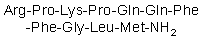Substance P
Purity: ≥95%
Biological Activity
Substance P is a sensory neuropeptide and inflammatory mediator. Exerts excitatory effects on central and peripheral neurons, constricts bronchioles and is involved in pain transmission.Technical Data
(Modifications: Met-11 = C-terminal amide)
The technical data provided above is for guidance only.
For batch specific data refer to the Certificate of Analysis.
Tocris products are intended for laboratory research use only, unless stated otherwise.
Background References
-
Substance P induction of itch-associated response mediated by cutaneous NK1 tachykinin receptors in mice.
Andoh et al.
J.Pharmacol.Exp.Ther., 1998;286:1140 -
Substance P.
Pernow et al.
Pharmacol.Rev., 1983;35:85 -
Substance P-induced inflammatory responses in guinea-pig skin: the effect of specific NK1 receptor antagonists and the role of endogenous mediators.
Walsh et al.
Br.J.Pharmacol., 1995;114:1343
Product Datasheets
Reconstitution Calculator
Molarity Calculator
Citations for Substance P
The citations listed below are publications that use Tocris products. Selected citations for Substance P include:
15 Citations: Showing 1 - 10
-
Neuropeptide-induced modulation of carcinogenesis in a metastatic breast cancer cell line (MDA-MB-231LUC+).
Authors: Gutierrez and Boada
Cancer Cell Int 2019;18:216
-
Substance P increases CCN2 dependent on TGF-beta yet Collagen Type I via TGF-beta1 dependent and independent pathways in tenocytes.
Authors: Frara Et al.
Connect Tissue Res 2018;59:30
-
Role of Corneal Stromal Cells on Epithelial Cell Function during Wound Healing.
Authors: Kowtharapu Et al.
Int J Mol Sci 2018;19
-
Endomorphin-2 Inhibition of Substance P Signaling within Lamina I of the Spinal Cord Is Impaired in Diabetic Neuropathic Pain Rats.
Authors: Wan Et al.
Front Mol Neurosci 2017;9:167
-
Retromer stops beta-arrestin 1 mediated signaling from internalized cannabinoid 2 receptors.
Authors: Nogueras-Ortiz
Mol Biol Cell 2017;28(24):3554
-
Increased CCN2, substance P and tissue fibrosis are associated with sensorimotor declines in a rat model of repetitive overuse injury.
Authors: Fisher Et al.
J Cell Commun Signal 2015;9:37
-
μ-Opioid receptor inhibition of substance P release from primary afferents disappears in neuropathic pain but not inflammatory pain.
Authors: Chen Et al.
Neuroscience 2014;267:67
-
Long-term potentiation of excitatory synaptic strength in spinothalamic tract neurons of the rat spinal cord.
Authors: Hur and Park
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 2013;17:553
-
Investigation of the functional expression of purine and pyrimidine receptors in porcine isolated pancreatic arteries.
Authors: Alsaqati Et al.
Purinergic Signal 2013;10:241
-
Evidence for regulatory diversity and auto-regulation at the TAC1 locus in sensory neurones.
Authors: Shanley Et al.
J Neurosci 2011;8:10
-
Investigating the effect of emetic compounds on chemotaxis in Dictyostelium identifies a non-sentient model for bitter and hot tastant research.
Authors: Robery Et al.
PLoS One 2011;6:e24439
-
Activation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 β is required for hyperDA and D2 receptor-mediated inhibition of synaptic NMDA receptor function in the rat prefrontal cortex.
Authors: Li Et al.
J Neurosci 2009;29:15551
-
A homogeneous fluorescent live-cell assay for measuring 7-transmembrane receptor activity and agonist functional selectivity through β-arrestin recruitment.
Authors: Hanson Et al.
Antioxid Redox Signal 2009;14:798
-
Substance P selectively decreases paired pulse depression in the rat hippocampal slice.
Authors: Wease and Davies
BMC Neurosci 2005;6:66
-
Role of neurokinin 3 receptors in supraoptic vasopressin and oxyt. neurons.
Authors: Howe Et al.
J Biomol Screen 2004;24:10103
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Peptide FAQsReviews for Substance P
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 1 Review)
Have you used Substance P?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:
Used to stimulate mast cells to degranulate.