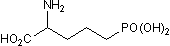
DL-AP5
Chemical Name: DL-2-Amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid
Purity: ≥98%
Biological Activity
DL-AP5 is a racemic mixture of the D- and L-isomers of AP5, a selective NMDA receptor antagonist that competes with glutamate binding and is commonly used to inhibit NMDA-dependent synaptic plasticity. D-AP5 (Cat. No. 0106) is the more active isomer and displays approximately 52-fold higher potency than the L-isomer, L-AP5 (Cat. No. 0107). In vitro D-AP5 reduces NMDA-induced depolarization of cortical neurons, with no effect on the response to L-Quisqualic acid (Cat. No. 0188) or Kainic acid (Cat. No. 0222). Following spinal injection of D-AP5, NMDA-response is rapidly reduced, with no effect seen on spontaneously active neurons.D-isomer, L-isomer and sodium salt also available.
Technical Data
The technical data provided above is for guidance only.
For batch specific data refer to the Certificate of Analysis.
Tocris products are intended for laboratory research use only, unless stated otherwise.
Additional Information
Background References
-
The effect of a series of ω-phosphonic-α-carboxylic amino acids on electrically evoked and amino acid induced responses in isolated spinal cord preparations.
Evans et al.
Br.J.Pharmacol., 1982;75:65 -
Actions of D and L forms of 2-amino-5-phosphonovalerate and 2-amino-4-phosphonobutyrate in the cat spinal cord.
Davies and Watkins
Brain Res., 1982;235:378
Product Datasheets
Reconstitution Calculator
Molarity Calculator
Citations for DL-AP5
The citations listed below are publications that use Tocris products. Selected citations for DL-AP5 include:
90 Citations: Showing 1 - 10
-
Multi-target action of β-alanine protects cerebellar tissue from ischemic damage.
Authors: Kopach Et al.
Cell Death Dis 2022;13:747
-
TMEM16B regulates anxiety-related behavior and GABAergic neuronal signaling in the central lateral amygdala.
Authors: Li Et al.
Elife 2019;8
-
Lmx1b is required at multiple stages to build expansive serotonergic axon architectures.
Authors: Donovan Et al.
Elife 2019;8
-
Differences in glutamate uptake between cortical regions impact neuronal NMDA receptor activation.
Authors: Romanos Et al.
Commun Biol 2019;2:127
-
Endocannabinoid Signaling Mediates Local Dendritic Coordination between Excitatory and Inhibitory Synapses.
Authors: Hu Et al.
Cell Rep 2019;27:666
-
Somatostatin Interneurons Promote Neuronal Synchrony in the Neonatal Hippocampus.
Authors: Flossmann Et al.
Cell Rep 2019;26:3173
-
Differential Regulation of Syngap1 Translation by FMRP Modulates eEF2 Mediated Response on NMDAR Activity.
Authors: Paul Et al.
Front Mol Neurosci 2019;12:97
-
Prenatal selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) exposure induces working memory and social recognition deficits by disrupting inhibitory synaptic networks in male mice.
Authors: Yu Et al.
Mol Brain 2019;12:29
-
Design and validation of a foldable and photovoltaic wide-field epiretinal prosthesis.
Authors: Ferlauto Et al.
Nat Commun 2018;9:992
-
Pathway-specific alterations of cortico-amygdala transmission in an arthritis pain model.
Authors: Kiritoshi and Neugebauer
ACS Chem Neurosci 2018;9:2252
-
Cerebrospinal Fluid-Contacting Neurons Sense pH Changes and Motion in the Hypothalamus.
Authors: Jalalvand Et al.
J Neurosci 2018;38:7713
-
AKAP150 Palmitoylation Regulates Synaptic Incorporation of Ca2+-Permeable AMPA Receptors to Control LTP.
Authors: Purkey Et al.
Cell Rep 2018;25:974
-
Excitotoxic inactivation of constitutive oxidative stress detoxification pathway in neurons can be rescued by PKD1.
Authors: Pose-Utrilla Et al.
Nat Commun 2017;8:2275
-
Transcriptional Architecture of Synaptic Communication Delineates GABAergic Neuron Identity.
Authors: Paul Et al.
Cell 2017;171:522
-
Astrocytes modulate thalamic sensory processing via mGlu2 receptor activation.
Authors: Copeland Et al.
Neuropharmacology 2017;121:100
-
Loss of MeCP2 in cholinergic neurons causes part of RTT-like phenotypes via α7 receptor in hippocampus.
Authors: Zhang Et al.
Cell Res 2016;26:728
-
Electrophysiological Assessment of Serotonin and GABA Neuron Function in the Dorsal Raphe during the Third Trimester Equivalent Developmental Period in Mice(1,2,3).
Authors: Morton Et al.
Eneuro 2016;2
-
Rapid dispersion of SynGAP from synaptic spines triggers AMPA receptor insertion and spine enlargement during LTP.
Authors: Araki Et al.
Neuron 2015;85:173
-
Development of a neuroprotective peptide that preserves survival pathways by preventing Kidins220/ARMS calpain processing induced by excitotoxicity.
Authors: Gamir-Morralla Et al.
Cell Death Dis 2015;6:e1939
-
IL-1 interacts with ethanol effects on GABAergic transmission in the mouse central amygdala.
Authors: Bajo Et al.
Front Pharmacol 2015;6:49
-
GluN2B-Containing NMDA Receptors Regulate AMPA Receptor Traffic through Anchoring of the Synaptic Proteasome.
Authors: Ferreira Et al.
J Neurosci 2015;35:8462
-
PAR1-activated astrocytes in the nucleus of the solitary tract stimulate adjacent neurons via NMDA receptors.
Authors: Vance Et al.
J Neurosci 2015;35:776
-
Cortical Synaptic Inhibition Declines during Auditory Learning.
Authors: Sarro Et al.
J Neurosci 2015;35:6318
-
Muscarinic receptors modulate dendrodendritic inhibitory synapses to sculpt glomerular output.
Authors: Liu Et al.
J Neurosci 2015;35:5680
-
IGF-1 Signaling Plays an Important Role in the Formation of Three-Dimensional Laminated Neural Retina and Other Ocular Structures From Human Embryonic Stem Cells.
Authors: Mellough Et al.
Stem Cells 2015;33:2416
-
In vivo activation of the SK channel in the spinal cord reduces the NMDA receptor antagonist dose needed to produce antinociception in an inflammatory pain model.
Authors: Hipólito Et al.
Pain 2015;156:849
-
Development and function of human cerebral cortex neural networks from pluripotent stem cells in vitro.
Authors: Kirwan Et al.
Development 2015;142:3178
-
Rosiglitazone Suppresses In Vitro Seizures in Hippocampal Slice by Inhibiting Presynaptic Glutamate Release in a Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy.
Authors: Wong Et al.
PLoS One 2015;10:e0144806
-
Both neurons and astrocytes exhibited tetrodotoxin-resistant metabotropic glutamate receptor-dependent spontaneous slow Ca2+ oscillations in striatum.
Authors: Tamura Et al.
PLoS One 2014;9:e85351
-
The Ca2+ sensor protein swiprosin-1/EFhd2 is present in neurites and involved in kinesin-mediated transport in neurons.
Authors: Purohit Et al.
PLoS One 2014;9:e103976
-
Dynamic properties of the alkaline vesicle population at hippocampal synapses.
Authors: Röther Et al.
PLoS One 2014;9:e102723
-
LTD expression is independent of glutamate receptor subtype.
Authors: Granger and Nicoll
Front Synaptic Neurosci 2014;6:15
-
Synapse elimination and learning rules co-regulated by MHC class I H2-Db.
Authors: Lee Et al.
Nature 2014;509:195
-
Repeated binge-like ethanol drinking alters ethanol drinking patterns and depresses striatal GABAergic transmission.
Authors: Wilcox Et al.
Neuropsychopharmacology 2014;39:579
-
Nociceptin/orphanin FQ decreases glutamate transmission and blocks ethanol-induced effects in the central amygdala of naive and ethanol-dependent rats.
Authors: Kallupi Et al.
Neuropsychopharmacology 2014;39:1081
-
Phasic, nonsynaptic GABA-A receptor-mediated inhibition entrains thalamocortical oscillations.
Authors: Rovó Et al.
J Neurosci 2014;34:7137
-
A novel mechanism for nicotinic potentiation of glutamatergic synapses.
Authors: Halff Et al.
J Neurosci 2014;34:2051
-
Moderate Alcohol Exposure during the Rat Equivalent to the Third Trimester of Human Pregnancy Alters Regulation of GABAA Receptor-Mediated Synaptic Transmission by DA in the Basolateral Amygdala.
Authors: Diaz Et al.
Front Pediatr 2014;2:46
-
GPR35 activation reduces Ca2+ transients and contributes to the kynurenic acid-dependent reduction of synaptic activity at CA3-CA1 synapses.
Authors: Berlinguer-Palmini Et al.
PLoS One 2013;8:e82180
-
Low voltage activation of KCa1.1 current by Cav3-KCa1.1 complexes.
Authors: Rehak Et al.
PLoS One 2013;8:e61844
-
Autism-related deficits via dysregulated eIF4E-dependent translational control.
Authors: Gkogkas Et al.
Nature 2013;493:371
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase and glycogen synthase kinase 3β regulate gephyrin postsynaptic aggregation and GABAergic synaptic function in a calpain-dependent mechanism.
Authors: Tyagarajan Et al.
J Biol Chem 2013;288:9634
-
Increased neuronal activity fragments the Golgi complex.
Authors: Thayer Et al.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2013;110:1482
-
Genetic inhibition of CaMKII in dorsal striatal medium spiny neurons reduces functional excitatory synapses and enhances intrinsic excitability.
Authors: Klug Et al.
PLoS One 2012;7:e45323
-
Local hypocretin-1 modulates terminal DA concentration in the nucleus accumbens shell.
Authors: Patyal Et al.
Front Behav Neurosci 2012;6:82
-
Chronic ethanol up-regulates the synaptic expression of the nuclear translational regulatory protein AIDA-1 in primary hippocampal neurons.
Authors: Mulholland Et al.
Alcohol 2012;46:569
-
Disruption of Eaat2b, a glutamate transporter, results in abnormal motor behaviors in developing zebrafish.
Authors: McKeown Et al.
Dev Biol 2012;362:162
-
Mixed electrical-chemical transmission between hippocampal mossy fibers and pyramidal cells.
Authors: Vivar Et al.
Eur J Neurosci 2012;35:76
-
Activity-dependent regulation of inhibition via GAD67.
Authors: Lau and Murthy
J Neurosci 2012;32:8521
-
LTP induction translocates cortactin at distant synapses in wild-type but not Fmr1 knock-out mice.
Authors: Seese Et al.
J Neurosci 2012;32:7403
-
Endocannabinoid-mediated long-term depression of afferent excitatory synapses in hippocampal pyramidal cells and GABAergic interneurons.
Authors: Peterfi Et al.
J Neurosci 2012;32:14448
-
Spinal cord NMDA receptor-mediated activation of mammalian target of rapamycin is required for the development and maintenance of bone cancer-induced pain hypersensitivities in rats.
Authors: Shih Et al.
J Pain 2012;13:338
-
Focal adhesion kinase regulates actin nucleation and neuronal filopodia formation during axonal growth.
Authors: Chacón Et al.
Development 2012;139:3200
-
Actin-dependent rapid recruitment of reluctant synaptic vesicles into a fast-releasing vesicle pool.
Authors: Lee Et al.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2012;109:E765
-
Specificity and actions of an arylaspartate inhibitor of glutamate transport at the Schaffer collateral-CA1 pyramidal cell synapse.
Authors: Sun Et al.
PLoS One 2011;6:e23765
-
GABAergic signalling in a neurogenic niche of the turtle spinal cord.
Authors: Reali Et al.
J Physiol 2011;589:5633
-
Neurogranin phosphorylation fine-tunes long-term potentiation.
Authors: Zhong Et al.
Eur J Neurosci 2011;33:244
-
Functional NMDA receptors at axonal growth cones of young hippocampal neurons.
Authors: Wang Et al.
J Neurosci 2011;31:9289
-
Homeostatic synaptic plasticity through changes in presynaptic calcium influx.
Authors: Zhao Et al.
J Neurosci 2011;31:7492
-
Neto1 is an auxiliary subunit of native synaptic kainate receptors.
Authors: Tang Et al.
J Neurosci 2011;31:10009
-
SynGAP moves out of the core of the postsynaptic density upon depolarization.
Authors: Yang Et al.
Neuroscience 2011;192:132
-
M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor expression confers differential cholinergic modulation to neurochemically distinct hippocampal basket cell subtypes.
Authors: Rio Et al.
J Neurosci 2010;30:6011
-
SAP102 is a highly mobile MAGUK in spines.
Authors: Zheng Et al.
J Neurosci 2010;30:4757
-
Control of CA3 output by feedforward inhibition despite developmental changes in the excitation-inhibition balance.
Authors: Torborg Et al.
J Neurosci 2010;30:15628
-
Reduction in synaptic GABA release contributes to target-selective elevation of PVN neuronal activity in rats with myocardial infarction.
Authors: Han Et al.
Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2010;299:R129
-
Glutamate co-release at GABA/glycinergic synapses is crucial for the refinement of an inhibitory map.
Authors: Noh Et al.
Nat Neurosci 2010;13:232
-
Regulation of stargazin synaptic trafficking by C-terminal PDZ ligand phosphorylation in bidirectional synaptic plasticity.
Authors: Stein and Chetkovich
J Neurochem 2010;113:42
-
A mouse model of the human Fragile X syndrome I304N mutation.
Authors: Zang Et al.
PLoS Genet 2009;5:e1000758
-
Compensatory enhancement of intrinsic spiking upon NKCC1 disruption in neonatal hippocampus.
Authors: Sipilä Et al.
J Neurosci 2009;29:6982
-
Co-transmission of DA and GABA in periglomerular cells.
Authors: Maher and Westbrook
J Neurophysiol 2008;99:1559
-
Electrophysiology and pharmacology of striatal neuronal dysfunction induced by mitochondrial complex I inhibition.
Authors: Costa Et al.
J Neurosci 2008;28:8040
-
NMDA receptor blockade with Mem. attenuates white matter injury in a rat model of periventricular leukomalacia.
Authors: Manning Et al.
J Neurosci 2008;28:6670
-
Competition between calcium-activated K+ channels determines cholinergic action on firing properties of basolateral amygdala projection neurons.
Authors: Power and Sah
J Neurosci 2008;28:3209
-
White matter vulnerability to ischemic injury increases with age because of enhanced excitotoxicity.
Authors: Baltan Et al.
J Neurosci 2008;28:1479
-
Sequential changes in AMPA receptor targeting in the developing neocortical excitatory circuit.
Authors: Brill and Huguenard
J Neurosci 2008;28:13918
-
DA enhances fast excitatory synaptic transmission in the extended amygdala by a CRF-R1-dependent process.
Authors: Kash Et al.
J Neurosci 2008;28:13856
-
Neuregulin-1 enhances depolarization-induced GABA release.
Authors: Woo Et al.
Neuron 2007;54:599
-
Long-term modifications in the strength of excitatory associative inputs in the piriform cortex.
Authors: Young and Sun
Chem Senses 2007;32:783
-
Metabotropic receptor-dependent long-term depression persists in the absence of protein synthesis in the mouse model of fragile X syndrome.
Authors: Nosyreva and Huber
J Neurophysiol 2006;95:3291
-
Regulation of thalamocortical patterning and synaptic maturation by NeuroD2.
Authors: Ince-Dunn Et al.
Neuron 2006;49:683
-
Insufficient sleep reversibly alters bidirectional synaptic plasticity and NMDA receptor function.
Authors: Kopp Et al.
J Neurosci 2006;26:12456
-
GAT-3 transporters regulate inhibition in the neocortex.
Authors: Kinney
J Neurophysiol 2005;94:4533
-
Glutamatergic regulation of the p70S6 kinase in primary mouse neurons.
Authors: Lenz and Avruch
J Biol Chem 2005;280:38121
-
Programmed and induced phenotype of the hippocampal granule cells.
Authors: Gómez-Lira Et al.
J Neurosci 2005;25:6939
-
Synchronized network activity in developing rat hippocampus involves regional hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channel function.
Authors: Bender Et al.
Eur J Neurosci 2005;22:2669
-
Metabotropic regulation of intrinsic excitability by synaptic activation of kainate receptors.
Authors: Melyan Et al.
J Neurosci 2004;24:4530
-
Disruption of endocannabinoid release and striatal long-term depression by postsynaptic blockade of endocannabinoid membrane transport.
Authors: Ronesi Et al.
J Neurosci 2004;24:1673
-
A role for ERK MAP kinase in physiologic temporal integration in hippocampal area CA1.
Authors: Selcher Et al.
Learn Mem 2003;10:26
-
A GDP/GTP exchange protein for the Rab3 small G protein family up-regulates a postdocking step of synaptic exocytosis in central synapses.
Authors: Yamaguchi Et al.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2002;99:14536
-
Kainate receptor-mediated synaptic currents in cerebellar Golgi cells are not shaped by diffusion of glutamate.
Authors: Bureau Et al.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2000;97:6838
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Small Molecule FAQsReviews for DL-AP5
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review DL-AP5 and earn rewards!
Have you used DL-AP5?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image