IL-27 p28/IL-30 Signaling Pathways
Click on the other IL-6 family cytokines listed below to see the signaling pathways that are activated by each cytokine. Refer to the table below each pathway to see a select list of cytokine-expressing cells or tissues and the primary biological effects induced by the different members of the IL-6 cytokine family.
IL-30
IL-30
Secretion
Secretion
Signaling
Signaling
IL-27 p28/IL-30
IL-27 p28/IL-30
Signaling
Signaling
alpha
alpha

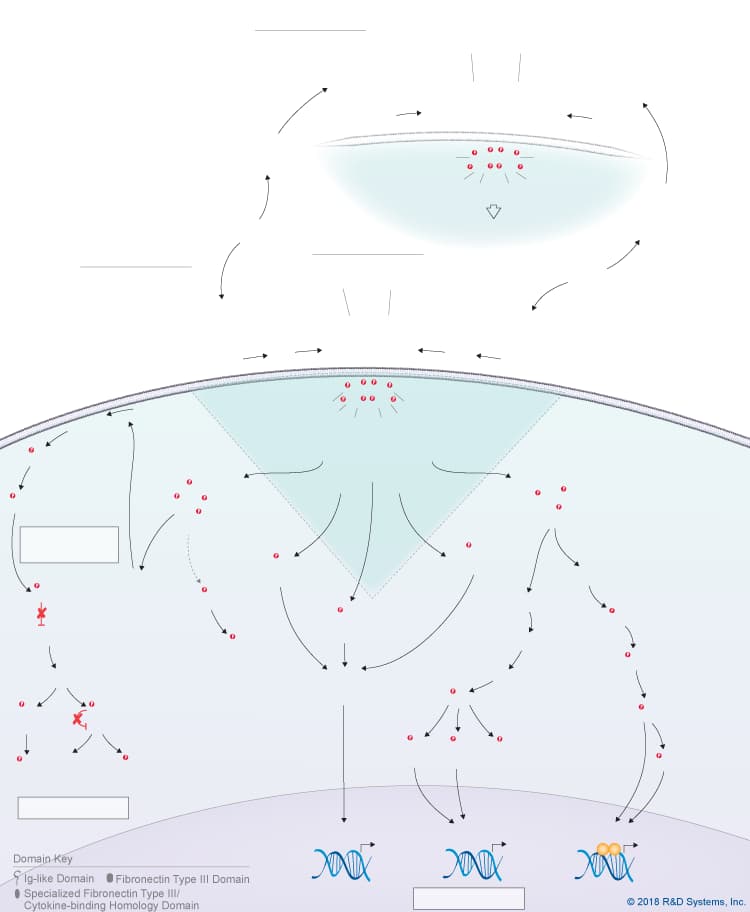
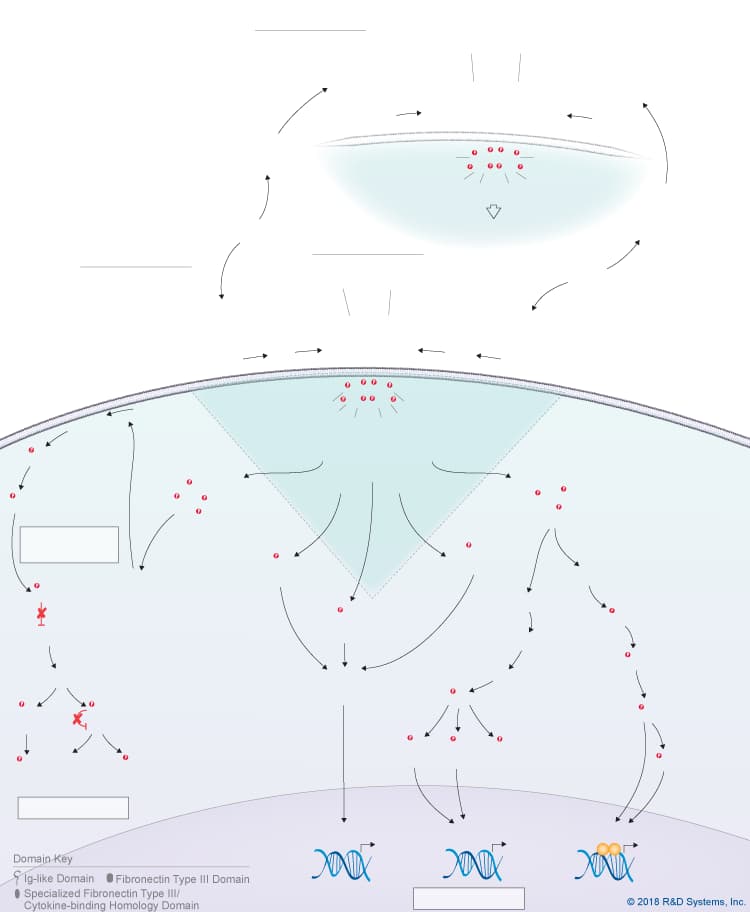
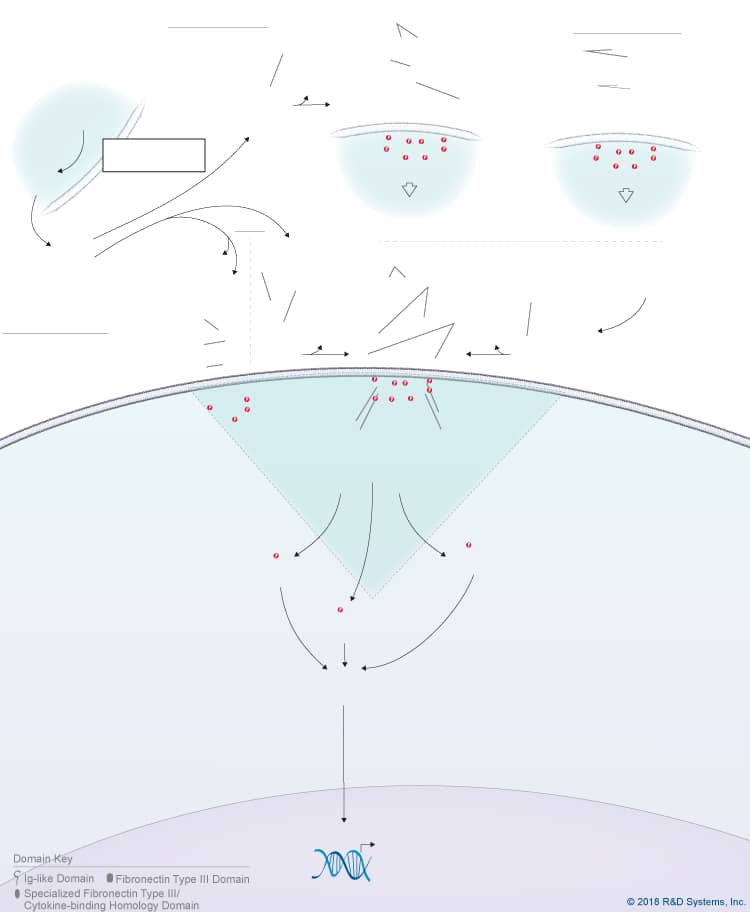
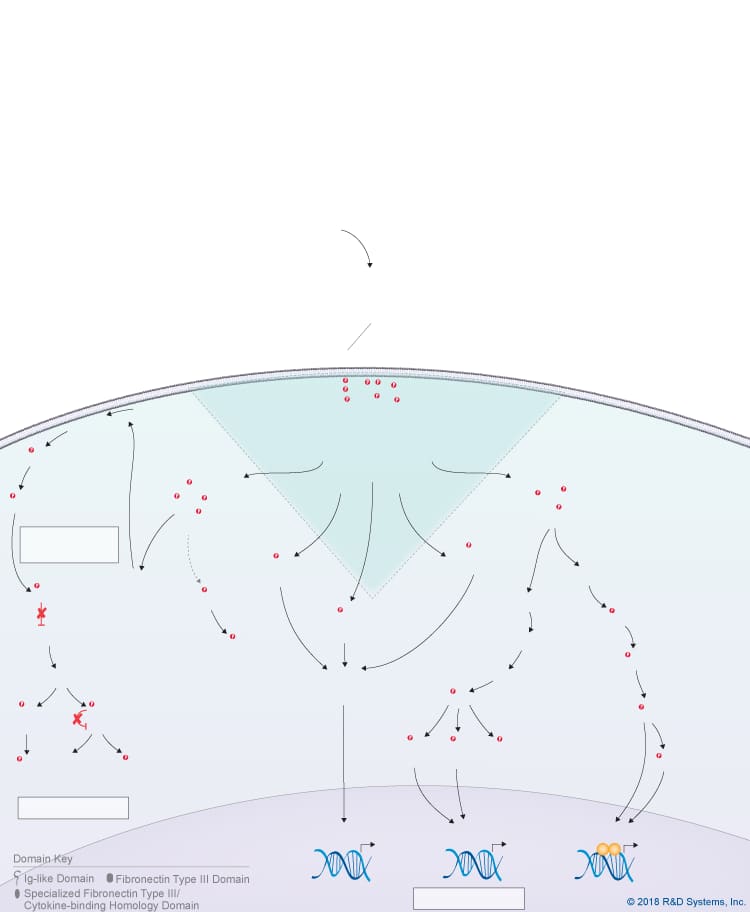
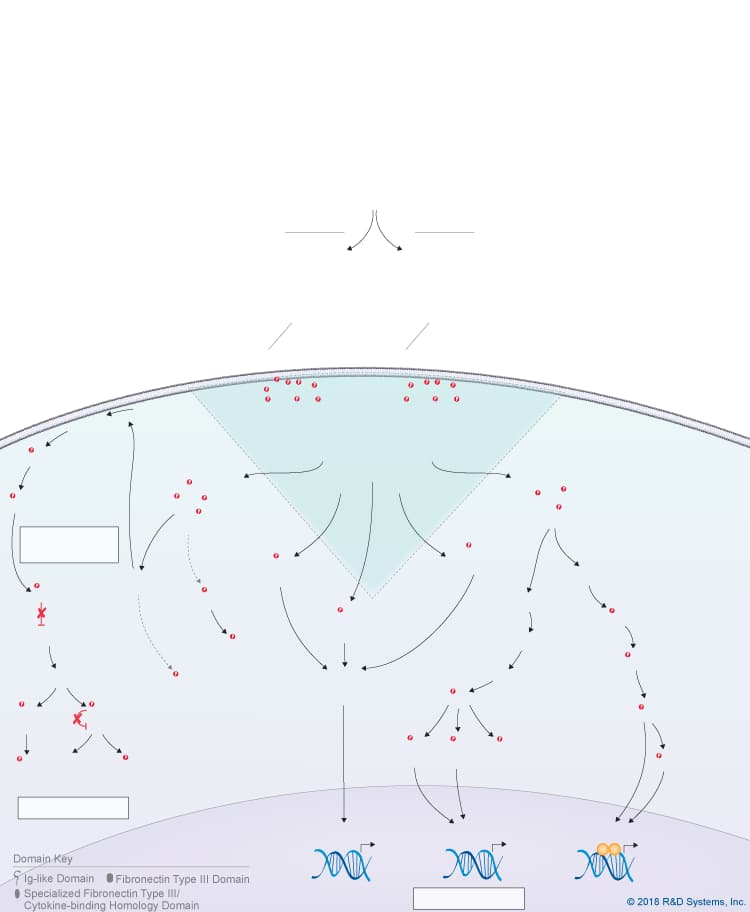
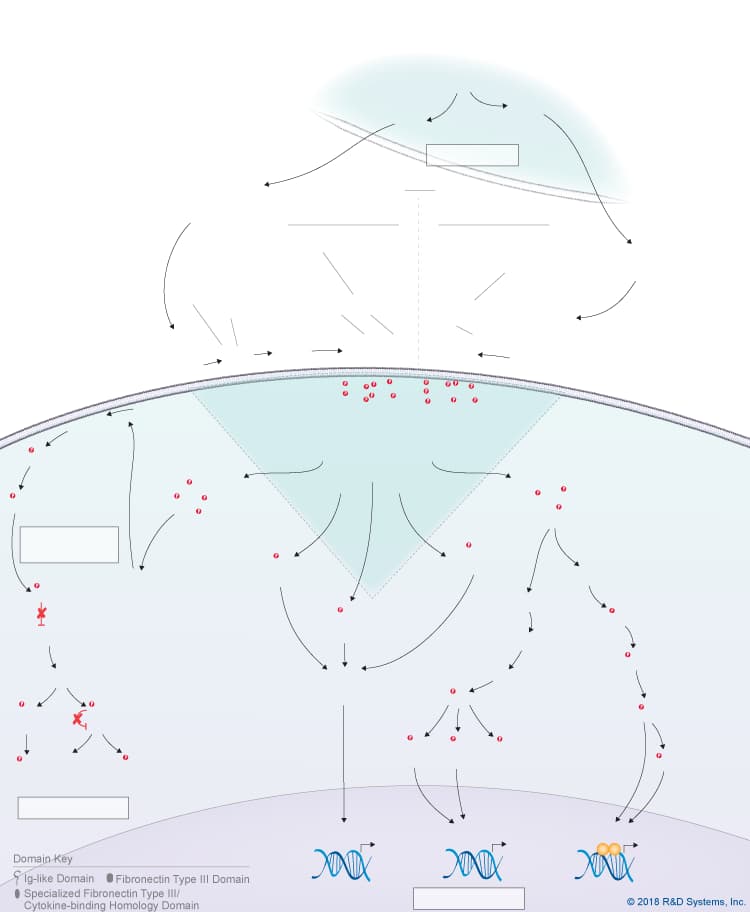
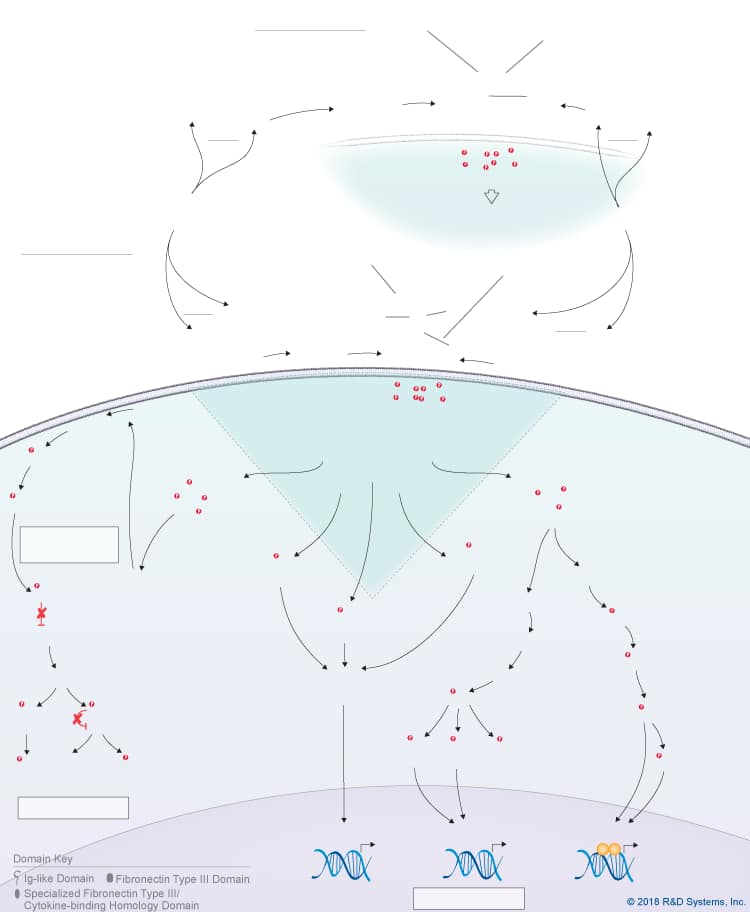
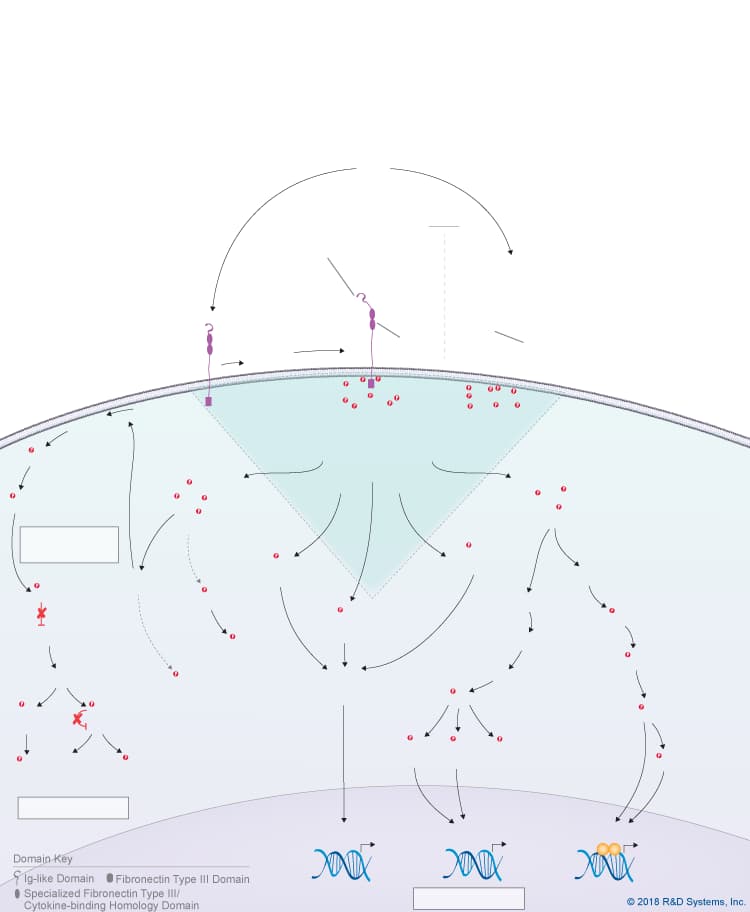
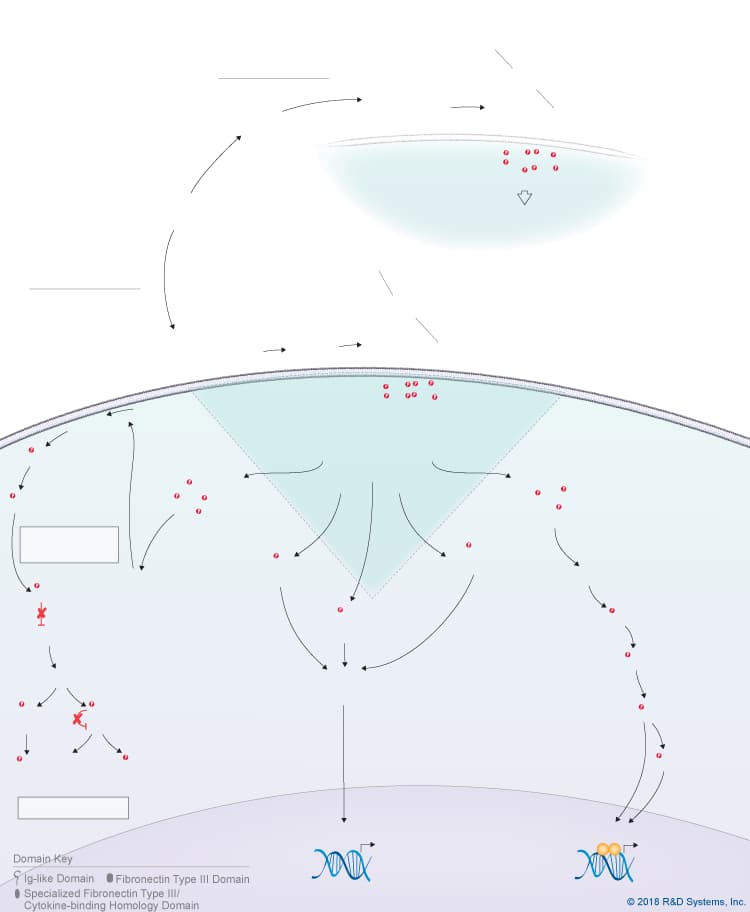
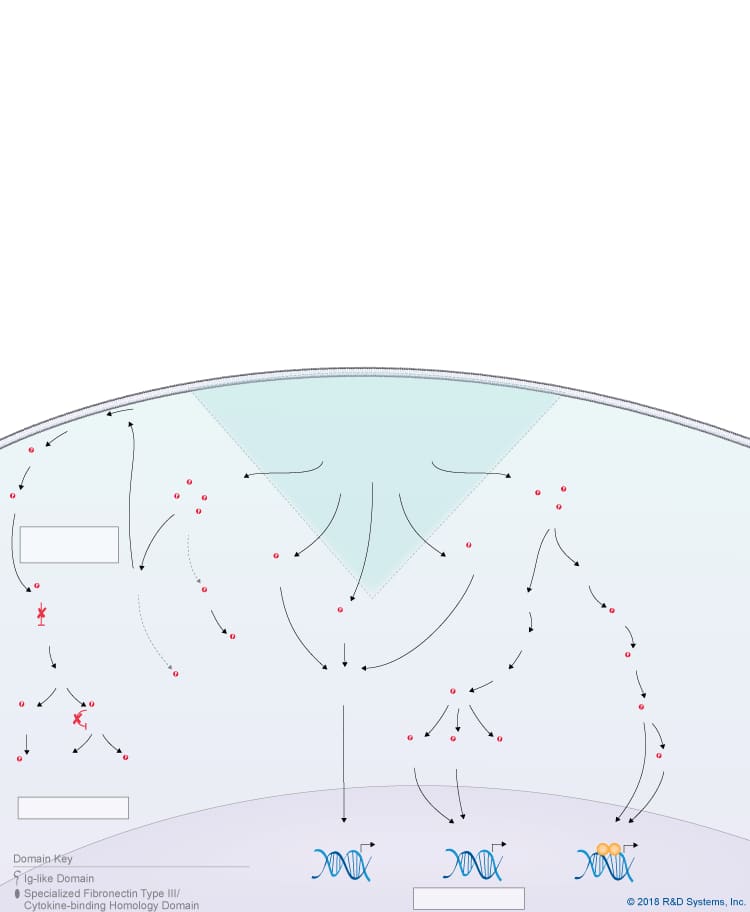
Overview of IL-27 p28/IL-30 Signaling Pathways
IL-27 p28/IL-30 is a member of the IL-6 cytokine family, which also includes IL-6, IL-11, IL-31, Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), Oncostatin M (OSM), Cardiotrophin-like cytokine (CLC), Ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF), Cardiotrophin-1 (CT-1), and Neuropoietin. IL-27 p28, also known as IL-30, is a four-helix bundle cytokine that associates with Epstein-Barr virus-induced gene 3 (EBI3) to form the heterodimeric IL-27 cytokine. In addition to its pairing with EBI3, IL-27 p28/IL-30 can also associate with Cytokine-like factor-1 (CLF-1), to form a complex that is secreted by dendritic cells. While CLF-1 is required for IL-27 p28/IL-30 secretion, it is not required for receptor recognition or downstream signaling. IL-27 p28/IL-30 has been reported to signal through either a tripartite receptor complex consisting of IL-6 R alpha, IL-27 R alpha/WSX-1, and gp130 or a multi-subunit receptor complex consisting of IL-6 R alpha coupled with a gp130 homodimer. Like IL-6, IL-27 p28/IL-30 is thought to be capable of initiating both classic and trans-signaling by binding to either the membrane-bound or soluble forms of IL-6 R alpha, respectively. Both the classic and trans-signaling ligand-receptor complexes induce STAT3 and STAT1 phosphorylation in target cells, and presumably, promote the activation of additional intracellular signaling pathways as well, although this hasn’t been directly shown. While the biological significance of the classic and trans-signaling pathways has yet to be clarified, the finding that IL-27 p28/IL-30 can activate both pathways suggests that IL-27 p28/IL-30 could have a wide range of effects on multiple different cell types. Additionally, IL-27 p28/IL-30 is reportedly capable of signaling through gp130 alone when present at high concentrations due to its high affinity for gp130. The biological effects associated with IL-27 p28/IL-30 to date include up-regulation of natural killer cell activation and IL-2- or IL-12-induced IFN-gamma production, inhibition of anti-CD3-, anti-CD28-induced CD4+ T cell proliferation, induction of T cell production of IL-10, promotion of Th17 differentiation in the presence of TGF-beta and inhibition of IL-6/ TGF-beta-induced Th17 differentiation, stimulation of plasma cell differentiation, and protection against cytokine-induced liver injury.
To learn more, please visit our IL-6 Family Research Area page.
| Primary IL-27 p28/IL-30-Expressing Cells | Primary Biological Effects of the IL-27 p28/IL-30:CLF-1 Composite Cytokine |
| Dendritic cells | Up-regulates natural killer cell activation and IFN-gamma production in the presence of IL-2 or IL-12 |
| Macrophages | Induces IL-10 secretion by CD4+ T cells and inhibits anti-CD3/CD28-induced proliferation |
| Promotes Th17 differentiation in the presence of TGF-beta in vitro and can inhibit IL-6-, TGF-beta-induced Th17 differentiation | |
| Induces the differentiation of B cells into antibody-secreting plasma cells | |
| Protects against cytokine-induced liver injury |
Get Print Copy of this Pathway