Recombinant Human Follistatin (aa 30-344) Protein Summary
Product Specifications
Analysis
Product Datasheets
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
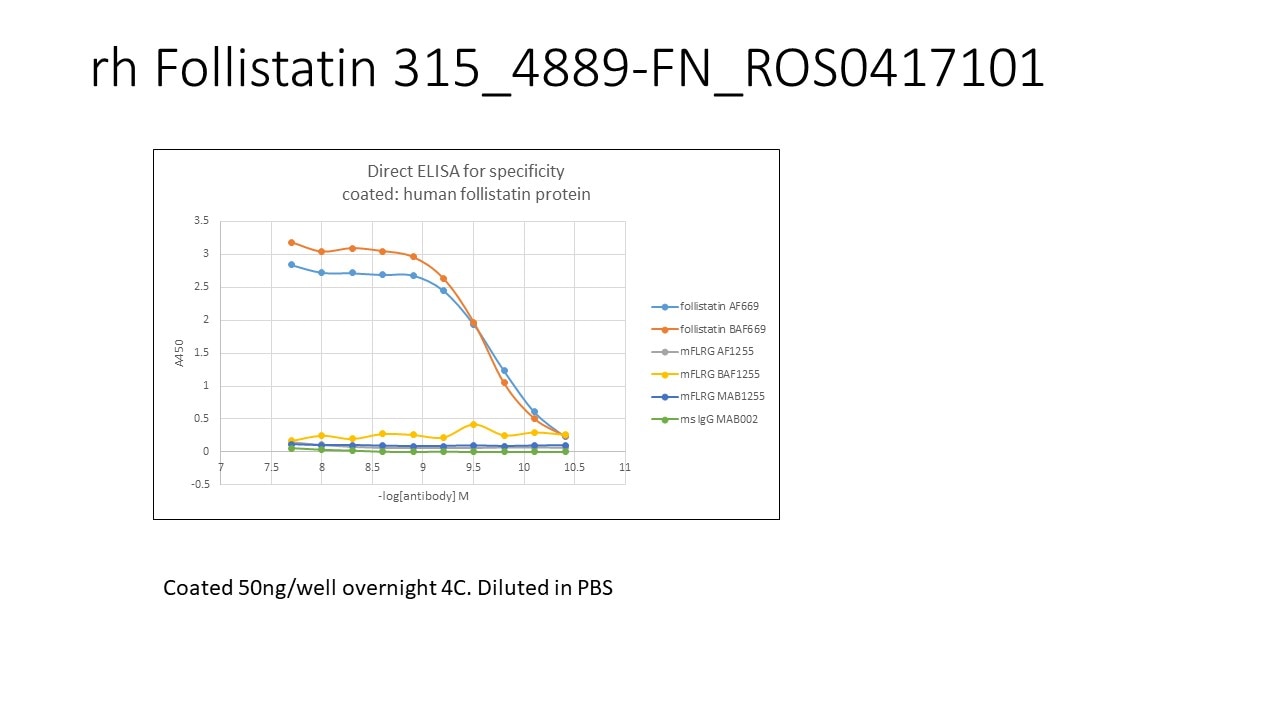
4889-FN
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose and with BSA as a carrier protein. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in sterile PBS containing at least 0.1% human or bovine serum albumin. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
4889-FN/CF
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in sterile PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Reconstitution Calculator
Background: Follistatin
Follistatin (FST) is a secreted glycoprotein that was first identified as a follicle-stimulating hormone inhibiting substance in ovarian follicular fluid (1, 2). Human Follistatin cDNA encodes a 344 amino acid (aa) protein with a 29 aa signal sequence, an N-terminal atypical TGF binding domain, three Follistatin domains that contain EGF-like and kazal-like motifs, and a highly acidic C-terminal tail. The first Follistatin domain (FS1) contains a heparin binding site, while FS1 and FS2 are most critical for activin binding and neutralization (3, 4). In addition to activin, Follistatin regulates bioavailability of many non-TGF-beta members of the TGF-beta superfamily, such as BMP6, BMP7 and myostatin (5). It also regulates hematopoietic stem cell adhesion to fibronectin via FS2, and binds angiogenin via FS2 and FS3 (6, 7). Some Follistatin binding partners will also bind Follistatin-like proteins such as FSL-3 (3, 5, 6). Of three Follistatin isoforms, the full-length mature Follistatin (FST315) is the most abundant and the sole form in plasma, but has lower binding affinity for both activins and heparins than alternative isoforms (5, 8, 9). The acidic tail is missing in the splice variant FST288 which shows the highest affinity for activins, while a partial tail exists in the proteolytically produced FST303, which shows intermediate activin affinity (5, 8, 9). FST315 shares 98% aa identity with mouse, rat, equine and ovine FST, 99% with porcine and 97% with bovine FST. Genetic deletion of Follistatin in mice, or expression of only the FST288 form, is perinatally lethal due to defects of lung, skin and musculoskeletal system (10). Expression of only the FST315 isoform allows survival, with defects in vascularization and female fertility (10).
- Shimasaki, S. et al. (1988) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85:4218.
- Thompson, T.B. et al. (2005) Dev. Cell 9:535.
- Sidis, Y. et al. (2005) Endocrinology 146:130.
- Keutmann, H.T. et al. (2004) Mol. Endocrinol. 18:228.
- Sidis, Y. et al. (2006) Endocrinology 147:3586.
- Maguer-Satta, V. et al. (2006) Exp. Cell Res. 312:434.
- Gao, X. et al. (2007) FEBS Lett. 581:5505.
- Lerch, T.F. et al. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282:15930.
- Schneyer, A.L. et al. (2004) J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 89:5067.
- Lin, S-Y. et al. (2008) Mol. Endocrinol. 22:415.
Citations for Recombinant Human Follistatin (aa 30-344) Protein
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
3
Citations: Showing 1 - 3
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Neuroadaptations in the dorsal hippocampus underlie cocaine seeking during prolonged abstinence
Authors: CT Werner, S Mitra, BD Auerbach, ZJ Wang, JA Martin, AF Stewart, PH Gobira, M Iida, C An, MM Cobb, A Caccamise, RJ Salvi, RL Neve, AM Gancarz, DM Dietz
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2020-10-05;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: In Vivo -
Involvement of activin signal pathway in cyclic apoptosis of the oviductal isthmic epithelium in cows
Authors: Y Yamamoto, S Ito, K Okuda, K Kimura
Theriogenology, 2020-05-18;153(0):143-150.
Species: Bovine
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Cell Culture -
Inhibition of bone morphogenic protein 4 restores endothelial function in db/db diabetic mice.
Authors: Zhang Y, Liu J, Tian X, Wong W, Chen Y, Wang L, Luo J, Cheang W, Lau C, Kwan K, Wang N, Yao X, Huang Y
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2013-11-07;34(1):152-9.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Bioassay
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsReviews for Recombinant Human Follistatin (aa 30-344) Protein
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 1 Review)
Have you used Recombinant Human Follistatin (aa 30-344) Protein?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by: