Microglia Activation During Neuroinflammation: Microglia Polarization
Click on one of the other stages of microglia activation to see the molecules involved in that process. Click on Overview to see the generalized process of microglia activation during neuroinflammation.
IFN-gamma
GM-CSF
IL-1 beta/IL-1F2
IL-6
IFN-gamma
GM-CSF
IL-1 beta/IL-1F2
IL-6
ROS
RNS
ROS
RNS
CCL3/MIP-1 alpha
CCL4/MIP-1 beta
CCL5/RANTES
CCL8/MCP-2
CCL11/Eotaxin
CCL12/MCP-5
CCL15/MIP-1 delta
CCL19/MIP-3 beta
CCL20/MIP-3 alpha
CXCL1/GRO alpha/KC/CINC-1
CXCL9/MIG
CXCL10/IP-10
CXCL11/I-TAC
CXCL13/BLC/BCA-1
CX3CL1/Fractalkine
CCL3/MIP-1 alpha
CCL4/MIP-1 beta
CCL5/RANTES
CCL8/MCP-2
CCL11/Eotaxin
CCL12/MCP-5
CCL15/MIP-1 delta
CCL19/MIP-3 beta
CCL20/MIP-3 alpha
CXCL1/GRO alpha/KC/CINC-1
CXCL9/MIG
CXCL10/IP-10
CXCL11/I-TAC
CXCL13/BLC/BCA-1
CX3CL1/Fractalkine
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
MMP-9
Glutamate
MMP-9
Glutamate
IL-2
IL-6
IL-12
IL-15
IL-17/IL-17A
IL-18/IL-1F4
IL-23
IFN-gamma
TNF-alpha
IL-2
IL-6
IL-12
IL-15
IL-17/IL-17A
IL-18/IL-1F4
IL-23
IFN-gamma
TNF-alpha
COX-2
COX-2
IL-13
IL-13
IGF-I
PDGF
IGF-I
PDGF
YM1/Chitinase 3-like 3
YM1/Chitinase 3-like 3
CCL14
CCL17/TARC
CCL18/PARC
CCL22/MDC
CCL23/MPIF-1
CCL24/Eotaxin-2/MPIF-2
CCL26/Eotaxin-3
CCL14
CCL17/TARC
CCL18/PARC
CCL22/MDC
CCL23/MPIF-1
CCL24/Eotaxin-2/MPIF-2
CCL26/Eotaxin-3
IL-4
IL-10
IL-13
TGF-beta
IL-4
IL-10
IL-13
TGF-beta
Transglutaminase 2/TGM2
PPAR gamma/NR1C3
Transglutaminase 2/TGM2
PPAR gamma/NR1C3
Functions of M1 Microglia- Inflammation
- Phagocytosis
- Blood-brain barrier permeabilization
- Neural death
- Recruitment and differentiation
of Th1 and Th17 cells - Antigen presentation
of Th1 and Th17 cells
Functions of M1 Microglia- Inflammation
- Phagocytosis
- Blood-brain barrier permeabilization
- Neural death
- Recruitment and differentiation
of Th1 and Th17 cells - Antigen presentation
of Th1 and Th17 cells
Functions of M2 Microglia- Attenuation of inflammatory response
- Phagocytosis
- Tissue remodeling, repair, and healing
- Recruitment and differentiation
of Th2 and Treg cells
of Th2 and Treg cells
Functions of M2 Microglia- Attenuation of inflammatory response
- Phagocytosis
- Tissue remodeling, repair, and healing
- Recruitment and differentiation
of Th2 and Treg cells
of Th2 and Treg cells
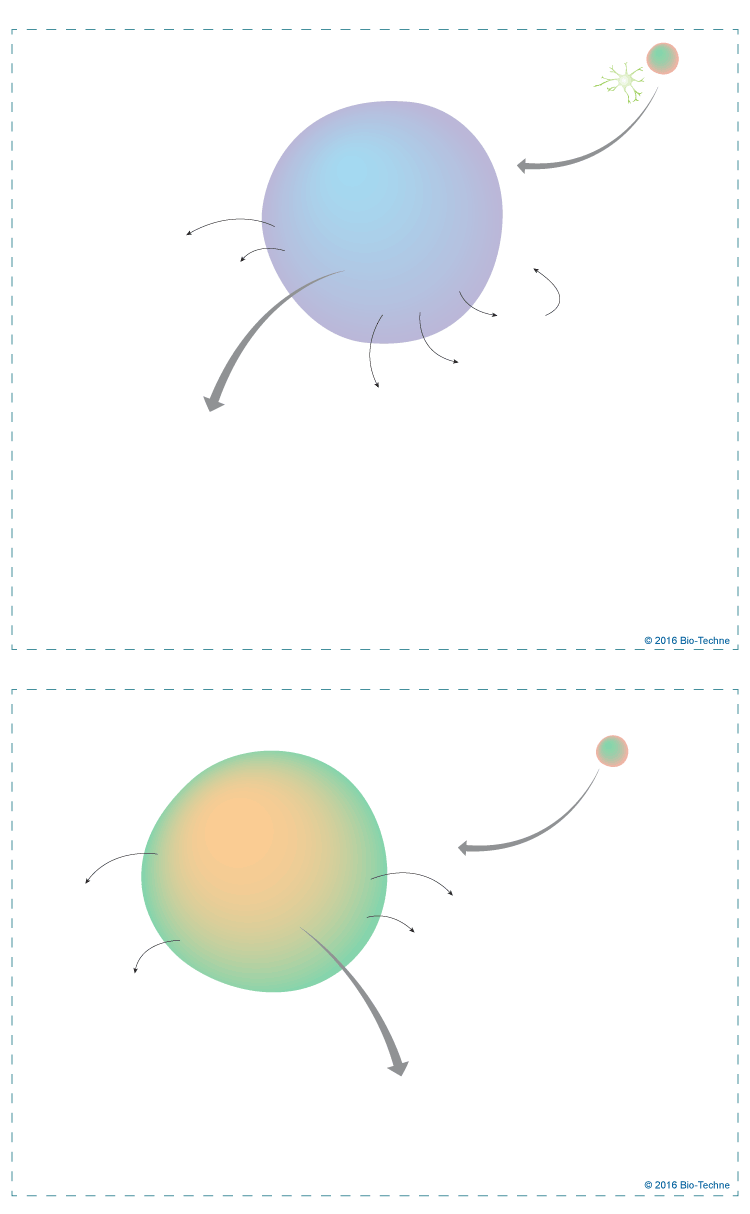
Upon activation, microglia are capable of acquiring diverse phenotypes that display different cell surface and intracellular markers, secrete different factors, and exhibit different functions. Furthermore, the cells are capable of shifting between the different phenotypes during an inflammatory response. M1 microglia are typically the initial responders to an insult. Cytokines released by astrocytes and Th1 cells, including IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha, bacterial-derived products, such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and trauma-induced cellular debris will polarize microglia toward the M1 phenotype. M1 microglia will produce proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and redox signaling molecules. They will also express scavenger receptors, and MHC class II and co-stimulatory molecules on their cell surface. These actions allow M1 microglia to kill and phagocytize foreign and cellular debris, and recruit and differentiate T cells in order to launch an immune response. Over time, the inflammatory response is shifted to be more anti-inflammatory, which is facilitated by M2 microglia. Microglia are polarized to the M2 phenotype following stimulation with IL-4 or IL-13, which are typically released from Th2 cells. M2 microglia secrete anti-inflammatory cytokines and growth factors that promote attenuation of the inflammatory response and repair of damaged tissue.
Recent research has shown that different M2 phenotypic variations, termed M2a, M2b, M2c, and M2d exist. In fact, it has been suggested that microglia activation is highly complex and dynamic. It is thought that there is a range of activation states for microglial cells that span from the M1 to M2 phenotypes, and the phenotype of the activated microglia will fall somewhere along this spectrum depending the signal encountered.
To learn more about our products for neuroinflammation, please visit our Neuroinflammation Research Area.
Get Print Copy of this Pathway

