Human CCL5/RANTES DuoSet ELISA Summary
* Provided that the recommended microplates, buffers, diluents, substrates and solutions are used, and the assay is run as summarized in the Assay Procedure provided.
This DuoSet ELISA Development kit contains the basic components required for the development of sandwich ELISAs to measure natural and recombinant human CCL5/RANTES. The suggested diluent is suitable for the analysis of most cell culture supernate samples. Diluents for complex matrices, such as serum and plasma, should be evaluated prior to use in this DuoSet.
Product Features
- Optimized capture and detection antibody pairings with recommended concentrations save lengthy development time
- Development protocols are provided to guide further assay optimization
- Assay can be customized to your specific needs
- Economical alternative to complete kits
Kit Content
- Capture Antibody
- Detection Antibody
- Recombinant Standard
- Streptavidin conjugated to horseradish-peroxidase (Streptavidin-HRP)
Other Reagents Required
DuoSet Ancillary Reagent Kit 2 (5 plates): (Catalog # DY008) containing 96 well microplates, plate sealers, substrate solution, stop solution, plate coating buffer (PBS), wash buffer, and Reagent Diluent Concentrate 2.
The components listed above may be purchased separately:
PBS: (Catalog # DY006), or 137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 8.1 mM Na2HPO4, 1.5 mM KH2PO4, pH 7.2 - 7.4, 0.2 µm filtered
Wash Buffer: (Catalog # WA126), or 0.05% Tween® 20 in PBS, pH 7.2-7.4
Reagent Diluent: (Catalog # DY995), or 1% BSA in PBS, pH 7.2-7.4, 0.2 µm filtered
Substrate Solution: 1:1 mixture of Color Reagent A (H2O2) and Color Reagent B (Tetramethylbenzidine) (Catalog # DY999)
Stop Solution: 2 N H2SO4 (Catalog # DY994)
Microplates: R&D Systems (Catalog # DY990)
Plate Sealers: ELISA Plate Sealers (Catalog # DY992)
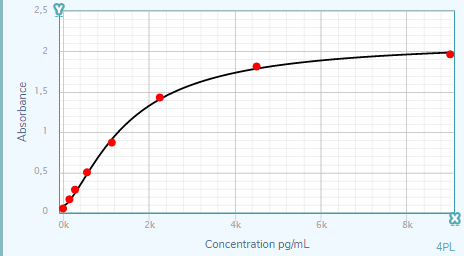
Scientific Data
Product Datasheets
Preparation and Storage
Background: CCL5/RANTES
RANTES (Regulated upon Activation, Normal T cell Expressed and presumably Secreted), also known as CCL5, is a member of the "CC" subfamily of chemokines. It plays a primary role in the inflammatory immune response via its ability to chemoattract leukocytes and modulate their function. The cDNA for RANTES was initially discovered by subtractive hybridization as a T cell specific sequence (1, 2). Human RANTES cDNA encodes a highly basic 91 amino acid (aa) residue precursor polypeptide with a 23 aa hydrophobic signal peptide that is cleaved to generate the 68 aa mature protein (1, 2). Human RANTES exhibits approximately 85% homology with mouse RANTES at the deduced aa level (3, 4).
Assay Procedure
GENERAL ELISA PROTOCOL
Plate Preparation
- Dilute the Capture Antibody to the working concentration in PBS without carrier protein. Immediately coat a 96-well microplate with 100 μL per well of the diluted Capture Antibody. Seal the plate and incubate overnight at room temperature.
- Aspirate each well and wash with Wash Buffer, repeating the process two times for a total of three washes. Wash by filling each well with Wash Buffer (400 μL) using a squirt bottle, manifold dispenser, or autowasher. Complete removal of liquid at each step is essential for good performance. After the last wash, remove any remaining Wash Buffer by aspirating or by inverting the plate and blotting it against clean paper towels.
- Block plates by adding 300 μL Reagent Diluent to each well. Incubate at room temperature for a minimum of 1 hour.
- Repeat the aspiration/wash as in step 2. The plates are now ready for sample addition.
Assay Procedure
- Add 100 μL of sample or standards in Reagent Diluent, or an appropriate diluent, per well. Cover with an adhesive strip and incubate 2 hours at room temperature.
- Repeat the aspiration/wash as in step 2 of Plate Preparation.
- Add 100 μL of the Detection Antibody, diluted in Reagent Diluent, to each well. Cover with a new adhesive strip and incubate 2 hours at room temperature.
- Repeat the aspiration/wash as in step 2 of Plate Preparation.
- Add 100 μL of the working dilution of Streptavidin-HRP to each well. Cover the plate and incubate for 20 minutes at room temperature. Avoid placing the plate in direct light.
- Repeat the aspiration/wash as in step 2.
- Add 100 μL of Substrate Solution to each well. Incubate for 20 minutes at room temperature. Avoid placing the plate in direct light.
- Add 50 μL of Stop Solution to each well. Gently tap the plate to ensure thorough mixing.
- Determine the optical density of each well immediately, using a microplate reader set to 450 nm. If wavelength correction is available, set to 540 nm or 570 nm. If wavelength correction is not available, subtract readings at 540 nm or 570 nm from the readings at 450 nm. This subtraction will correct for optical imperfections in the plate. Readings made directly at 450 nm without correction may be higher and less accurate.
Citations for Human CCL5/RANTES DuoSet ELISA
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
58
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
MYC promotes immune-suppression in triple-negative breast cancer via inhibition of interferon signaling
Authors: D Zimmerli, CS Brambillas, F Talens, J Bhin, R Linstra, L Romanens, A Bhattachar, SEP Joosten, AM Da Silva, N Padrao, MD Wellenstei, K Kersten, M de Boo, M Roorda, L Henneman, R de Bruijn, S Annunziato, E van der Bu, AP Drenth, C Lutz, T Endres, M van de Ven, M Eilers, L Wessels, KE de Visser, W Zwart, RSN Fehrmann, MATM van Vugt, J Jonkers
Nature Communications, 2022-11-02;13(1):6579.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Development of an Electrochemical CCL5 Chemokine Immunoplatform for Rapid Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis
Authors: S Guerrero, E Sánchez-Ti, L Agüí, A González-C, P Yáñez-Sede, JM Pingarrón
Biosensors, 2022-08-07;12(8):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
RANTES and CD40L under Conditions of Long-Term Physical Exercise: A Potential Link to Adaptive Immunity
Authors: M Lenz, R Schönbauer, S Stojkovic, J Lee, C Gatterer, M Lichtenaue, V Paar, M Emich, M Fritzer-Sz, J Strametz-J, S Graf, M Sponder
Oncogene, 2022-07-16;19(14):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Blood
-
Th1 cytokines synergize to change gene expression and promote corticosteroid insensitivity in pediatric airway smooth muscle
Authors: D Jackson, J Walum, P Banerjee, BW Lewis, YS Prakash, V Sathish, Z Xu, RD Britt
Respiratory Research, 2022-05-16;23(1):126.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Blockade of Autocrine CCL5 Responses Inhibits Zika Virus Persistence and Spread in Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells
Authors: MC Mladinich, JN Conde, WR Schutt, SY Sohn, ER Mackow
MBio, 2021-08-17;12(4):e0196221.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Rapid Internalization and Nuclear Translocation of CCL5 and CXCL4 in Endothelial Cells
Authors: A Dickhout, DM Kaczor, ACA Heinzmann, SLN Brouns, JWM Heemskerk, MAMJ van Zandvo, RR Koenen
International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021-07-08;22(14):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
-
Adipocytokines in Untreated Newly Diagnosed Rheumatoid Arthritis: Association with Circulating Chemokines and Markers of Inflammation
Authors: GK Vasileiadi, AC Lundell, Y Zhang, K Andersson, I Gjertsson, A Rudin, C Maglio
Biomolecules, 2021-02-21;11(2):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Resveratrol treatment reduces expression of MCP-1, IL-6, IL-8 and RANTES in endometriotic stromal cells
Authors: R Kolahdouz-, F Shidfar, S Khodaverdi, T Arablou, S Heidari, N Rashidi, AA Delbandi
Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 2020-12-15;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Clinical Relevance of the Anti-inflammatory Effects of Roflumilast on Human Bronchus: Potentiation by a Long-Acting Beta-2-Agonist
Authors: H Salvator, A Buenestado, M Brollo, E Naline, T Victoni, E Longchamp, H Tenor, S Grassin-De, P Devillier
Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2020-12-08;11(0):598702.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
TASL is the SLC15A4-associated adaptor for IRF5 activation by TLR7-9
Authors: LX Heinz, J Lee, U Kapoor, F Kartnig, V Sedlyarov, K Papakostas, A César-Razq, P Essletzbic, U Goldmann, A Stefanovic, JW Bigenzahn, S Scorzoni, MD Pizzagalli, A Bensimon, AC Müller, FJ King, J Li, E Girardi, ML Mbow, CE Whitehurst, M Rebsamen, G Superti-Fu
Nature, 2020-05-13;581(7808):316-322.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Human BCL-G regulates secretion of inflammatory chemokines but is dispensable for induction of apoptosis by IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha in intestinal epithelial cells
Authors: JA Woznicki, P Flood, M Bustamante, P Stamou, G Moloney, A Fanning, SA Zulquernai, J McCarthy, F Shanahan, S Melgar, K Nally
Cell Death Dis, 2020-01-27;11(1):68.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
HIV and HCV augments inflammatory responses through increased TREM-1 expression and signaling in Kupffer and Myeloid cells
Authors: J Hyun, RS McMahon, AL Lang, JS Edwards, AD Badilla, ME Greene, GW Stone, S Pallikkuth, M Stevenson, DM Dykxhoorn, S Kottilil, S Pahwa, E Thomas
PLoS Pathog., 2019-07-01;15(7):e1007883.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote colorectal cancer progression via CCR5
Authors: G Nishikawa, K Kawada, J Nakagawa, K Toda, R Ogawa, S Inamoto, R Mizuno, Y Itatani, Y Sakai
Cell Death Dis, 2019-03-19;10(4):264.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Toll-like receptor 3 regulates Zika virus infection and associated host inflammatory response in primary human astrocytes
Authors: CR Ojha, M Rodriguez, MKM Karuppan, J Lapierre, F Kashanchi, N El-Hage
PLoS ONE, 2019-02-08;14(2):e0208543.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus Nonstructural Protein NS5 Induces RANTES Expression Dependent on the RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Activity
Authors: Z Zheng, J Yang, X Jiang, Y Liu, X Zhang, M Li, M Zhang, M Fu, K Hu, H Wang, MH Luo, P Gong, Q Hu
J. Immunol., 2018-05-14;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Genetic Polymorphism at CCL5 Is Associated With Protection in Chagas' Heart Disease: Antagonistic Participation of CCR1+ and CCR5+ Cells in Chronic Chagasic Cardiomyopathy.
Authors: Angelica Martins Batista, Lucia Elena Alvarado-, Silvia Marinho Alves, Gloria Melo, Isabela Resende Pereira, Leonardo Alexandre de Sou Ruivo, Andrea Alice Da Silva, Daniel Gibaldi, Thayse Do E S Protásio Da Silva, Virginia Maria Barros De Lorena, Adriene Siqueira De Melo, Ana Karine De Araújo, Michelle Da Silva Barros, Vláudia Maria Assis Costa, Cynthia C Cardoso, Antonio G Pacheco, Cristina Carrazzon, Wilson Oliveira, Milton Ozório Moraes, Joseli Lannes-Vi
Frontiers in Immunology, 2018-04-11;0(0):1664-3224.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
The effects of repeated Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 stimulation in COPD alveolar macrophages
Authors: SR Lea, SL Reynolds, M Kaur, KD Simpson, SR Hall, EM Hessel, D Singh
Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis, 2018-03-02;13(0):771-780.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Pivotal role for the ESCRT-II complex subunit EAP30/SNF8 in IRF3-dependent innate antiviral defense
Authors: K Kumthip, D Yang, NL Li, Y Zhang, M Fan, A Sethuraman, K Li
PLoS Pathog., 2017-10-30;13(10):e1006713.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Zika Virus Persistently Infects and Is Basolaterally Released from Primary Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells
Authors: MC Mladinich, J Schwedes, ER Mackow
MBio, 2017-07-11;8(4):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Malaria pigment stimulates chemokine production by human microvascular endothelium
Authors: N Basilico, Y Corbett, S Alessandro, S Parapini, M Prato, D Girelli, P Misiano, P Olliaro, D Taramelli
Acta Trop., 2017-05-02;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
IFI16 and cGAS cooperate in the activation of STING during DNA sensing in human keratinocytes
Authors: JF Almine, CA O'Hare, G Dunphy, IR Haga, RJ Naik, A Atrih, DJ Connolly, J Taylor, IR Kelsall, AG Bowie, PM Beard, L Unterholzn
Nat Commun, 2017-02-13;8(0):14392.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Mitochondrial proteins NIP-SNAP-1 and -2 are a target for the immunomodulatory activity of clarithromycin, which involves NF-?B-mediated cytokine production
Authors: Soh Yamamoto
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun, 2016-12-18;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Forsythia suspensa Suppresses House Dust Mite Extract-Induced Atopic Dermatitis in NC/Nga Mice
PLoS ONE, 2016-12-09;11(12):e0167687.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
A Role for Human Skin Mast Cells in Dengue Virus Infection and Systemic Spread
Authors: Tonya M Colpitts
J. Immunol., 2016-10-31;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Inflammatory and immunological profiles in patients with COPD: relationship with FEV 1 reversibility
Authors: Cleriston Farias Queiroz
J Bras Pneumol, 2016-07-01;42(4):241-247.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
-
Unfractionated Heparin Selectively Modulates the Expression of CXCL8, CCL2 and CCL5 in Endometrial Carcinoma Cells
Authors: A Doster, U Schwarzig, M Zygmunt, J Rom, F Schütz, H Fluhr
Anticancer Res, 2016-04-01;36(4):1535-44.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Experimental hyperglycemia induces an increase of monocyte and T-lymphocyte content in adipose tissue of healthy obese women.
Authors: Tencerova M, Kracmerova J, Krauzova E, Malisova L, Kovacova Z, Wedellova Z, Siklova M, Stich V, Rossmeislova L
PLoS ONE, 2015-04-20;10(3):e0122872.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Role of hydrogen sulfide in paramyxovirus infections.
Authors: Li H, Ma Y, Escaffre O, Ivanciuc T, Komaravelli N, Kelley J, Coletta C, Szabo C, Rockx B, Garofalo R, Casola A
J Virol, 2015-03-04;89(10):5557-68.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Necroptosis suppresses inflammation via termination of TNF- or LPS-induced cytokine and chemokine production.
Authors: Kearney C, Cullen S, Tynan G, Henry C, Clancy D, Lavelle E, Martin S
Cell Death Differ, 2015-01-23;22(8):1313-27.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Resolving cancer-stroma interfacial signalling and interventions with micropatterned tumour-stromal assays.
Authors: Shen K, Luk S, Hicks D, Elman J, Bohr S, Iwamoto Y, Murray R, Pena K, Wang F, Seker E, Weissleder R, Yarmush M, Toner M, Sgroi D, Parekkadan B
Nat Commun, 2014-12-09;5(0):5662.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Human osteoarthritic cartilage shows reduced in vivo expression of IL-4, a chondroprotective cytokine that differentially modulates IL-1beta-stimulated production of chemokines and matrix-degrading enzymes in vitro.
Authors: Assirelli E, Pulsatelli L, Dolzani P, Platano D, Olivotto E, Filardo G, Trisolino G, Facchini A, Borzi R, Meliconi R
PLoS ONE, 2014-05-12;9(5):e96925.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Controlled intramyocardial release of engineered chemokines by biodegradable hydrogels as a treatment approach of myocardial infarction.
Authors: Projahn D, Simsekyilmaz S, Singh S, Kanzler I, Kramp B, Langer M, Burlacu A, Bernhagen J, Klee D, Zernecke A, Hackeng T, Groll J, Weber C, Liehn E, Koenen R
J Cell Mol Med, 2014-02-06;18(5):790-800.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Proteome-wide analysis and CXCL4 as a biomarker in systemic sclerosis
Authors: L van Bon, AJ Affandi, J Broen, RB Christmann, RJ Marijnisse, L Stawski, GA Farina, G Stifano, AL Mathes, M Cossu, M York, C Collins, M Wenink, R Huijbens, R Hesselstra, T Saxne, M DiMarzio, D Wuttge, SK Agarwal, JD Reveille, S Assassi, M Mayes, Y Deng, JP Drenth, J de Graaf, M den Heijer, CG Kallenberg, M Bijl, A Loof, WB van den Be, LA Joosten, V Smith, F de Keyser, R Scorza, C Lunardi, PL van Riel, M Vonk, W van Heerde, S Meller, B Homey, L Beretta, M Roest, M Trojanowsk, R Lafyatis, TR Radstake
N. Engl. J. Med, 2013-12-18;370(5):433-43.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
The small GTPase Arf6 is essential for the Tram/Trif pathway in TLR4 signaling.
Authors: Van Acker T, Eyckerman S, Vande Walle L, Gerlo S, Goethals M, Lamkanfi M, Bovijn C, Tavernier J, Peelman F
J Biol Chem, 2013-12-02;289(3):1364-76.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 protects against macrophage-induced activation of NFkappaB and MAPK signalling and chemokine release in human adipocytes.
Authors: Ding C, Wilding J, Bing C
PLoS ONE, 2013-04-24;8(4):e61707.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Human cytomegalovirus induces a biphasic inflammatory response in primary endothelial cells.
Authors: Jeffery H, Soderberg-Naucler C, Butler L
J Virol, 2013-03-27;87(11):6530-5.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Intradermal delivery of TLR agonists in a human explant skin model: preferential activation of migratory dendritic cells by polyribosinic-polyribocytidylic acid and peptidoglycans.
Authors: Oosterhoff D, Heusinkveld M, Lougheed S, Kosten I, Lindstedt M, Bruijns S, van Es T, van Kooyk Y, van der Burg S, de Gruijl T
J Immunol, 2013-03-06;190(7):3338-45.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Characterisation of P2Y(12) receptor responsiveness to cysteinyl leukotrienes.
Authors: Foster H, Fuerst E, Lee T, Cousins D, Woszczek G
PLoS ONE, 2013-03-05;8(3):e58305.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
Measles virus causes immunogenic cell death in human melanoma.
Authors: Donnelly, O G, Errington-Mais, F, Steele, L, Hadac, E, Jennings, V, Scott, K, Peach, H, Phillips, R M, Bond, J, Pandha, H, Harrington, K, Vile, R, Russell, S, Selby, P, Melcher, A A
Gene Ther, 2011-12-15;20(1):7-15.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
IRF5 promotes inflammatory macrophage polarization and T(H)1-T(H)17 responses.
Authors: Krausgruber T, Blazek K, Smallie T
Nat. Immunol., 2011-01-16;12(3):231-8.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Thrombocytopenia in early malaria is associated with GP1b shedding in absence of systemic platelet activation and consumptive coagulopathy.
Authors: de Mast Q, de Groot PG, van Heerde WL, Roestenberg M, van Velzen JF, Verbruggen B, Roest M, McCall M, Nieman AE, Westendorp J, Syafruddin D, Fijnheer R, van Dongen-Lases EC, Sauerwein RW, van der Ven AJ
Br. J. Haematol., 2010-10-19;151(5):495-503.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Plasma
-
A role for the human nucleotide-binding domain, leucine-rich repeat-containing family member NLRC5 in antiviral responses.
Authors: Neerincx A, Lautz K, Menning M, Kremmer E, Zigrino P, Hosel M, Buning H, Schwarzenbacher R, Kufer TA
J. Biol. Chem., 2010-06-10;285(34):26223-32.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
IL-17 amplifies human contact hypersensitivity by licensing hapten nonspecific Th1 cells to kill autologous keratinocytes.
Authors: Pennino D, Eyerich K, Scarponi C, Carbone T, Eyerich S, Nasorri F, Garcovich S, Traidl-Hoffmann C, Albanesi C, Cavani A
J. Immunol., 2010-03-31;184(9):4880-8.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Novel markers of inflammation identified in tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS) by transcriptomic analysis of effects of TRAPS-associated tumor necrosis factor receptor type I mutations in an endothelial cell line.
Authors: Rebelo SL, Amel-Kashipaz MR, Radford PM, Bainbridge SE, Fiets R, Fang J, McDermott EM, Powell RJ, Todd I, Tighe PJ
Arthritis Rheum., 2009-01-01;60(1):269-80.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
CD8 chemokine receptors in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Authors: Smyth LJ, Starkey C, Gordon FS, Vestbo J, Singh D
Clin. Exp. Immunol., 2008-08-22;154(1):56-63.
Species: Human
Sample Types: BALF
-
Altered levels of CC chemokines during pulmonary CMV predict BOS and mortality post-lung transplantation.
Authors: Weigt SS, Elashoff RM, Keane MP, Strieter RM, Gomperts BN, Xue YY, Ardehali A, Gregson AL, Kubak B, Fishbein MC, Saggar R, Ross DJ, Lynch JP, Zisman DA, Belperio JA
Am. J. Transplant., 2008-07-01;8(7):1512-22.
Species: Human
Sample Types: BALF
-
Vitamin D and glucocorticoids differentially modulate chemokine expression in human airway smooth muscle cells.
Authors: Banerjee A, Damera G, Bhandare R, Gu S, Lopez-Boado Y, Panettieri R, Tliba O
Br. J. Pharmacol., 2008-06-16;155(1):84-92.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Expanded-polyglutamine huntingtin protein suppresses the secretion and production of a chemokine (CCL5/RANTES) by astrocytes.
Authors: Chou SY, Weng JY, Lai HL, Liao F, Sun SH, Tu PH, Dickson DW, Chern Y
J. Neurosci., 2008-03-26;28(13):3277-90.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Preadipocyte response and impairment of differentiation in an inflammatory environment.
Authors: Poulain-Godefroy O, Froguel P
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2007-03-19;356(3):662-7.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
PAPP-A and osteoprotegerin, together with interleukin-8 and RANTES, are elevated in the peritoneal fluid of women with endometriosis.
Authors: Bersinger NA, von Roten S, Wunder DM, Raio L, Dreher E, Mueller MD
Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol., 2006-04-25;195(1):103-8.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Peritoneal Fluid
-
The cytokine IL-1beta activates IFN response factor 3 in human fetal astrocytes in culture.
Authors: Rivieccio MA, John GR, Song X, Suh HS, Zhao Y, Lee SC, Brosnan CF
J. Immunol., 2005-03-15;174(6):3719-26.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Manipulation of host cytokine network by ticks: a potential gateway for pathogen transmission.
Authors: Hajnicka V, Vancova I, Kocakova P, Slovak M, Gasperik J, Slavikova M, Hails RS, Labuda M, Nuttall PA
Parasitology, 2005-03-01;130(0):333-42.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Saliva
-
Involvement of Fc gamma RI (CD64) in the mechanism of HIV-1 inhibition by polyclonal IgG purified from infected patients in cultured monocyte-derived macrophages.
Authors: Holl V, Hemmerter S, Burrer R, Schmidt S, Bohbot A, Aubertin AM, Moog C
J. Immunol., 2004-11-15;173(10):6274-83.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Rapid chemokine secretion from endothelial cells originates from 2 distinct compartments.
Authors: Oynebraten I, Bakke O, Brandtzaeg P, Johansen FE, Haraldsen G
Blood, 2004-03-25;104(2):314-20.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Virally stimulated plasmacytoid dendritic cells produce chemokines and induce migration of T and NK cells.
Authors: Megjugorac NJ, Young HA, Amrute SB, Olshalsky SL, Fitzgerald-Bocarsly P
J. Leukoc. Biol., 2004-01-23;75(3):504-14.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Chemokine secretion of rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts stimulated by Toll-like receptor 2 ligands.
Authors: Pierer M, Rethage J, Seibl R, Lauener R, Brentano F, Wagner U, Hantzschel H, Michel BA, Gay RE, Gay S, Kyburz D
J. Immunol., 2004-01-15;172(2):1256-65.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
-
Phenotypic and functional analysis of T cells homing into the CSF of subjects with inflammatory diseases of the CNS.
Authors: Giunti D, Borsellino G, Benelli R, Marchese M, Capello E, Valle MT, Pedemonte E, Noonan D, Albini A, Bernardi G, Mancardi GL, Battistini L, Uccelli A
J. Leukoc. Biol., 2003-05-01;73(5):584-90.
Species: Human
Sample Types: CSF
-
Differential production of RANTES and MCP-1 in synovial fluid from the inflamed human knee.
Authors: Conti P, Reale M, Barbacane RC, Castellani ML, Orso C
Immunol. Lett., 2002-02-01;80(2):105-11.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all ELISA FAQsReviews for Human CCL5/RANTES DuoSet ELISA
Average Rating: 4.7 (Based on 3 Reviews)
Have you used Human CCL5/RANTES DuoSet ELISA?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by: