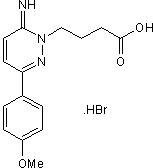
SR 95531 hydrobromide
Chemical Name: 6-Imino-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1(6H)-pyridazinebutanoic acid hydrobromide
Purity: ≥98%
Biological Activity
SR 95531 hydrobromide is a selective, competitive GABAA receptor antagonist and allosteric inhibitor (IC50 = 200 nM). SR 95531 displaces [3H]-GABA from rat brain membranes with a Ki of 150 nM. Unlike Bicuculline (Cat. No. 0130), SR 95531 selectively antagonizes GABA-induced Cl- currents with little action on Pentobarbitone-induced currents (Cat. No. 4579). SR 95531 can act as an agonist at high concentrations (>100 μM) and is a weak agonist at GABAA receptors with α1β2(Y157S)γ2L subunits. SR 95531 also acts as a competitive antagonist of recombinant glycine receptors and exhibits greater potency at glycine receptors containing β subunits.Technical Data
The technical data provided above is for guidance only.
For batch specific data refer to the Certificate of Analysis.
Tocris products are intended for laboratory research use only, unless stated otherwise.
Background References
-
The kinetics of inhibition of rat recombinant heterotrimeric α1β glycine receptors by the low affinity antagonist SR-95531.
Beato et al.
J.Physiol., 2007;580:171 -
Biochemical characterization of the interaction of three pyridazinyl-GABA derivatives with the GABAA receptor site.
Heaulme et al.
Brain Res., 1986;384:224 -
The differential antagonism by bicuculline and SR95531 of pentobarbitone-induced currents in cultured hippocampal neurons.
Uchida et al.
Eur.J.Pharmacol., 1996;307:89
Product Datasheets
Reconstitution Calculator
Molarity Calculator
Citations for SR 95531 hydrobromide
The citations listed below are publications that use Tocris products. Selected citations for SR 95531 hydrobromide include:
171 Citations: Showing 1 - 10
-
Voltage-gated potassium channels ensure action potential shape fidelity in distal axons.
Authors: Sabater Et al.
J Neurosci 2021;41:5372
-
Oxytocin shapes spontaneous activity patterns in the developing visual cortex by activating somatostatin interneurons.
Authors: Maldonado Et al.
Curr Biol 2021;31:322
-
Axonal mechanisms mediating γ-aminobutyric acid receptor type A (GABA-A) inhibition of striatal dopamine release
Authors: Kramer Et al.
ELife 2020;9
-
Functional Dissection of Basal Ganglia Inhibitory Inputs onto Substantia Nigra Dopaminergic Neurons.
Authors: Evans Et al.
Cell Rep 2020;32
-
Polysynaptic inhibition between striatal cholinergic interneurons shapes their network activity patterns in a dopamine-dependent manner.
Authors: Dorst Et al.
Nat Comms 2020;11:5113
-
Hippocampal hub neurons maintain distinct connectivity throughout their lifetime.
Authors: Bocchio Et al.
Nat Commun 2020;11:4559
-
Overlapping Activities of Two Neuronal Splicing Factors Switch the GABA Effect from Excitatory to Inhibitory by Regulating REST.
Authors: Nakano Et al.
Cell Rep 2019;27:860
-
Functional Coupling of Cav2.3 and BK Potassium Channels Regulates Action Potential Repolarization and Short-Term Plasticity in the Mouse Hippocampus.
Authors: Gutzmann Et al.
Front Cell Neurosci 2019;13:27
-
Optically Induced Calcium-Dependent Gene Activation and Labeling of Active Neurons Using CaMPARI and Cal-Light.
Authors: Ebner Et al.
Front Synaptic Neurosci 2019;11:16
-
A Retinal Circuit Generating a Dynamic Predictive Code for Oriented Features.
Authors: Johnston Et al.
Neuron 2019;
-
A hippocampal circuit linking dorsal CA2 to ventral CA1 critical for social memory dynamics.
Authors: Meira Et al.
Nat.Commun. 2018;9:4163
-
Reciprocal Circuits Linking the Prefrontal Cortex with Dorsal and Ventral Thalamic Nuclei.
Authors: Collins Et al.
Neuron 2018;98:366
-
GABAergic inhibition in dual-transmission cholinergic and GABAergic striatal interneurons is abolished in Parkinson disease.
Authors: Lozovaya Et al.
Nat Commun 2018;9(1):1422
-
OXT functions as a spatiotemporal filter for excitatory synaptic inputs to VTA DA neurons.
Authors: Xiao Et al.
Elife 2018;7
-
A circuit from hippocampal CA2 to lateral septum disinhibits social aggression.
Authors: Leroy Et al.
Nature 2018;564:213
-
Cerebrospinal Fluid-Contacting Neurons Sense pH Changes and Motion in the Hypothalamus.
Authors: Jalalvand Et al.
J Neurosci 2018;38:7713
-
The Mouse Pulvinar Nucleus Links the Lateral Extrastriate Cortex, Striatum, and Amygdala.
Authors: Zhou Et al.
J Neurosci 2018;38:347
-
Heparan Sulfate Organizes Neuronal Synapses through Neurexin Partnerships.
Authors: Zhang Et al.
Cell 2018;174:1450
-
Proximodistal Heterogeneity of Hippocampal CA3 Pyramidal Neuron Intrinsic Properties, Connectivity, and Reactivation during Memory Recall.
Authors: Sun Et al.
Neuron 2017;95:656
-
Biased OXTergic Modulation of Midbrain DA Systems.
Authors: Xiao Et al.
Neuron 2017;95:368
-
Neurotransmitter Switching Regulated by miRNAs Controls Changes in Social Preference.
Authors: Dulcis Et al.
Neuron 2017;95:1319
-
Input-Timing-Dependent Plasticity in the Hippocampal CA2 Region and Its Potential Role in Social Memory.
Authors: Leroy Et al.
Neuron 2017;95:1089
-
Chronic Loss of CA2 Transmission Leads to Hippocampal Hyperexcitability.
Authors: Boehringer Et al.
Neuron 2017;94:642
-
Serotonin enhances excitability and gamma frequency temporal integration in mouse prefrontal fast-spiking interneurons.
Authors: Athilingam Et al.
Elife 2017;6
-
Subtype-specific effects of DArgic D2 receptor activation on synaptic trains in layer V pyramidal neurons in the mouse prefrontal cortex.
Authors: Leyrer-Jackson
Physiol Rep 2017;5(22):e13499
-
Effect of temperature on FAD and NADH-derived signals and neurometabolic coupling in the mouse auditory and motor cortex.
Authors: Ibrahim Et al.
Pflugers Arch 2017;469:1631
-
DA Regulation of GABAA Receptors Contributes to Light/Dark Modulation of the ON-Cone Bipolar Cell Receptive Field Surround in the Retina.
Authors: Chaffiol Et al.
Curr Biol 2017;27:2600
-
Measuring Feedforward Inhibition and Its Impact on Local Circuit Function.
Authors: Hull
Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2017;2017
-
Ion channel expression patterns in glioblastoma stem cells with functional and therapeutic implications for malignancy.
Authors: Pollak Et al.
PLoS One 2017;12:e0172884
-
Monoaminergic modulation of GABAergic transmission onto cerebellar globular cells.
Authors: Hirono
Neuropharmacology 2017;118:79
-
Spontaneous release regulates synaptic scaling in the embryonic spinal network in vivo.
Authors: Miguel Angel Garcia-Bereguiain Et al.
The Journal of Neuroscience 2016;6:7268
-
Differential somatic Ca2+ channel profile in midbrain DArgic neurons.
Authors: Philippart Et al.
The Journal of Neuroscience 2016;6:7234
-
Cortico-fugal output from visual cortex promotes plasticity of innate motor behaviour.
Authors: Liu Et al.
Nature 2016;538:383
-
A cholinergic basal forebrain feeding circuit modulates appetite suppression
Authors: Herman Et al.
Nature 2016;538:253
-
A deleterious Nav1.1 mutation selectively impairs telencephalic inhibitory neurons derived from Dravet Syndrome patients.
Authors: Sun Et al.
Elife 2016;5
-
17β-OE Acutely Potentiates Glutamatergic Synaptic Transmission in the Hippocampus through Distinct Mechanisms in Males and Females.
Authors: Oberlander
J Neurosci 2016;36:2677
-
Cell-Autonomous Regulation of Dendritic Spine Density by PirB.
Authors: Vidal Et al.
Eneuro 2016;3
-
Electrophysiological Assessment of Serotonin and GABA Neuron Function in the Dorsal Raphe during the Third Trimester Equivalent Developmental Period in Mice(1,2,3).
Authors: Morton Et al.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2016;2
-
Diminished KCC2 confounds synapse specificity of LTP during senescence.
Authors: Ferando Et al.
Nat Neurosci 2016;19:1197
-
Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide Excites GnRH Neurons in Male and Female Mice.
Authors: Piet Et al.
Endocrinology. 2016;157:3621
-
Acetylcholine induces GABA release onto rod bipolar cells through heteromeric nicotinic receptors expressed in A17 amacrine cells.
Authors: Elgueta Et al.
Microvasc Res 2015;9:6
-
Cell-type-specific tuning of Cav1.3 Ca(2+)-channels by a C-terminal automodulatory domain.
Authors: Scharinger Et al.
Elife 2015;9:309
-
Stretch induced hyperexcitability of mice callosal pathway.
Authors: Fan Et al.
J Neurophysiol 2015;9:292
-
An excitatory GABA loop operating in vivo.
Authors: Astorga Et al.
Front Cell Neurosci 2015;9:275
-
Interaction of electrically evoked activity with intrinsic dynamics of cultured cortical networks with and without functional fast GABAergic synaptic transmission.
Authors: Baltz and Voigt
Front Cell Neurosci 2015;9:272
-
Acetylcholine release in mouse hippocampal CA1 preferentially activates inhibitory-selective interneurons via α4β2* nicotinic receptor activation.
Authors: Bell Et al.
J Neurosci 2015;9:115
-
High salt intake increases blood pressure via BDNF-mediated downregulation of KCC2 and impaired baroreflex inhibition of vasopressin neurons.
Authors: Choe Et al.
Front Cell Neurosci 2015;85:549
-
Chloride transporter KCC2-dependent neuroprotection depends on the N-terminal protein domain.
Authors: Winkelmann Et al.
Cell Death Dis 2015;6:e1776
-
Optical control of NMDA receptors with a diffusible photoswitch.
Authors: Laprell Et al.
Front Cell Neurosci 2015;6:8076
-
RBFOX3/NeuN is Required for Hippocampal Circuit Balance and Function.
Authors: Wang Et al.
Sci Rep 2015;5:17383
-
Increased serotonin transporter expression reduces fear and recruitment of parvalbumin interneurons of the amygdala.
Authors: Bocchio Et al.
Neuropsychopharmacology 2015;40:3015
-
An excitatory amacrine cell detects object motion and provides feature-selective input to ganglion cells in the mouse retina.
Authors: Kim Et al.
Elife 2015;4
-
CaRuby-Nano: a novel high affinity calcium probe for dual color imaging.
Authors: Collot Et al.
Front Cell Neurosci 2015;4
-
Corelease of acetylcholine and GABA from cholinergic forebrain neurons.
Authors: Saunders Et al.
Elife 2015;4
-
BK Channels Localize to the Paranodal Junction and Regulate Action Potentials in Myelinated Axons of Cerebellar Purkinje Cells.
Authors: Hirono Et al.
Eneuro 2015;35:7082
-
Prototypic and arkypallidal neurons in the DA-intact external globus pallidus.
Authors: Abdi Et al.
J Neurosci 2015;35:6667
-
Muscarinic receptors modulate dendrodendritic inhibitory synapses to sculpt glomerular output.
Authors: Liu Et al.
J Negat Results Biomed 2015;35:5680
-
Abnormal excitability and episodic low-frequency oscillations in the cerebral cortex of the tottering mouse.
Authors: Cramer Et al.
Physiol Rep 2015;35:5664
-
Ectopic Expression of α6 and δ GABAA Receptor Subunits in Hilar Somatostatin Neurons Increases Tonic Inhibition and Alters Network Activity in the Dentate Gyrus.
Authors: Tong Et al.
J Neurosci 2015;35:16142
-
The Synaptic and Morphological Basis of Orientation Selectivity in a Polyaxonal Amacrine Cell of the Rabbit Retina.
Authors: Murphy-Baum and Taylor
Brain 2015;35:13336
-
Sex Differences in Molecular Signaling at Inhibitory Synapses in the Hippocampus.
Authors: Tabatadze Et al.
J Neurosci 2015;35:11252
-
Afterhyperpolarization (AHP) regulates the frequency and timing of action potentials in the mitral cells of the olfactory bulb: role of olfactory experience.
Authors: Duménieu Et al.
PLoS One 2015;3
-
Traumatic Brain Injury Increases Cortical Glutamate Network Activity by Compromising GABAergic Control.
Authors: Cantu Et al.
Cereb Cortex 2015;25:2306
-
Selective Effects of PDE10A Inhibitors on Striatopallidal Neurons Require Phosphatase Inhibition by DARPP-32(1,2,3).
Authors: Polito Et al.
J Neurosci 2015;2
-
Ethanol exposure during the third trimester equivalent does not affect GABAA or AMPA receptor-mediated spontaneous synaptic transmission in rat CA3 pyramidal neurons.
Authors: Baculis and Valenzuela
J Neurophysiol 2015;14:19
-
Tectal microcircuit generating visual selection commands on gaze-controlling neurons.
Authors: Kardamakis Et al.
PLoS One 2015;112:E1956
-
Apamin Boosting of Synaptic Potentials in CaV2.3 R-Type Ca2+ Channel Null Mice.
Authors: Wang Et al.
Eneuro 2015;10:e0139332
-
The effect of Dflu. on neuronal communication at a central synapse.
Authors: Mapelli Et al.
Nat Commun 2015;10:e0123534
-
Spatially reciprocal inhibition of inhibition within a stimulus selection network in the avian midbrain.
Authors: Goddard Et al.
PLoS One 2014;9:e85865
-
Nitric oxide modulates the temporal properties of the glutamate response in type 4 OFF bipolar cells.
Authors: Vielma Et al.
PLoS One 2014;9:e114330
-
Neonatal NMDA receptor blockade disrupts spike timing and glutamatergic synapses in fast spiking interneurons in a NMDA receptor hypofunction model of schizophrenia.
Authors: Jones Et al.
Nature 2014;9:e109303
-
mGluR1-mediated excitation of cerebellar GABAergic interneurons requires both G protein-dependent and Src-ERK1/2-dependent signaling pathways.
Authors: Kubota Et al.
PLoS One 2014;9:e106316
-
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene knock-down in post-mitotic neurons.
Authors: Straub Et al.
J Neurophysiol 2014;9:e105584
-
Inhibitory projections from the ventral nucleus of the trapezoid body to the medial nucleus of the trapezoid body in the mouse.
Authors: Albrecht Et al.
Front Neural Circuits 2014;8:83
-
Laser-scanning astrocyte mapping reveals increased glutamate-responsive domain size and disrupted maturation of glutamate uptake following neonatal cortical freeze-lesion.
Authors: Armbruster Et al.
Front Cell Neurosci 2014;8:277
-
Regulation of output spike patterns by phasic inhibition in cerebellar granule cells.
Authors: Nieus Et al.
Front Cell Neurosci 2014;8:246
-
Lamina-specific contribution of glutamatergic and GABAergic potentials to hippocampal sharp wave-ripple complexes.
Authors: Schönberger Et al.
J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2014;8:103
-
DA neurons control striatal cholinergic neurons via regionally heterogeneous DA and glutamate signaling.
Authors: Chuhma Et al.
PLoS One 2014;81:901
-
HSF1 transcriptional activity mediates alcohol induction of Vamp2 expression and GABA release.
Authors: Varodayan and Harrison
J Neurophysiol 2014;7:89
-
Synaptic and cellular organization of layer 1 of the developing rat somatosensory cortex.
Authors: Muralidhar Et al.
Front Neuroanat 2014;7:52
-
Synapse elimination and learning rules co-regulated by MHC class I H2-Db.
Authors: Lee Et al.
Nat Neurosci 2014;509:195
-
Cross-synaptic synchrony and transmission of signal and noise across the mouse retina.
Authors: Grimes Et al.
Elife 2014;3:e03892
-
Gap junction networks can generate both ripple-like and fast ripple-like oscillations.
Authors: Simon Et al.
Eur J Neurosci 2014;39:46
-
Glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation in neurons and astrocytes during network activity in hippocampal slices.
Authors: Ivanov Et al.
J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2014;34:397
-
Three distinct blue-green color pathways in a mammalian retina.
Authors: Mills Et al.
J Neurosci 2014;34:1760
-
Moderate Alcohol Exposure during the Rat Equivalent to the Third Trimester of Human Pregnancy Alters Regulation of GABAA Receptor-Mediated Synaptic Transmission by DA in the Basolateral Amygdala.
Authors: Diaz Et al.
J Neurosci 2014;2:46
-
Cav1.3 channels control D2-autoreceptor responses via NCS-1 in substantia nigra DA neurons.
Authors: Dragicevic Et al.
Neuron 2014;137:2287
-
Depressed GABA and glutamate synaptic signaling by 5-HT1A receptors in the nucleus tractus solitarii and their role in cardiorespiratory function.
Authors: Ostrowski Et al.
J Neurosci 2014;111:2493
-
Effects of ethanol on glycinergic synaptic currents in mouse spinal cord neurons.
Authors: Mariqueo Et al.
Front Pediatr 2014;111:1940
-
GPR35 activation reduces Ca2+ transients and contributes to the kynurenic acid-dependent reduction of synaptic activity at CA3-CA1 synapses.
Authors: Berlinguer-Palmini Et al.
PLoS One 2013;8:e82180
-
Effects of a metabotropic glutamate 1 receptor antagonist on light responses of retinal ganglion cells in a rat model of retinitis pigmentosa.
Authors: Jensen
PLoS One 2013;8:e79126
-
Intersecting circuits generate precisely patterned retinal waves.
Authors: Akrouh and Kerschensteiner
Neuron 2013;79:322
-
Weaker control of the electrical properties of cerebellar granule cells by tonically active GABAA receptors in the Ts65Dn mouse model of Down's syndrome.
Authors: Szemes Et al.
Mol Brain 2013;6:33
-
Properties of the ON bistratified ganglion cell in the rabbit retina.
Authors: Hoshi Et al.
J Comp Neurol 2013;521:1497
-
Autism-related deficits via dysregulated eIF4E-dependent translational control.
Authors: Gkogkas Et al.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2013;493:371
-
Postnatal loss of P/Q-type channels confined to rhombic-lip-derived neurons alters synaptic transmission at the parallel fiber to purkinje cell synapse and replicates genomic Cacna1a mutation phenotype of ataxia and seizures in mice.
Authors: Maejima Et al.
J Neurosci 2013;33:5162
-
PrPC controls via protein kinase A the direction of synaptic plasticity in the immature hippocampus.
Authors: Caiati Et al.
J Neurosci 2013;33:2973
-
Ovarian hormone loss impairs excitatory synaptic transmission at hippocampal CA3-CA1 synapses.
Authors: Wu Et al.
J Neurosci 2013;33:16158
-
A reorganized GABAergic circuit in a model of epilepsy: evidence from optogenetic labeling and stimulation of somatostatin interneurons.
Authors: Peng Et al.
PLoS One 2013;33:14392
-
Behavioural and functional characterization of Kv10.1 (Eag1) knockout mice.
Authors: Ufartes Et al.
Hum Mol Genet 2013;22:2247
-
GABA(A) receptors implicated in REM sleep control express a benzodiazepine binding site.
Authors: Nguyen Et al.
J Biol Chem 2013;1527:131
-
Synaptic and extrasynaptic transmission of kidney-related neurons in the rostral ventrolateral medulla.
Authors: Gao and Derbenev
J Neurosci 2013;110:2637
-
Contribution of near-threshold currents to intrinsic oscillatory activity in rat medial entorhinal cortex layer II stellate cells.
Authors: Boehlen Et al.
J Neurophysiol 2013;109:445
-
Olfactory bulb glomerular NMDA receptors mediate olfactory nerve potentiation and odor preference learning in the neonate rat.
Authors: Lethbridge Et al.
Mol Pain 2012;7:e35024
-
Pre and post synaptic NMDA effects targeting Purkinje cells in the mouse cerebellar cortex.
Authors: Lonchamp Et al.
PLoS One 2012;7:e30180
-
Cerebellar globular cells receive monoaminergic excitation and monosynaptic inhibition from Purkinje cells.
Authors: Hirono Et al.
PLoS One 2012;7:e29663
-
Opposing Effects of Intrinsic Conductance and Correlated Synaptic Input on V-Fluctuations during Network Activity.
Authors: Kolind Et al.
Front Comput Neurosci 2012;6:40
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor activation of CaM-kinase kinase via transient receptor potential canonical channels induces the translation and synaptic incorporation of GluA1-containing calcium-permeable AMPA receptors.
Authors: Fortin Et al.
J Neurosci 2012;32:8127
-
Optimization of a GCaMP calcium indicator for neural activity imaging.
Authors: Akerboom Et al.
J Neurosci 2012;32:13819
-
Intrinsic modulators of auditory thalamocortical transmission.
Authors: Lee and Sherman
Hear Res 2012;287:43
-
ZD7288 enhances long-term depression at early postnatal medial perforant path-granule cell synapses.
Authors: Guli Et al.
Neural Plast 2012;2012:237913
-
Focal adhesion kinase regulates actin nucleation and neuronal filopodia formation during axonal growth.
Authors: Chacón Et al.
Brain Res 2012;139:3200
-
5-hydroxytryptamine 2C receptors tonically augment synaptic currents in the nucleus tractus solitarii.
Authors: Austgen Et al.
Cereb Cortex 2012;108:2292
-
Age-dependent effect of hearing loss on cortical inhibitory synapse function.
Authors: Takesian Et al.
J Neurophysiol 2012;107:937
-
Synaptic responses evoked by tactile stimuli in Purkinje cells in mouse cerebellar cortex Crus II in vivo.
Authors: Chu Et al.
PLoS One 2011;6:e22752
-
Capsaicin-induced changes in LTP in the lateral amygdala are mediated by TRPV1.
Authors: Zschenderlein Et al.
PLoS One 2011;6:e16116
-
GABAergic signalling in a neurogenic niche of the turtle spinal cord.
Authors: Reali Et al.
J Physiol 2011;589:5633
-
Development of asymmetric inhibition underlying direction selectivity in the retina.
Authors: Wei Et al.
J Neurophysiol 2011;469:402
-
Fast oscillatory activity induced by kainate receptor activation in the rat basolateral amygdala in vitro.
Authors: Randall Et al.
Eur J Neurosci 2011;33:914
-
Ovarian hormone deficiency reduces intrinsic excitability and abolishes acute estrogen sensitivity in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons.
Authors: Wu Et al.
J Neurosci 2011;31:2638
-
SK2 channels are neuroprotective for ischemia-induced neuronal cell death.
Authors: Allen Et al.
J Neurosci 2011;31:2302
-
A diversity of synaptic filters are created by temporal summation of excitation and inhibition.
Authors: George Et al.
J Neurosci 2011;31:14721
-
NMDA receptor signaling in oligodendrocyte progenitors is not required for oligodendrogenesis and myelination.
Authors: Biase Et al.
J Neurophysiol 2011;31:12650
-
Endogenous brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the nucleus tractus solitarius tonically regulates synaptic and autonomic function.
Authors: Clark Et al.
J Neurosci 2011;31:12318
-
Prolonged postinhibitory rebound firing in the cerebellar nuclei mediated by group I metabotropic glutamate receptor potentiation of L-type calcium currents.
Authors: Zheng and Raman
J Neurosci 2011;31:10283
-
Rapid developmental maturation of neocortical FS cell intrinsic excitability.
Authors: Goldberg Et al.
Front Cell Neurosci 2011;21:666
-
The SK2-long isoform directs synaptic localization and function of SK2-containing channels.
Authors: Allen Et al.
Nat Neurosci 2011;14:744
-
Hydrogen sulfide augments synaptic neurotransmission in the nucleus of the solitary tract.
Authors: Austgen Et al.
J Neurophysiol 2011;106:1822
-
A portable laser photostimulation and imaging microscope.
Authors: Nikolenko Et al.
J Neural Eng 2010;7:45001
-
Deactivation of L-type Ca current by inhibition controls LTP at excitatory synapses in the cerebellar nuclei.
Authors: Person and Raman
Neuron 2010;66:550
-
High-Pass Filtering and Dynamic Gain Regulation Enhance Vertical Bursts Transmission along the Mossy Fiber Pathway of Cerebellum.
Authors: Mapelli Et al.
Nature 2010;4:14
-
Excitability and synaptic communication within the oligodendrocyte lineage.
Authors: Biase Et al.
J Neurosci 2010;30:3600
-
Orientation selectivity in rabbit retinal ganglion cells is mediated by presynaptic inhibition.
Authors: Venkataramani and Taylor
J Neurosci 2010;30:15664
-
Control of CA3 output by feedforward inhibition despite developmental changes in the excitation-inhibition balance.
Authors: Torborg Et al.
J Neurosci 2010;30:15628
-
Glutamine is required for persistent epileptiform activity in the disinhibited neocortical brain slice.
Authors: Tani Et al.
J Neurosci 2010;30:1288
-
Substitution of 5-HT1A receptor signaling by a light-activated G protein-coupled receptor.
Authors: Oh Et al.
Front Neural Circuits 2010;285:30825
-
Presynaptic 5-HT(1B) receptor-mediated serotonergic inhibition of glutamate transmission in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis.
Authors: Guo and Rainnie
Neuroscience 2010;165:1390
-
Network mechanisms of theta related neuronal activity in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons.
Authors: Losonczy Et al.
Nat Neurosci 2010;13:967
-
Reduction in endocannabinoid tone is a homeostatic mechanism for specific inhibitory synapses.
Authors: Kim and Alger
Nat Neurosci 2010;13:592
-
Glutamate co-release at GABA/glycinergic synapses is crucial for the refinement of an inhibitory map.
Authors: Noh Et al.
PLoS One 2010;13:232
-
Non-cell-autonomous factor induces the transition from excitatory to inhibitory GABA signaling in retina independent of activity.
Authors: Barkis Et al.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010;107:22302
-
ATP-dependent infra-slow (0.1 Hz) oscillations in thalamic networks.
Authors: Lörincz Et al.
PLoS One 2009;4:e4447
-
Synaptic network activity induces neuronal differentiation of adult hippocampal precursor cells through BDNF signaling.
Authors: Babu Et al.
Front Neurosci 2009;3:49
-
Millisecond timescale disinhibition mediates fast information transmission through an avian basal ganglia loop.
Authors: Leblois Et al.
J Neurosci 2009;29:15420
-
Synaptic circuit abnormalities of motor-frontal layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons in an RNA interference model of methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 deficiency.
Authors: Wood Et al.
Chem Senses 2009;29:12440
-
PropF. inhibits pressure-stimulated macrophage phagocytosis via the GABAA receptor and dysregulation of p130cas phosphorylation.
Authors: Shiratsuchi Et al.
Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2009;296:C1400
-
DA neuron glutamate cotransmission: frequency-dependent modulation in the mesoventromedial projection.
Authors: Chuhma Et al.
Neuroscience 2009;164:1068
-
Differential endocannabinoid regulation of baroreflex-evoked sympathoinhibition in normotensive versus hypertensive rats.
Authors: Brozoski Et al.
Auton Neurosci 2009;150:82
-
Activity-dependent modulation of glutamatergic signaling in the developing rat dorsal horn by early tissue injury.
Authors: Li Et al.
Cereb Cortex 2009;102:2208
-
Co-transmission of DA and GABA in periglomerular cells.
Authors: Maher and Westbrook
J Neurophysiol 2008;99:1559
-
Effects of striatal GABA A-receptor blockade on striatal and cortical activity in monkeys.
Authors: Darbin and Wichmann
Front Cell Neurosci 2008;99:1294
-
Synapse-specific adaptations to inactivity in hippocampal circuits achieve homeostatic gain control while dampening network reverberation.
Authors: Kim and Tsien
Neuron 2008;58:925
-
Hearing loss prevents the maturation of GABAergic transmission in the auditory cortex.
Authors: Kotak Et al.
Cereb Cortex 2008;18:2098
-
Dendritic glutamate release produces autocrine activation of mGluR1 in cerebellar Purkinje cells.
Authors: Shin Et al.
J Neurosci 2008;105:746
-
Presynaptic and postsynaptic NMDA receptors mediate distinct effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on synaptic transmission.
Authors: Madara and Levine
J Neurophysiol 2008;100:3175
-
Selective, state-dependent activation of somatostatin-expressing inhibitory interneurons in mouse neocortex.
Authors: Fanselow Et al.
J Neurophysiol 2008;100:2640
-
Coupling of L-type Ca2+ channels to KV7/KCNQ channels creates a novel, activity-dependent, homeostatic intrinsic plasticity.
Authors: Wu Et al.
J Neurophysiol 2008;100:1897
-
Modulation of inhibitory activity by nitric oxide in the thalamus.
Authors: Yang
J Neurophysiol 2007;97:3386
-
Long-term modifications in the strength of excitatory associative inputs in the piriform cortex.
Authors: Young and Sun
Neuron 2007;32:783
-
Differential effects of endocannabinoids on glutamatergic and GABAergic inputs to layer 5 pyramidal neurons.
Authors: Fortin and Levine
Development 2007;17:163
-
Vesicular release of glutamate from unmyelinated axons in white matter.
Authors: Ziskin Et al.
Front Integr Neurosci 2007;10:321
-
Regulation of thalamocortical patterning and synaptic maturation by NeuroD2.
Authors: Ince-Dunn Et al.
Neuron 2006;49:683
-
Altered balance of glutamatergic/GABAergic synaptic input and associated changes in dendrite morphology after BDNF expression in BDNF-deficient hippocampal neurons.
Authors: Singh Et al.
Nature 2006;26:7189
-
GABA regulates dendritic growth by stabilizing lamellipodia in newly generated interneurons of the olfactory bulb.
Authors: Gascon Et al.
J Neurosci 2006;26:12956
-
Inhibitory sharpening of receptive fields contributes to whisker map plasticity in rat somatosensory cortex.
Authors: Foeller Et al.
J Neurophysiol 2005;94:4387
-
Modulation of spontaneous firing in rat subthalamic neurons by 5-HT receptor subtypes.
Authors: Xiang Et al.
J Neurophysiol 2005;93:1145
-
PropF. suppresses synaptic responsiveness of somatosensory relay neurons to excitatory input by potentiating GABA(A) receptor chloride channels.
Authors: Ying and Goldstein
J Neurosci 2005;1:2
-
HCN2 and HCN1 channels govern the regularity of autonomous pacemaking and synaptic resetting in globus pallidus neurons.
Authors: Chan Et al.
J Neurosci 2004;24:9921
-
Astrocyte glutamate transporters regulate metabotropic glutamate receptor-mediated excitation of hippocampal interneurons.
Authors: Huang Et al.
J Neurosci 2004;24:4551
-
Baseline glutamate levels affect group I and II mGluRs in layer V pyramidal neurons of rat sensorimotor cortex.
Authors: Bandrowski Et al.
J Neurophysiol 2003;89:1308
-
Localization and function of ATP and GABAA receptors expressed by nociceptors and other postnatal sensory neurons in rat.
Authors: Labrakakis Et al.
J Physiol 2003;549:131
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Small Molecule FAQsReviews for SR 95531 hydrobromide
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review SR 95531 hydrobromide and earn rewards!
Have you used SR 95531 hydrobromide?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image