Human Fas Ligand/TNFSF6 Antibody Summary
Pro134-Leu281
Accession # P48023
Applications
Human Fas Ligand/TNFSF6 Sandwich Immunoassay
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
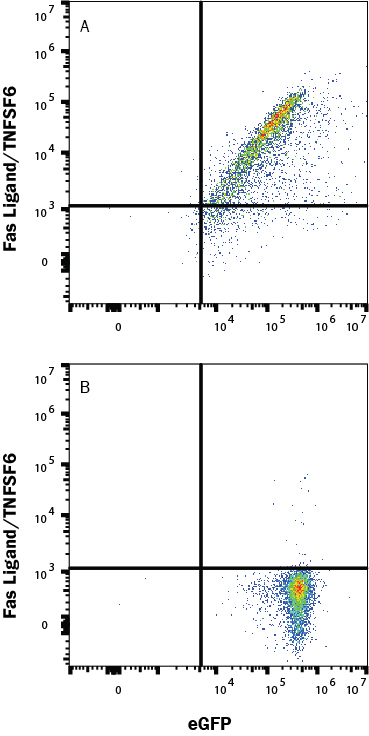 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Fas Ligand/TNFSF6 in HEK293 Human Cell Line Transfected with Human Fas Ligand/TNFSF6 and eGFP by Flow Cytometry. HEK293 human embryonic kidney cell line transfected with (A) Fas Ligand/TNFSF6 or (B) irrelevant protein, and eGFP were stained with Mouse Anti-Human Fas Ligand/TNFSF6 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB126) followed by Allophycocyanin-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # F0101B). Quadrant markers were set based Mouse IgG2B Isotype Control Antibody staining (Catalog # MAB0041, data not shown). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.
 View Larger
View Larger
Cytotoxicity Induced by Fas Ligand/TNFSF6 and Neutralization by Human Fas Ligand/TNFSF6 Antibody. In the presence of a cross-linking antibody, Mouse polyHistidine Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB050), Recombinant Human Fas Ligand/TNFSF6 (Catalog # 126-FL) induces cytotoxicity in the Jurkat human acute T cell leukemia cell line in a dose-dependent manner (orange line). Under these conditions, cytotoxicity elicited by Recombinant Human Fas Ligand/TNFSF6 (2 ng/mL) is neutralized (green line) by increasing concentrations of Human Fas Ligand/TNFSF6 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB126). The ND50 is typically 1-5 ng/mL.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Fas Ligand/TNFSF6
Fas Ligand (FasL), also known as CD178, CD95L, or TNFSF6, is a 40 kDa type II transmembrane member of the TNF superfamily of proteins. Its ability to induce apoptosis in target cells plays an important role in the development, homeostasis, and function of the immune system (1). Mature human Fas Ligand consists of a 179 amino acid (aa) extracellular domain (ECD), a 22 aa transmembrane segment, and a 80 aa cytoplasmic domain (2). Within the ECD, human Fas Ligand shares 81% and 78% aa sequence identity with mouse and rat Fas Ligand, respectively. Both mouse and human Fas Ligand are active on mouse and human cells (2, 3). Fas Ligand is expressed on the cell surface as a nondisulfide-linked homotrimer on activated CD4+ Th1 cells, CD8+ cytotoxic T cells, and NK cells (1). Fas Ligand binding to Fas/CD95 on an adjacent cell triggers apoptosis in the Fas‑expressing cell (2, 4). Fas Ligand also binds DcR3 which is a soluble decoy receptor that interferes with Fas Ligand-induced apoptosis (5). Fas Ligand can be released from the cell surface by metalloproteinases as a 26 kDa soluble molecule which remains trimeric (6, 7). Shed Fas Ligand retains the ability to bind Fas, although its ability to trigger apoptosis is dramatically reduced (6, 7). In the absence of TGF‑ beta, however, Fas Ligand/Fas interactions instead promote neutrophil-mediated inflammatory responses (3, 8). Fas Ligand itself transmits reverse signals that costimulate the proliferation of freshly antigen-stimulated T cells (9). Fas Ligand-induced apoptosis plays a central role in the development of immune tolerance and the maintance of immune privileged sites (10). This function is exploited by tumor cells which evade immune surveillance by upregulating Fas Ligand to kill tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (8, 11). In gld mice, a Fas Ligand point mutation is the cause of severe lymphoproliferation and systemic autoimmunity (12, 13).
- Lettau, M. et al. (2008) Curr. Med. Chem. 15:1684.
- Takahashi, T. et al. (1994) Int. Immunol. 6:1567.
- Seino, K-I. et al. (1998) J. Immunol. 161:4484.
- Suda, T. et al. (1993) Cell 75:1169.
- Pitti, R.M. et al. (1998) Nature 396:699.
- Schneider, P. et al. (1998) J. Exp. Med. 187:1205.
- Tanaka, M. et al. (1998) Nature Med. 4:31.
- Chen, J-J. et al. (1998) Science 282:1714.
- Suzuki, I. and P.J. Fink (2000) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97:1707.
- Ferguson, T.A. and T.S. Griffith (2006) Immunol. Rev. 213:228.
- Ryan, A.E. et al. (2005) Cancer Res. 65:9817.
- Takahashi, T. et al. (1994) Cell 76:969.
- Lynch, D.H. et al. (1994) Immunity 1:131.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human Fas Ligand/TNFSF6 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
15
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Ex vivo-expanded human CD19+TIM-1+ regulatory B cells suppress immune responses in vivo and are dependent upon the TIM-1/STAT3 axis
Authors: S Shankar, J Stolp, SC Juvet, J Beckett, PS Macklin, F Issa, J Hester, KJ Wood
Nature Communications, 2022-06-03;13(1):3121.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
The bioactivity of soluble Fas ligand is modulated by key amino acids of its stalk region
Authors: O Kajikawa, R Herrero, YH Chow, CF Hung, G Matute-Bel
PLoS ONE, 2021-06-17;16(6):e0253260.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Functional Assay -
Leucine-rich repeat neuronal protein-1 suppresses apoptosis of gastric cancer cells through regulation of Fas/FasL
Authors: B Liu, Y Zhang, Y Fan, S Wang, Z Li, M Deng, C Li, J Wang, R Ma, X Wang, Y Wang, L Xu, K Hou, X Che, Y Liu, X Qu
Cancer Sci., 2019-06-10;110(7):2145-2155.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Immunological Properties of Human Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells
Authors: M Idelson, R Alper, A Obolensky, N Yachimovic, J Rachmilewi, A Ejzenberg, E Beider, E Banin, B Reubinoff
Stem Cell Reports, 2018-08-16;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Folate receptor 1 (FOLR1) targeted chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells for the treatment of gastric cancer
Authors: M Kim, S Pyo, CH Kang, CO Lee, HK Lee, SU Choi, CH Park
PLoS ONE, 2018-06-06;13(6):e0198347.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Granulocytic myeloid derived suppressor cells from human cord blood modulate T-helper-cell response towards an anti-inflammatory phenotype
Authors: N Köstlin, M Vogelmann, B Spring, J Schwarz, J Feucht, C Härtel, TW Orlikowsky, CF Poets, C Gille
Immunology, 2017-06-08;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Interleukin-10-producing LAG3(+) regulatory T cells are associated with disease activity and abatacept treatment in rheumatoid arthritis
Authors: S Nakachi, S Sumitomo, Y Tsuchida, H Tsuchiya, M Kono, R Kato, K Sakurai, N Hanata, Y Nagafuchi, S Tateishi, H Kanda, T Okamura, K Yamamoto, K Fujio
Arthritis Res. Ther., 2017-05-16;19(1):97.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Combination of IAP antagonist and IFN? activates novel caspase-10- and RIPK1-dependent cell death pathways
Authors: MC Tanzer, N Khan, JA Rickard, N Etemadi, N Lalaoui, SK Spall, JM Hildebrand, D Segal, M Miasari, D Chau, WL Wong, M McKinlay, SK Chunduru, CA Benetatos, SM Condon, JE Vince, MJ Herold, J Silke
Cell Death Differ, 2017-01-20;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Biliary tract instillation of a SMAC mimetic induces TRAIL-dependent acute sclerosing cholangitis-like injury in mice
Authors: ME Guicciardi, A Krishnan, SF Bronk, P Hirsova, TS Griffith, GJ Gores
Cell Death Dis, 2017-01-05;8(1):e2535.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
The Therapeutic Effect of Pamidronate on Lethal Avian Influenza A H7N9 Virus Infected Humanized Mice.
Authors: Zheng J, Wu W, Liu Y, Xiang Z, Liu M, Chan K, Lau S, Lam K, To K, Chan J, Li L, Chen H, Lau Y, Yuen K, Tu W
PLoS ONE, 2015-08-18;10(8):e0135999.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Reciprocal complementation of the tumoricidal effects of radiation and natural killer cells.
Authors: Yang, Kai-Lin, Wang, Yu-Shan, Chang, Chao-Chu, Huang, Su-Chen, Huang, Yi-Chun, Chi, Mau-Shin, Chi, Kwan-Hwa
PLoS ONE, 2013-04-25;8(4):e61797.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Potent anti-tumor killing activity of the multifunctional Treg cell line HOZOT against human tumors with diverse origins.
Authors: Inoue T, Tashiro Y, Takeuchi M
Int. J. Oncol., 2011-03-03;38(5):1299-306.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
KiSS1 metastasis suppressor gene product induces suppression of tyrosine kinase receptor signaling to Akt, tumor necrosis factor family ligand expression, and apoptosis.
Authors: Navenot JM, Fujii N, Peiper SC
Mol. Pharmacol., 2009-02-06;75(5):1074-83.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase unmasks a CD30-triggered apoptotic pathway in anaplastic large cell lymphoma cells.
Authors: Krysov SV, Krysov</LastName><ForeNam SV</Initia, Rowley TF, Al-Shamkhani A
Mol. Cancer Ther., 2007-02-01;6(2):703-11.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
A novel mechanism of CD40-induced apoptosis of carcinoma cells involving TRAF3 and JNK/AP-1 activation.
Authors: Georgopoulos NT, Steele LP, Thomson MJ, Selby PJ, Southgate J, Trejdosiewicz LK
Cell Death Differ., 2006-01-20;13(10):1789-801.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human Fas Ligand/TNFSF6 Antibody
Average Rating: 4.5 (Based on 2 Reviews)
Have you used Human Fas Ligand/TNFSF6 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:
the Fas/FasL pathways in CAR-T cell apoptosis is significant rescued upon blockade by combined Anti-Fas and Anti-FasL Antibody.






