Neuropoietin Signaling Pathways
Click on the other IL-6 family cytokines shown in the Explore Pathways box below to see the signaling pathways that are activated by each cytokine. Refer to the table below each pathway to see a select list of cytokine-expressing cells or tissues and the primary biological effects induced by the different members of the IL-6 cytokine family.
alpha
alpha
alpha
alpha
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Cell Proliferation
Cell Proliferation
(Inactive)
(Inactive)
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.

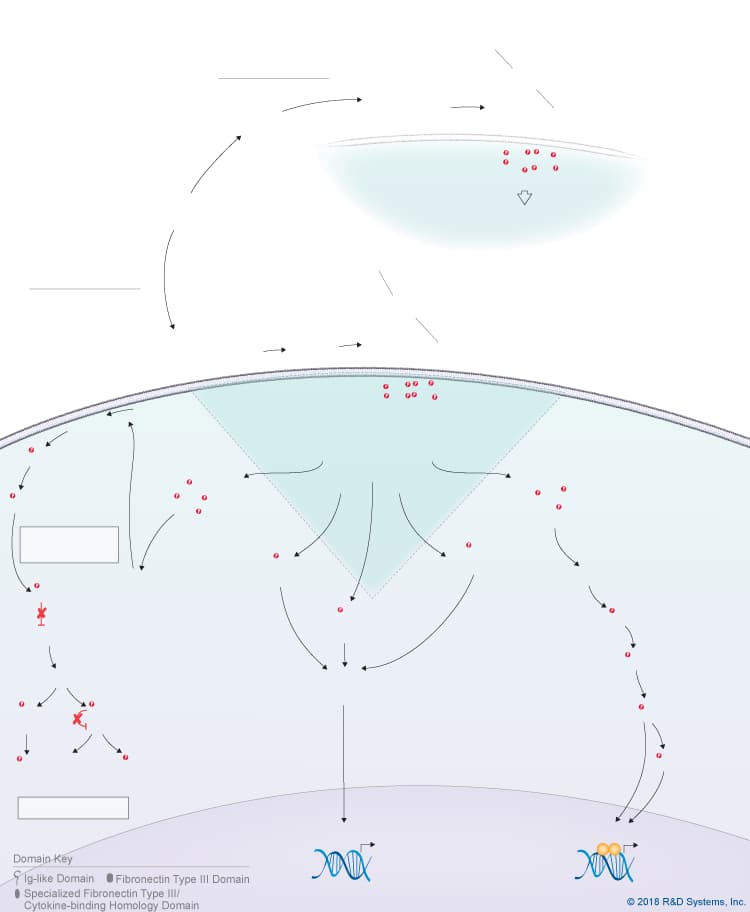
Overview of Neuropoietin (NP) Signaling Pathways
Neuropoietin (NP), also known as Cardiotrophin-2, is a member of the IL-6 cytokine family, which also includes IL-6, IL-11, IL-27 p28/IL-30, IL-31, Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), Oncostatin M (OSM), Cardiotrophin-like cytokine (CLC), Ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF), and Cardiotrophin-1 (CT-1). In mice, NP is a long chain four-helix bundle cytokine that is considered to be the product of a gene duplication event involving CT-1. In humans, NP is not expressed due to an 8-nucleotide deletion, suggesting that it exists only as a pseudogene. Mouse NP, similar to CNTF, initially binds to the glycophosphatidylinositol-linked, non-signaling CNTF R alpha receptor subunit, which then recruits the signal-transducing receptor subunits, LIF R and gp130, to form a tripartite receptor complex. Assembly of the LIF R:gp130 heterodimer is enhanced by Sortilin, a member of the Vps10p domain family of type I transmembrane receptors, which binds to CNTF, CLC/CLF-1, and Neuropoietin with high affinity. NP is also thought to be capable of initiating trans-signaling by binding to soluble CNTF R alpha, which is released from the cell surface by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. Both the classic and trans-signaling pathways lead to CNTF R:LIF R:gp130 complex formation, and presumably the activation of multiple downstream signaling pathways. Based on the formation of this same tripartite receptor complex by other related IL-6 family cytokines, NP is thought to trigger activation of the Jak-STAT pathway, the Ras-MAPK pathway, and the PI 3-K-Akt pathway. While research on NP has been slow due to the lack of a functional human orthologue, NP has been shown to be specifically expressed during mouse embryonic development. Similar to CLC, CNTF, and CT-1, NP has been shown to promote embryonic motor neuron survival, neural precursor cell proliferation, and astrocyte differentiation in vitro. Significantly, however, NP is expressed when the expression of these other IL-6 family cytokines is low, suggesting that NP may have a unique role in mouse nervous system development.
To learn more, please visit our IL-6 Family Research Area page.
| Primary NP-Expressing Tissues | Primary Biological Effects of NP |
| Embryonic neuroepithelium (mouse) | Mediates embryonic motor neuron survival |
| Embryonic cranial and dorsal root sensory ganglia (mouse) | Promotes neural precursor cell proliferation |
| Embryonic spinal cord (mouse) | Promotes astrocyte differentiation |
| Embryonic vibrissae and dermis (mouse) | Suggested to have a key role in mouse nervous system development |
| Embryonic skeletal muscle (mouse) | Inhibits adipocyte differentiation and limits glucose uptake by mature adipocytes |
| Neuropoietin is not expressed in humans suggesting that it exists only as a pseudogene |
Get Print Copy of this Pathway