ZM 447439
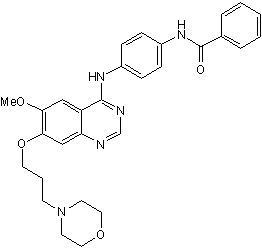
Chemical Name: N-[4-[[6-Methoxy-7-[3-(4-morpholinyl)propoxy]-4-quinazolinyl]amino]phenyl]benzamide
Purity: ≥98%
Biological Activity
ZM 447439 is a novel, selective ATP-competitive inhibitor of Aurora B kinase in vitro (IC50 values are 50, 250 and 1000 nM for Aurora B, C and A kinases respectively). Selective over a range of other kinases including cdk1 and PLK1 (IC50 > 10 μM). Inhibits cell division and displays selective toxicity towards proliferating tumor cells versus non-dividing cells.Technical Data
The technical data provided above is for guidance only.
For batch specific data refer to the Certificate of Analysis.
Tocris products are intended for laboratory research use only, unless stated otherwise.
Additional Information
Background References
-
Aurora B couples chromosome alignment with anaphase by targeting BubR1, Mad2, and Cenp-E to kinetochores.
Ditchfield et al.
J.Cell Biol., 2003;161:267 -
Discovery of novel and potent thiazoloquinazolines as selective Aurora A and B kinase inhibitors.
Jung et al.
J.Med.Chem., 2006;49:955 -
Validating Aurora B as an anti-cancer drug target.
Girdler et al.
J.Cell Sci., 2006;119:3664
Product Datasheets
Reconstitution Calculator
Molarity Calculator
Citations for ZM 447439
The citations listed below are publications that use Tocris products. Selected citations for ZM 447439 include:
50 Citations: Showing 1 - 10
-
PI(3,4)P2-mediated cytokinetic abscission prevents early senescence and cataract formation.
Authors: Gulluni Et al.
Science 2021;374
-
Oncogenic MYC amplifies mitotic perturbations.
Authors: Littler Et al.
Open Biol 2019;9:190136
-
Spatiotemporal control of mitotic exit during anaphase by an aurora B-Cdk1 crosstalk.
Authors: Afonso Et al.
Elife 2019;8
-
Interactions between N-terminal Modules in MPS1 Enable Spindle Checkpoint Silencing.
Authors: Pachis Et al.
Cell Rep 2019;26:2101
-
Lipid accumulation facilitates mitotic slippage-induced adaptation to anti-mitotic drug treatment.
Authors: Wong Et al.
Cell Death Discov 2018;4:109
-
Atypical Cadherin Dachsous1b Interacts with Ttc28 and Aurora B to Control Microtubule Dynamics in Embryonic Cleavages.
Authors: Chen Et al.
Dev Cell 2018;45:376
-
Dynamic kinetochore size regulation promotes microtubule capture and chromosome biorientation in mitosis.
Authors: Sacristan Et al.
Nat Cell Biol 2018;20:800
-
Mps1 kinase-dependent Sgo2 centromere localisation mediates cohesin protection in mouse oocyte meiosis I.
Authors: Yakoubi Et al.
Nat Commun 2017;8:694
-
Aurora-B kinase pathway controls the lateral to end-on conversion of kinetochore-microtubule attachments in human cells.
Authors: Shrestha
Nat Commun 2017;8(1):150
-
Distinct Roles of the Chromosomal Passenger Complex in the Detection of and Response to Errors in Kinetochore-Microtubule Attachment.
Authors: Haase Et al.
Dev Cell 2017;42:640
-
Haspin inhibition reveals functional differences of interchromatid axis-localized AURKB and AURKC.
Authors: Quartuccio Et al.
Mol Biol Cell 2017;28:2233
-
Ska3 Phosphorylated by Cdk1 Binds Ndc80 and Recruits Ska to Kinetochores to Promote Mitotic Progression.
Authors: Zhang Et al.
Curr Biol 2017;27:1477
-
Baculoviral delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 facilitates efficient genome editing in human cells.
Authors: Hindriksen Et al.
PLoS One 2017;12:e0179514
-
Kif4 Is Essential for Mouse Oocyte Meiosis.
Authors: Camlin Et al.
PLoS One 2017;12:e0170650
-
Aurora-A mediated histone H3 phosphorylation of threonine 118 controls condensin I and cohesin occupancy in mitosis.
Authors: Wike Et al.
Elife 2016;5:e11402
-
Haspin kinase regulates microtubule-organizing center clustering and stability through Aurora kinase C in mouse oocytes.
Authors: Balboula Et al.
J Cell Sci 2016;129:3648
-
Stable kinetochore-microtubule attachment is sufficient to silence the spindle assembly checkpoint in human cells.
Authors: Tauchman Et al.
J Cell Sci 2015;6:10036
-
Mio depletion links mTOR regulation to Aurora A and Plk1 activation at mitotic centrosomes.
Authors: Platani Et al.
J Cell Biol 2015;210:45
-
Multiple assembly mechanisms anchor the KMN spindle checkpoint platform at human mitotic kinetochores.
Authors: Kim and Yu
J Cell Biol 2015;208:181
-
Phosphorylation of myosin II-interacting guanine nucleotide exchange factor (MyoGEF) at threonine 544 by aurora B kinase promotes the binding of polo-like kinase 1 to MyoGEF.
Authors: Wu Et al.
J Biol Chem 2014;289:7142
-
Centmitor-1, a novel acridinyl-acetohydrazide, possesses similar molecular interaction field and antimitotic cellular phenotype as rigosertib, on 01910.Na.
Authors: Mäki-Jouppila Et al.
Nat Commun 2014;13:1054
-
Selective disruption of aurora C kinase reveals distinct functions from aurora B kinase during meiosis in mouse oocytes.
Authors: Balboula and Schindler
PLoS Genet 2014;10:e1004194
-
Oocytes isolated from dairy cows with reduced ovarian reserve have a high frequency of aneuploidy and alterations in the localization of progesterone receptor membrane component 1 and aurora kinase B.
Authors: Luciano Et al.
Biol Reprod 2013;88:58
-
Aurora B spatially regulates EB3 phosphorylation to coordinate daughter cell adhesion with cytokinesis.
Authors: Ferreira Et al.
J Cell Biol 2013;201:709
-
Spatiotemporal organization of Aurora-B by APC/CCdh1 after mitosis coordinates cell spreading through FHOD1.
Authors: Floyd Et al.
Cell Cycle 2013;126:2845
-
In vivo FRET imaging revealed a regulatory role of RanGTP in kinetochore-microtubule attachments via Aurora B kinase.
Authors: Lee Et al.
PLoS One 2012;7:e45836
-
A cell cycle role for the epigenetic factor CTCF-L/BORIS.
Authors: Rosa-Garrido Et al.
PLoS One 2012;7:e39371
-
Haspin inhibitors reveal centromeric functions of Aurora B in chromosome segregation.
Authors: Wang Et al.
J Cell Biol 2012;199:251
-
Appearance and heterochromatin localization of HP1α in early mouse embryos depends on cytoplasmic clock and H3S10 phosphorylation.
Authors: Meglicki Et al.
Cell Cycle 2012;11:2189
-
The chromosomal passenger complex activates Polo kinase at centromeres.
Authors: Carmena Et al.
PLoS Biol 2012;10:e1001250
-
Quantitative phosphoproteomics identifies substrates and functional modules of Aurora and Polo-like kinase activities in mitotic cells.
Authors: Kettenbach Et al.
Sci Signal 2011;4:rs5
-
Aurora kinase B activity is modulated by thyroid hormone during transcriptional activation of pituitary genes.
Authors: Tardáguila Et al.
Mol Endocrinol 2011;25:385
-
Zwint-1 is a novel Aurora B substrate required for the assembly of a dynein-binding platform on kinetochores.
Authors: Kasuboski Et al.
Mol Biol Cell 2011;22:3318
-
Polo-box domain inhibitor poloxin activates the spindle assembly checkpoint and inhibits tumor growth in vivo.
Authors: Yuan Et al.
Am J Pathol 2011;179:2091
-
Formation of stable attachments between kinetochores and microtubules depends on the B56-PP2A phosphatase.
Authors: Foley Et al.
Nat Cell Biol 2011;13:1265
-
Role of a novel coiled-coil domain-containing protein CCDC69 in regulating central spindle assembly.
Authors: Pal Et al.
J Am Soc Nephrol 2010;9:4117
-
VHL inactivation induces HEF1 and Aurora kinase A.
Authors: Xu Et al.
J Cell Biol 2010;21:2041
-
Relocation of the chromosomal passenger complex prevents mitotic checkpoint engagement at anaphase.
Authors: Vázquez-Novelle and Petronczki
Curr Biol 2010;20:1402
-
Plk1 negatively regulates Cep55 recruitment to the midbody to ensure orderly abscission.
Authors: Bastos and Barr
J Cell Biol 2010;191:751
-
Release of Mps1 from kinetochores is crucial for timely anaphase onset.
Authors: Jelluma Et al.
Cell Cycle 2010;191:281
-
Epigenetic centromere specification directs aurora B accumulation but is insufficient to efficiently correct mitotic errors.
Authors: Bassett Et al.
Mol Cancer Ther 2010;190:177
-
Targeting mitotic exit leads to tumor regression in vivo: Modulation by Cdk1, Mastl, and the PP2A/B55α,δ phosphatase.
Authors: Manchado Et al.
Cancer Cell 2010;18:641
-
The Aurora kinase inhibitor ZM447439 accelerates first meiosis in mouse oocytes by overriding the spindle assembly checkpoint.
Authors: Lane Et al.
Reproduction 2010;140:521
-
Human condensin function is essential for centromeric chromatin assembly and proper sister kinetochore orientation.
Authors: Samoshkin Et al.
PLoS One 2009;4:e6831
-
Discovery and exploitation of inhibitor-resistant aurora and polo kinase mutants for the analysis of mitotic networks.
Authors: Scutt Et al.
J Biol Chem 2009;284:15880
-
The Nup107-160 nucleoporin complex promotes mitotic events via control of the localization state of the chromosome passenger complex.
Authors: Platani Et al.
Mol Biol Cell 2009;20:5260
-
Cell cycle dependent degradation of MCAK: evidence against a role in anaphase chromosome movement.
Authors: Ganguly Et al.
Toxins (Basel) 2008;7:3187
-
A mitotic GlcNAcylation/phosphorylation signaling complex alters the posttranslational state of the cytoskeletal protein vimentin.
Authors: Slawson Et al.
Mol Biol Cell 2008;19:4130
-
Cancer cells display profound intra- and interline variation following prolonged exposure to antimitotic drugs.
Authors: Gascoigne and Taylor
Cancer Cell 2008;14:111
-
Frequent overexpression of aurora B kinase, a novel drug target, in non-small cell lung carcinoma patients.
Authors: Vischioni Et al.
Mol Cancer Ther 2006;5:2905
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Small Molecule FAQsReviews for ZM 447439
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review ZM 447439 and earn rewards!
Have you used ZM 447439?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image