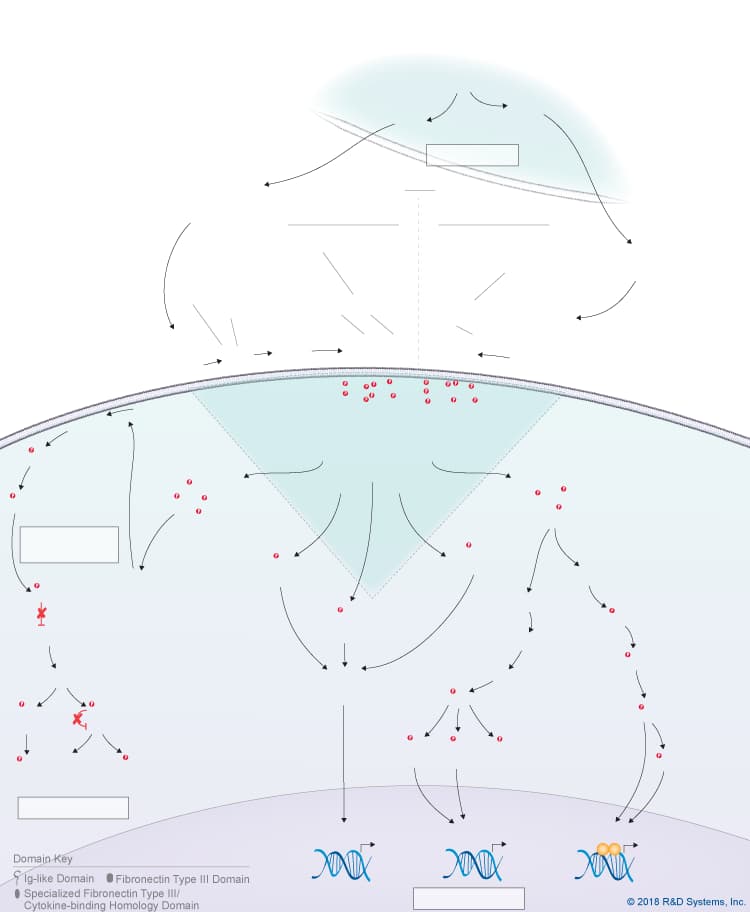
Cardiotrophin-like Cytokine CLC Signaling Pathways
Click on the other IL-6 family cytokines shown in the Explore Pathways box below to see the signaling pathways that are activated by each cytokine. Refer to the table below each pathway to see a select list of cytokine-expressing cells or tissues and the primary biological effects induced by the different members of the IL-6 cytokine family.
cytokine (CLC)
cytokine (CLC)
Complex
Complex
Receptor Complex
Receptor Complex
alpha
alpha
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Cell Proliferation
Cell Proliferation
(Inactive)
(Inactive)
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
(Unknown)
(Unknown)
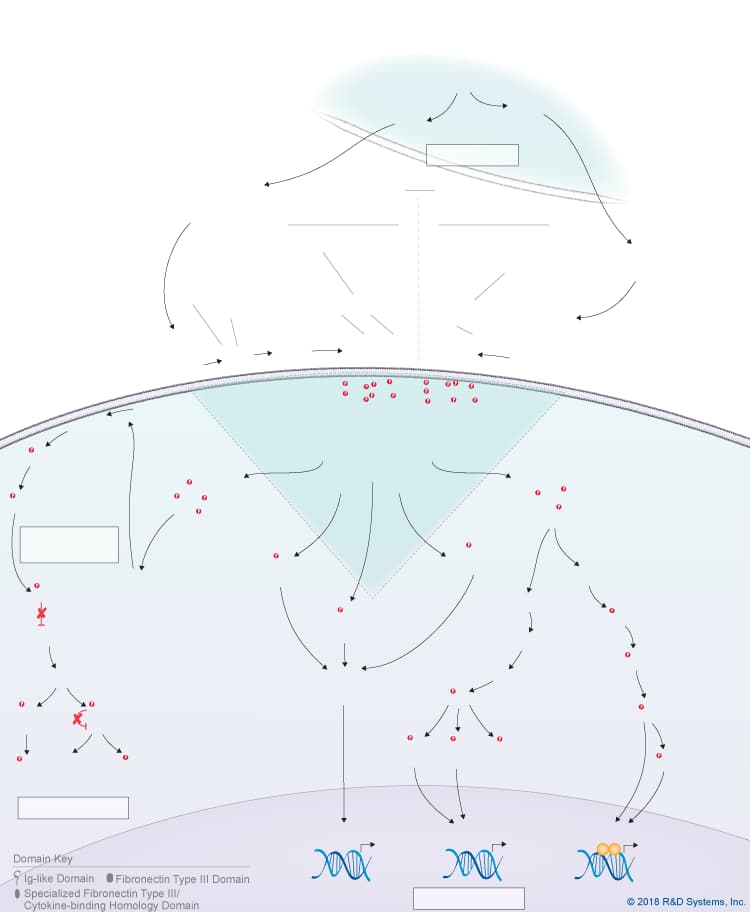
Overview of Cardiotrophin-like cytokine (CLC) Signaling Pathways
Cardiotrophin-like cytokine (CLC), also known as novel neurotrophin-1 (NNT-1) and B cell stimulatory factor-3 (BSF-3), is a member of the IL-6 cytokine family, which also includes IL-6, IL-11, IL-27 p28/IL-30, IL-31, Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), Oncostatin M (OSM), Ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF), Cardiotrophin-1 (CT-1), and Neuropoietin. IL-6 family cytokines are structurally related and with the exception of IL-31, they typically activate receptor complexes that include the signal-transducing gp130 receptor subunit. Like other IL-6 family cytokines, CLC is a four-helix bundle cytokine. Although it contains a signal peptide, CLC must be associated with either a second soluble cytokine receptor known as Cytokine-like factor-1 (CLF-1) or soluble CNTF R alpha to be efficiently secreted. Following secretion, the CLC:CLF-1 composite cytokine binds to the glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored, non-signaling CNTF R alpha receptor subunit. This complex of CLC:CLF-1 and membrane-bound CNTF R alpha or the CLC:soluble CNTF R alpha complex can then recruit the signal-transducing receptor subunits, LIF R and gp130. As both CLF-1 and LIF R were found to interact with CLC through the same site, it has been suggested that CLF-1 may be removed from the receptor complex. If this is the case, the CLC receptor complex consists of either membrane-bound or soluble CNTF R alpha , LIF R, and gp130. Sortilin, a member of the Vps10p domain family of type I transmembrane receptors, may also be part of the CLC receptor complex as it has been shown to bind to CNTF, CLC/CLF-1, and Neuropoietin with high affinity and enhance the assembly of LIF R and gp130. Following receptor complex formation, multiple intracellular signaling pathways are activated downstream of the CLC composite cytokines including the Jak-STAT pathway, the Ras-MAPK pathway, the PI 3-K-Akt pathway, and the p38 and JNK MAPK pathways, which mediate various biological effects in different cell types. CLC composite cytokines have been shown to support motor and sympathetic neuron survival, promote astrocyte differentiation, inhibit locomotor activity during the circadian rest period, inhibit osteoblast differentiation, and have immunomodulatory effects. Unlike CNTF, the CLC:CLF-1 composite cytokine also plays an important role during development as mice lacking CLC or CLF-1 die soon after birth due to a suckling defect that is associated with a reduction in facial motor neurons. Similarly, mutations in CLF-1 or CLC in humans are associated with a rare autosomal recessive disorder known as Crisponi/cold-induced sweating syndrome, which is characterized by musculoskeletal abnormalities, facial weakness, and suckling defects that can be lethal early in life.
To learn more, please visit our IL-6 Family Research Area page.
| Primary CLC-Expressing Tissues | Primary Biological Effects of CLC Composite Cytokines |
| Embryonic skeletal muscle fibers | CLC-CLF plays an important role during development |
| Adult tissues including the heart, liver, lymph nodes, colon, kidney, spleen, and ovary | Supports motor and sympathetic neuron survival and promotes astrocyte differentiation |
| May inhibit locomotor activity during the circadian rest period | |
| Stimulates an acute phase response, a reduction in body weight, and B cell hyperplasia in mice | |
| CLC-CLF mutations are associated with Crisponi or cold-induced sweating syndromes and lead to early neonatal death due to a suckling defect associated with a reduced number of facial motor nuerons and musculoskeletal abnormalities | |
| Inhibits osteoblast differentiation | |
| Overexpression of CLC stimulates B cell differentiation and antibody production |
Get Print Copy of this Pathway