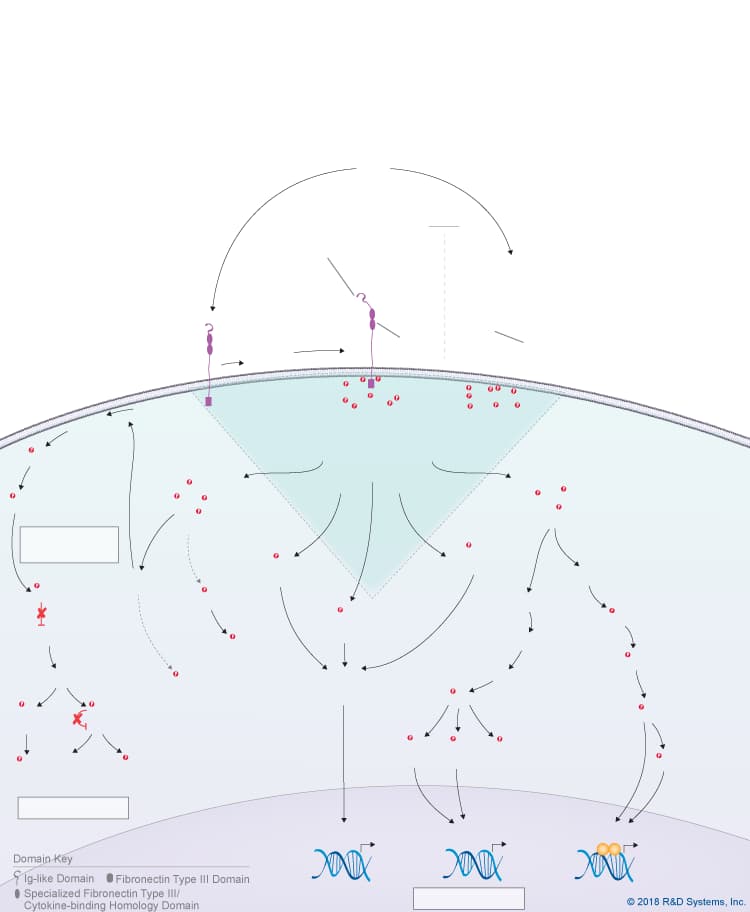
Cardiotrophin-1 Signaling Pathways
Click on the other IL-6 family cytokines shown in the Explore Pathways box below to see the signaling pathways that are activated by each cytokine. Refer to the table below each pathway to see a select list of cytokine-expressing cells or tissues and the primary biological effects induced by the different members of the IL-6 cytokine family.
alpha chain
receptor
alpha chain
receptor
chain receptor
chain receptor
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Cell Proliferation
Cell Proliferation
(Inactive)
(Inactive)
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
(Unknown)
(Unknown)
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.

Overview of Cardiotrophin-1 (CT-1) Signaling Pathways
Cardiotrophin-1 (CT-1) is a member of the IL-6 cytokine family, which also includes IL-6, IL-11, IL-27 p28/IL-30, IL-31, Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), Oncostatin M (OSM), Cardiotrophin-like cytokine (CLC), Ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF), and Neuropoietin. CT-1 was identified as a factor produced by mouse embryoid bodies that induced a hypertrophic response in neonatal cardiac myocytes. It was subsequently shown to promote cardiomyocyte maturation and to have cardioprotective effects. Similar to other IL-6 family cytokines, CT-1 is a four-helix bundle cytokine that signals through a receptor complex containing the gp130 receptor subunit. CT-1, like CNTF, lacks a hydrophobic signal peptide and is therefore not thought to be secreted by conventional mechanisms. CT-1 initiates intracellular signaling by binding to either a CT-1-specific alpha receptor that associates with LIF R and then recruits gp130, or by binding directly with low affinity to LIF R, which promotes its heterodimerization with gp130 and the formation of a high affinity receptor complex. Both LIF R and gp130 associate with members of the Jak family of tyrosine kinases, leading to the phosphorylation of STAT proteins, predominantly STAT1 and STAT3, which then homodimerize and translocate to the nucleus where they regulate the expression of specific target genes. In addition to the Jak-STAT pathway, CT-1 also activates the Ras-MAPK pathway, the PI 3-K-Akt pathway, the MEK5-ERK5 pathway, and the MAPKs, p38 and JNK. Besides its effects on cardiovascular tissue, CT-1 has been found to have significant protective effects on other tissues as well. In the nervous system, these effects include promoting the survival and maintenance of motor neurons during development, stimulating the development, differentiation, and survival of neural stem cells, promoting astrogenesis and gliogenesis, protecting motor, dopaminergic, and ciliary ganglion neurons against injuries and dysfunctions, and promoting myelination. In the liver, CT-1 protects against liver damage and is a potent inducer of the acute phase response. Additionally, CT-1 has been shown to regulate energy metabolism and inflammation.
To learn more, please visit our IL-6 Family Research Area page.
| Primary CT-1-Expressing Cells/Tissues | Primary Biological Effects of CT-1 |
| Cardiomyocytes | Induces cardiomyocyte hypertrophy |
| Adipocytes | Promotes cardiomyocyte differentiation |
| Fetal forebrain | Has cardioprotective activity |
| Fetal, postnatal, and adult choroid plexus cells | Stimulates the development, differentiation, and survival of neural stem cells; Promotes astrogenesis and gliogenesis |
| Embryonic cortex | Protects motor neurons, dopaminergic neurons, and ciliary ganglion neurons against a variety of injuries and dysfunctions |
| Ependymal cells | Has promyelinating effects |
| Leptomeninges | Acts as a hepatoprotective molecule; Protects against liver damage |
| Hepatocytes | Induces the acute phase response in primary hepatocytes |
| Hepatic non-parenchymal cells | Inhibits the spontaneous differentiation of embryonic stem cells |
| Skeletal myocytes | Regulates energy metabolism, reduces lipid accumulation, improves insulin sensitivity |
| Regulates inflammation |
Get Print Copy of this Pathway