SU 5416
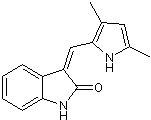
Chemical Name: 3-[(3,5-Dimethyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene]-1,3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-one
Purity: ≥99%
Biological Activity
SU 5416, an angiogenesis inhibitor, is a potent vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase 1/2 inhibitor (IC50 = 40 nM). SU 5416 also potently inhibits c-Kit, FLT3 and RET tyrosine kinases (IC50 values are 30 nM, 160 nM and 170 nM, respectively). SU 5416 shows inhibition of tumour growth and vascularization and can be used to generate an animal model of pulmonary arterial hypertension.Technical Data
The technical data provided above is for guidance only.
For batch specific data refer to the Certificate of Analysis.
Tocris products are intended for laboratory research use only, unless stated otherwise.
Background References
-
SU5416 is a potent and selective inhibitor of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (Flk-1/KDR) that inhibits tyrosine kinase catalysis, tumor vascularisation, and growth of multiple tumor types.
Fong et al.
Cancer Res., 1999;59:99 -
The antiangiogenic protein kinase inhibitors SU5416 and SU6668 inhibit the SCF receptor (c-Kit) in a human myeloid leukemia cell line and in acute myeloid leukemia blasts.
Smolich et al.
Blood, 2001;97:1413 -
Inhibition of RET tyrosine kinase by SU5416.
Mologni et al.
J.Mol.Endocrinol., 2006;37:199
Product Datasheets
Reconstitution Calculator
Molarity Calculator
Citations for SU 5416
The citations listed below are publications that use Tocris products. Selected citations for SU 5416 include:
12 Citations: Showing 1 - 10
-
Amino Acid Restriction Triggers Angiogenesis via GCN2/ATF4 Regulation of VEGF and H2S Production.
Authors: Longchamp Et al.
Cell 2018;173:117
-
TNFα drives pulmonary arterial hypertension by suppressing the BMP type-II receptor and altering NOTCH signalling.
Authors: Hurst
Nat Commun 2017;8:14079
-
Implication of Inflammation and Epigenetic Readers in Coronary Artery Remodeling in Patients With Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.
Authors: Meloche Et al.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2017;37:1513
-
Chronic Embolic Pulmonary Hypertension Caused by Pulmonary Embolism and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Inhibition.
Authors: Neto-Neves Et al.
Am J Pathol 2017;187:700
-
Pneumonectomy combined with SU5416 induces severe pulmonary hypertension in rats.
Authors: Happé Et al.
Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2016;310:L1088
-
Desert Hedgehog/Patch2 Axis Contributes to Vascular Permeability and Angiogenesis in Glioblastoma.
Authors: Azzi Et al.
Pulm Circ 2015;6:281
-
Selective enhancement of endothelial BMPR-II with BMP9 reverses pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Authors: Long Et al.
Nat Med 2015;21:777
-
Role of vascular endothelial growth factor signaling in Schistosoma-induced experimental pulmonary hypertension.
Authors: Chabon Et al.
J Neurophysiol 2014;4:289
-
KRIT1 protein depletion modifies endothelial cell behavior via increased vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling.
Authors: DiStefano Et al.
J Biol Chem 2014;289:33054
-
Effects of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGFR-2) inhibitor SU5416 on in vitro cultures of Plasmodium falciparum.
Authors: Hempel Et al.
Malar J 2014;13:201
-
Reversal of severe angioproliferative pulmonary arterial hypertension and right ventricular hypertrophy by combined phosphodiesterase-5 and endothelin receptor inhibition.
Authors: Cavasin Et al.
J Transl Med 2014;12:314
-
Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor treatment in combination with chemotherapy delays hematopoietic recovery due to decreased proliferation of bone marrow hematopoietic progenitor cells.
Authors: Novitskiy Et al.
J Thorac Oncol 2010;5:1410
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Small Molecule FAQsReviews for SU 5416
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 1 Review)
Have you used SU 5416?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:
We study rodent models of pulmonary hypertension where we inject SU5416 in addition to placing the animals in hypoxia to exacerbate the PH phenotype