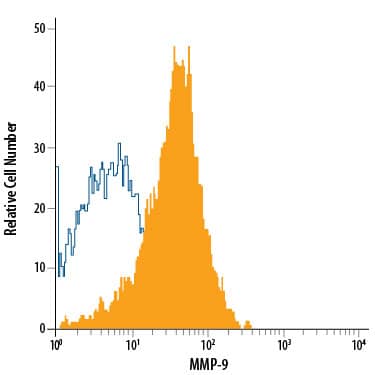
Intracellular Flow Cytometry Overview
Flow cytometry can be used to stain a wide range of intracellular molecules. Cells will first need to be fixed in suspension and then permeabilized before the detection antibody is added to successful analyze intracellular targets by flow cytometry. The process of fixation and permeabilization allows the antibody to pass through the plasma membrane and move to inside the cell while leaving the morphological characteristics used to sort the cells intact. Alcohols, such as methanol or ethanol, are commonly used to permeabilize cells. Cold methanol is typically used as a permeabilization agent when using flow cytometry to detect phosphorylated proteins and transcription factors because it can increase the reactivity of antibodies to certain nuclear antigens.
The following flow cytometry staining protocol has been developed and optimized by R&D Systems Flow Cytometry Laboratory. This protocol is designed for intracellular staining of proteins. It is recommended that experimental conditions, such as antibody concentration, incubation time, and temperature, be optimized for each flow cytometry experiment.
Please read the following flow cytometry staining protocol in its entirety before beginning.

Reagents Required
- PBS (1X): 0.137 M NaCl, 0.05 M NaH2PO4, pH 7.4 or Hank’s Balanced Salt Solution (HBSS; 1X)
- Flow Cytometry Fixation Buffer (Catalog # FC004) or an equivalent solution containing 1 - 4% paraformaldehyde
- -20 °C Methanol
- Fc Receptor Blocking Reagents (These include Fc receptor blocking antibodies or IgG solutions)
- Fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies suitable for use in flow cytometry
- Isotype Control Antibodies
Materials Required
- FACS™ Tubes (5 mL round-bottom polystyrene tubes)
- Pipette Tips and Pipettes
- Centrifuge
- Vortex
Procedure
When performing surface and intracellular staining in the same sample, it is advisable that the staining of cell surface antigens be performed first since fixation and permeabilization treatments might decrease the availability of surface antigens. Take care to avoid using PE or APC conjugates prior to methanol permeabilization. Methanol can affect PE and APC and cause a loss of signal.
- Harvest cells and wash 2 times by adding 2 mL of PBS (or HBSS), centrifuging at 1250-1500 rpm/350-500 x g for 5 minutes, and then decanting buffer from pelleted cells.
- Aliquot up to 1 x 106 cells/100 μL into FACS tubes. Add 0.5 mL of cold Flow Cytometry Fixation Buffer (Catalog # FC004) and vortex. Incubate at room temperature for 10 minutes. Vortex cells intermittently in order to maintain a single cell suspension.
- Centrifuge cells and decant the Flow Cytometry Fixation Buffer. Wash the cells 2 times with PBS (or HBSS) as described in step 1.
- Resuspend cells in 900 μL of -20 °C methanol. Incubate for 30 minutes at 4 °C.
- Centrifuge cells for 5 minutes at 1250-1500 rpm/350-500 x g. Remove and discard the supernatant. Wash 2 times with PBS (or HBSS) as described in step 1.
- Fc-block cells with blocking IgG (1 μg IgG/106 cells) for 15 minutes at room temperature.
Note: Do not wash excess blocking IgG from this reaction. - Add conjugated antibody (5-10 μL/106 cells or a previously titrated amount) and vortex. Incubate cells for 30 minutes at room temperature in the dark.
- Wash cells 2 times with PBS (or HBSS) as described in step 1.
Note: If an unconjugated primary antibody is used, incubation with an appropriate secondary antibody should occur now. Dilute the secondary antibody in PBS (or HBSS), starting with the concentration suggested in the product datasheet. Incubate for 20-30 minutes in the dark and wash as in step 1. - Resuspend cell pellet in 200 - 400 μL of PBS for flow cytometric analysis
It is recommended to run a negative control. A separate set of cells should be stained with an Isotype Control Antibody using the steps outlined above.
FACS is a trademark of Becton Dickinson and Company.
Flow Cytometry Intracellular Staining Example