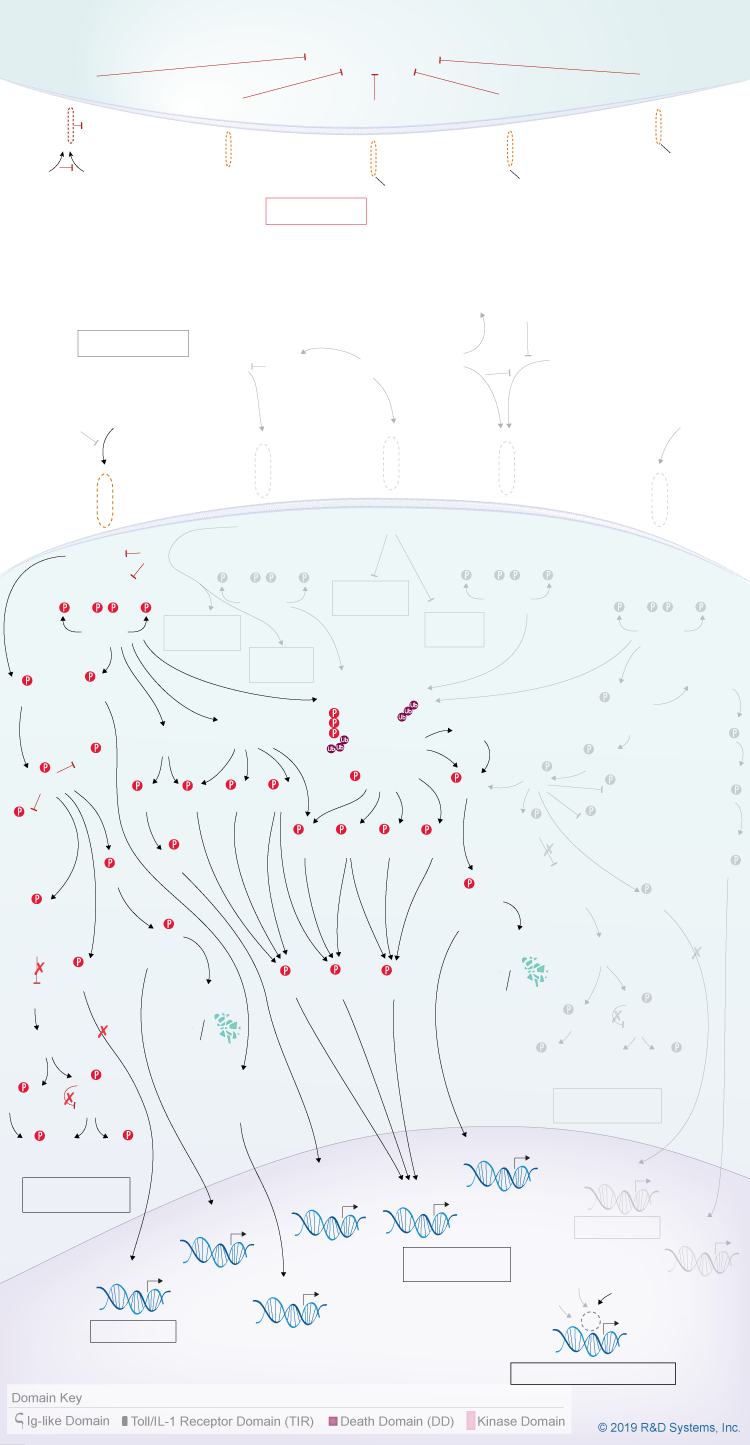
IL-1 Family Signaling Pathways
Click on one of the IL-1 family cytokines shown in the Explore Pathways box below to highlight the signaling pathway and overall effect induced by each cytokine along with the intrinsic inhibitors that may alter its activity.
IL-1 beta
IL-1 beta
IL-36 beta
IL-36 gamma
IL-36 beta
IL-36 gamma
IL-1RAcP
IL-1RAcP
IL-18 R alpha
IL-18 R alpha
IL-18 R beta
IL-18 R beta
IL-18 R alpha
IL-18 R alpha
SIGIRR
SIGIRR
IL-1R1
IL-1R1
IL-1Rrp2
IL-1Rrp2
IL-1RAcP
IL-1RAcP
ST2
ST2
Signaling
Signaling
Signaling
Signaling
Signaling
Signaling
Signaling
Signaling
(Inactive)
(Inactive)
(Inactive)
(Inactive)
(Inactive)
(Inactive)
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Proliferation
Proliferation
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Homodimer
Homodimer
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Factor
Factor
MAP3K3
MAP3K3
Response
Response
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
(Inactive)
(Inactive)
(Inactive)
(Inactive)
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Proliferation
Proliferation
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
IL-1 beta
IL-1RAcP
IL-1 beta
SIGIRR
IL-1 beta
IL-1R3/IL-1RAcP
IL-1 beta
IL-1RAcP
IL-1 beta
IL-1 beta
IL-18 R alpha
IL-18 R alpha
IL-18 R beta
IL-36 beta
IL-36 gamma
IL-1RAcP
IL-1Rrp2
IL-18 R beta
IL-1 Inhibitors
IL-1raAn IL-1 family cytokine that acts as an IL-1 receptor antagonist by preventing IL-1 alpha or IL-1 beta from binding to IL-1 RI; Binding of IL-1ra to IL-1 RI inhibits recruitment of IL-1R3/IL-1RAcP and downstream signaling
IL-1R2/IL-1RII
An IL-1 decoy receptor with a short cytoplasmic domain that is incapable of transducing an IL-1 signal; May also be capable of binding to pro-IL-1 alpha intracellularly and inhibiting its maturation
IL-1R8/SIGIRR
Single immunoglobulin domain containing IL-1 receptor-related (SIGIRR) molecule; A subtype of the IL-1R family that contains a single extracellular immunoglobulin-like domain and may inhibit signaling by IL-1 family cytokines in a context-dependent manner by competing with activated receptor complexes for association with intracellular regulators of IL-1 family signaling such as MyD88, IRAK, or TRAF-6; Also suggested to act as a co-receptor for IL-37-mediated anti-inflammatory signaling
Soluble IL-1R3/IL-1RAcP
A soluble receptor that can bind to IL-1 - IL-1R1 but is incapable of propagating a signal; Enhances IL-1 binding to soluble IL-1R2/IL-1RII
Soluble IL-1R1/IL-1RI or IL-1R2/IL-1RII
Soluble receptors that can bind to IL-1 and IL-1R3/IL-1RAcP, but are incapable of propagating a signal
IL-1 Inhibitor
IL-1raAn IL-1 family cytokine that acts as an IL-1 receptor antagonist by preventing IL-1 alpha or IL-1 beta from binding to IL-1R1; Binding of IL-1ra to IL-1R1 inhibits recruitment of IL-1R3/IL-1RAcP and downstream signaling
IL-18 Inhibitors
Soluble IL-1R5/IL-18 R alphaA soluble receptor that can bind to IL-18 but is incapable of propagating a signal; A weak inhibitor compared to IL-18 BP
IL-1R8/SIGIRR
Single immunoglobulin domain containing IL-1 receptor-related (SIGIRR) molecule; A subtype of the IL-1 R family that contains a single extracellular immunoglobulin-like domain and may inhibit signaling by IL-1 family cytokines in a context-dependent manner by competing with activated receptor complexes for association with intracellular regulators of IL-1 family signaling such as MyD88, IRAK, or TRAF-6; Also suggested to act as a co-receptor for IL-37-mediated anti-inflammatory signaling
IL-18 BP
IL-18 binding protein (IL-18 BP); A soluble protein with a single immunoglobulin-like domain that binds to IL-18 with higher affinity than either the cell bound or soluble forms of IL-18 R and prevents
IL-18 signaling
IL-37
Both the precursor and mature forms of the longest isoform of IL-37, IL-37b, are secreted and bind to IL-18 BP, enhancing its ability to inhibit IL-18 activity; IL-37-IL-18 BP-IL-1R7/IL-18 R beta have also been suggested to form an inactive tripartite complex that prevents the formation of an active
IL-18 receptor complex; Pro- and mature IL-37b also bind to IL-1R5/IL-18 R alpha but do not act as direct agonists or antagonists of the IL-18 receptor complex
IL-33 Inhibitors
IL-1R8/SIGIRRSingle immunoglobulin domain containing IL-1 receptor-related (SIGIRR) molecule; A subtype of the IL-1R family that contains a single extracellular immunoglobulin-like domain and may inhibit signaling by IL-1 family cytokines in a context-dependent manner by competing with activated receptor complexes for association with intracellular regulators of IL-1 family signaling such as MyD88, IRAK, or TRAF-6; Also suggested to act as a co-receptor for IL-37-mediated anti-inflammatory signaling
Soluble IL-1R4/ST2
A soluble receptor that can bind to IL-33 but is incapable of propagating a signal
IL-36 Inhibitors
IL-36RaAn IL-1 family cytokine that acts as a partial IL-36 receptor antagonist by preventing IL-36 alpha, IL-36 beta, or IL-36 gamma from binding to IL-1R6/IL-1Rrp2 at low concentrations; Binding of IL-36Ra to IL-1R6/IL-1Rrp2 inhibits recruitment of IL-1R3/IL-1RAcP and downstream signaling
IL-38
Similar to IL-36Ra, IL-38 binds to IL-1R6/IL-1Rrp2 and prevents IL-36 alpha, IL-36 beta, or IL-36 gamma from binding to its receptor; Binding of IL-38 to IL-1R6/IL-1Rrp2 inhibits recruitment of IL-1R3/IL-1RAcp and downstream signaling; Due to its activity as a partial IL-1R6/IL-1Rrp2 receptor antagonist, IL-38 has anti-inflammatory effects although it has been suggested that it may act as an agonist at higher concentrations
IL-1R8/SIGIRR
Single immunoglobulin domain containing IL-1 receptor-related (SIGIRR) molecule; A subtype of the IL-1R family that contains a single extracellular immunoglobulin-like domain and may inhibit signaling by IL-1 family cytokines in a context-dependent manner by competing with activated receptor complexes for association with intracellular regulators of IL-1 family signaling such as MyD88, IRAK, or TRAF-6; Also suggested to act as a co-receptor for IL-37-mediated anti-inflammatory signaling
IL-36 Inhibitor
IL-36RaAn IL-1 family cytokine that acts as a partial IL-36 receptor antagonist by preventing IL-36 alpha, IL-36 beta, or IL-36 gamma from binding to IL-1R6/IL-1Rrp2 at low concentrations; Binding of IL-36Ra to IL-1R6/IL-1Rrp2 inhibits recruitment of IL-1R3/IL-1RAcP and downstream signaling
Effects of IL-37
• Five different splice variants of IL-37 (IL-37a-e) have been identified• IL-37b is the longest isoform, the most abundant, and the most extensively studied to date
• IL-37b is expressed at low levels in human cells and tissues but is upregulated by inflammatory stimuli
• Following Caspase-1-mediated cleavage, IL-37b translocates to the nucleus, where it suppresses the expression of pro-inflammatory genes
• Both the precursor and mature forms of IL-37b are also secreted and bind to IL-18 BP, enhancing its ability to inhibit IL-18 activity
• IL-37-IL-18 BP-IL-1R7/IL-18 R beta have been suggested to form an inactive tripartite complex that prevents the formation of an active IL-18 receptor complex
• Pro- and mature IL-37b also bind to IL-1R5/IL-18 R alpha but do not act as direct agonists or antagonists of the IL-18 receptor complex; Rather, the IL-37-IL-1R5 complex recruits IL-1R8/SIGIRR as a co-receptor, and this tripartite complex inhibits the kinase signaling pathways required for the production of pro-inflammatory mediators and activates anti-inflammatory signaling pathways
• A mouse homologue of human IL-37 has not been identified
Effects of IL-38
• Similar to IL-36Ra, IL-38 binds to IL-1R6/IL-1Rrp2 and prevents IL-36 alpha, IL-36 beta, or IL-36 gamma from binding to its receptor• Binding of IL-38 to IL-1R6/IL-1Rrp2 inhibits recruitment of IL-1R3/IL-1RAcp and downstream signaling
• Due to its activity as a partial IL-1R6/IL-1Rrp2 receptor antagonist, IL-38 has anti-inflammatory effects, although it has been suggested that it may act as an agonist at higher concentrations

Featured Literature
Inflammasomes: Intracellular Regulators of Pathogen Recognition, Host Defense, and Inflammation Poster
View PosterOverview of the IL-1 Family Signaling Pathway
The IL-1 cytokine family consists of eleven members that play important roles in regulating inflammation. Members include IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, IL-1ra, IL-18, IL-33, IL-36Ra, IL-36 alpha, IL-36 beta, IL-36 gamma, IL-37, and IL-38. While most of these cytokines are biologically active as full-length molecules, activation and secretion of IL-1 beta and IL-18 requires inflammasome/Caspase-1-dependent processing. Other IL-1 family cytokines do not require Caspase-1 cleavage for activation but may undergo some form of protease processing since more potent forms of many of these cytokines can be generated by trimming amino acids at their N-terminal ends.
IL-1 family cytokines mediate their effects by binding to a primary IL-1 family receptor subunit, such as IL-1 RI, IL-18 R alpha, IL-1 Rrp2, or ST2, which subsequently recruits an accessory receptor, IL-1 RAcP or IL-18 R beta, to activate downstream signaling. IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, IL-18, IL-33, IL-36 alpha, IL-36 beta, and IL-36 gamma trigger intracellular signaling cascades that induce the NF-kappa B- and AP-1-dependent expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and secondary mediators of the inflammatory response. In addition, unprocessed forms of IL-1 alpha and IL-33 and the mature form of IL-37b can translocate to the nucleus where they may act as transcriptional regulators. In contrast to the pro-inflammatory members of the IL-1 family, IL-1ra, IL-36Ra, IL-37, and IL-38 have anti-inflammatory effects. IL-1ra antagonizes IL-1 activity by binding to IL-1 RI. This prevents IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta from interacting with their primary receptor subunit and inhibits recruitment of IL-1 RAcP. Similarly, IL-36Ra binds to IL-1 Rrp2 and inhibits IL-36 signaling. Less is known about IL-37 and IL-38, but both have also been suggested to have anti-inflammatory effects. Five splice variants of IL-37 (IL-37a-e) exist with four containing a putative Caspase-1 cleavage site. Both the immature and mature forms of the longest isoform, IL-37b, bind to IL-18 binding protein (IL-18 BP) and enhance its ability to inhibit IL-18 activity. IL-38 binds to the IL-36 receptor, IL-1 Rrp2, and soluble IL-1 RI. Initial data suggests that the interaction between IL-38 and IL-1 Rrp2 has anti-inflammatory effects similar to those induced by IL-36Ra.
In addition to IL-1ra and IL-36Ra, the pro-inflammatory effects of IL-1, IL-18, IL-33, and IL-36 are regulated by several other endogenous inhibitors. IL-I RII is an IL-1 family receptor that, unlike other receptors in this family, lacks a TIR domain. It can bind to IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta and recruit IL-1 RAcP, but it is incapable of transducing a signal. As a result, it acts as an IL-1 decoy receptor. Soluble IL-1 RI and IL-I RII can also bind to IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta and recruit IL-1 RAcP but cannot activate intracellular signaling. Similarly, soluble ST-2/IL-1 R4 and soluble IL-18 R alpha have been shown to negatively regulate IL-33 and IL-18 signaling, respectively. IL-18 signaling is also regulated by IL-18 BP. IL-18 BP is a soluble protein that binds to IL-18 with higher affinity than either the cell-bound or soluble forms of IL-18 R and prevents IL-18 signaling. Single immunoglobulin domain containing IL-1 receptor-related (SIGIRR) molecule is another potential endogenous inhibitor of IL-1, IL-18, IL-33, and IL-36 signaling. SIGIRR is a transmembrane protein with one extracellular Ig-like domain that has been shown to bind to several IL-1 family cytokines and inhibit signaling in a context-dependent manner.
To learn more, please visit our IL-1 Family Research Area.
Get Print Copy of this Pathway