research use only, unless stated otherwise.
Background References
-
Relative DA D1 and D2 receptor affinity and efficacy determine whether DA agonists induce hyperactivity or oral stereotypy in rats.
Arnt et al.
Pharmacol.Toxicol., 1988;62:121 -
The effects of DA D1 and D2 receptor agonists and antagonists in monkeys withdrawn from long-term neuroleptic treatment.
Peacock et al.
Eur.J.Pharmacol., 1990;186:49 -
Pharmacological characterization of the discriminative stimulus properties of the DA D1 agonist, SKF 81297.
Reavill et al.
Behav.Pharmacol., 1993;4:135
Product Datasheets
Reconstitution Calculator
Molarity Calculator
Citations for SKF 81297 hydrobromide
The citations listed below are publications that use Tocris products. Selected citations for SKF 81297 hydrobromide include:
25 Citations: Showing 1 - 10
-
Polysynaptic inhibition between striatal cholinergic interneurons shapes their network activity patterns in a dopamine-dependent manner.
Authors: Dorst Et al.
Nat Commun 2020;11:5113
-
Functional roles of ST8SIA3-mediated sialylation of striatal DA D2 and adenosine A2A receptors.
Authors: Lin Et al.
Transl Psychiatry 2019;9:209
-
Chemokine CXCL1 is responsible for cocaine-induced reward in mice.
Authors: Saika
NeurosciPharm Reports 2018;38(3):145
-
A Sensitized IGF1 Treatment Restores Corticospinal Axon-Dependent Functions.
Authors: Liu Et al.
Neuron 2017;95:817
-
Distinct retinoic acid receptor (RAR) isotypes control differentiation of embryonal carcinoma cells to dopaminergic or striatopallidal medium spiny neurons.
Authors: Podleśny-Drabiniok Et al.
Sci Rep 2017;7:13671
-
DA D4 receptor activation restores CA1 LTP in hippocampal slices from aged mice.
Authors: Guo
Aging Cell 2017;16(6):1323
-
The First Alcohol Drink Triggers mTORC1-Dependent Synaptic Plasticity in Nucleus Accumbens DA D1 Receptor Neurons.
Authors: Beckley Et al.
J Neurosci 2016;36:701
-
DArgic modulation of appetitive trace conditioning: the role of D1 receptors in medial prefrontal cortex.
Authors: Pezze Et al.
Mol Med Rep 2015;232:2669
-
Effect of DArgic D1 receptors on plasticity is dependent of serotoninergic 5-HT1A receptors in L5-pyramidal neurons of the prefrontal cortex.
Authors: Meunier Et al.
PLoS One 2015;10:e0120286
-
PFOS induces behavioral alterations, including spontaneous hyperactivity that is corrected by dexamfetamine in zebrafish larvae.
Authors: Spulber Et al.
PLoS One 2014;9:e94227
-
Glucocorticoid receptor gene inactivation in DA-innervated areas selectively decreases behavioral responses to amphetamine.
Authors: Parnaudeau Et al.
Front Behav Neurosci 2014;8:35
-
Differential role of D1 and D2 receptors in the perifornical lateral hypothalamus in controlling ethanol drinking and food intake: possible interaction with local orexin neurons.
Authors: Chen Et al.
Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2014;38:777
-
DArgic modulation of GABAergic transmission in the entorhinal cortex: concerted roles of α1 adrenoreceptors, inward rectifier K+, and T-type Ca2+ channels.
Authors: Cilz Et al.
Cereb Cortex 2014;24:3195
-
DA signaling leads to loss of Polycomb repression and aberrant gene activation in experimental parkinsonism.
Authors: Södersten Et al.
PLoS Genet 2014;10:e1004574
-
GPR88 reveals a discrete function of primary cilia as selective insulators of GPCR cross-talk.
Authors: Marley Et al.
Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2013;8:e70857
-
Coincidence signaling of DA D1-like and M1 muscarinic receptors in the regulation of cyclic AMP formation and CREB phosphorylation in mouse prefrontal cortex.
Authors: Olianas Et al.
Neurosignals 2012;21:61
-
DArgic modulation of the hippocampal neuropil proteome identified by bioorthogonal noncanonical amino acid tagging (BONCAT).
Authors: Hodas Et al.
Proteomics 2012;12:2464
-
Stimulation of the D5 DA receptor acidifies the lysosomal pH of retinal pigmented epithelial cells and decreases accumulation of autofluorescent photoreceptor debris.
Authors: Guha Et al.
J Neurochem 2012;122:823
-
CODA-RET reveals functional selectivity as a result of GPCR heteromerization.
Authors: Urizar Et al.
Nat Neurosci 2011;7:624
-
DA-induced plasticity, phospholipase D (PLD) activity and cocaine-cue behavior depend on PLD-linked metabotropic glutamate receptors in amygdala.
Authors: Krishnan Et al.
PLoS One 2011;6:e25639
-
Casein kinase 1 enables nucleus accumbens amphetamine-induced locomotion by regulating AMPA receptor phosphorylation.
Authors: Li Et al.
J Neurochem 2011;118:237
-
MeCP2 in the nucleus accumbens contributes to neural and behavioral responses to psychostimulants.
Authors: Deng Et al.
PLoS One 2010;13:1128
-
D1/5 receptor-mediated enhancement of LTP requires PKA, Src family kinases, and NR2B-containing NMDARs.
Authors: Stramiello
Neuropharmacology 2008;55:871
-
D1-like DA receptor activation modulates GABAergic inhibition but not electrical coupling between neocortical fast-spiking interneurons.
Authors: Towers and Hestrin
J Neurosci 2008;28:2633
-
DArgic regulation of inhibitory and excitatory transmission in the basolateral amygdala-prefrontal cortical pathway.
Authors: Floresco and Tse
J Neurosci 2007;27:2045
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Small Molecule FAQsReviews for SKF 81297 hydrobromide
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review SKF 81297 hydrobromide and earn rewards!
Have you used SKF 81297 hydrobromide?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image